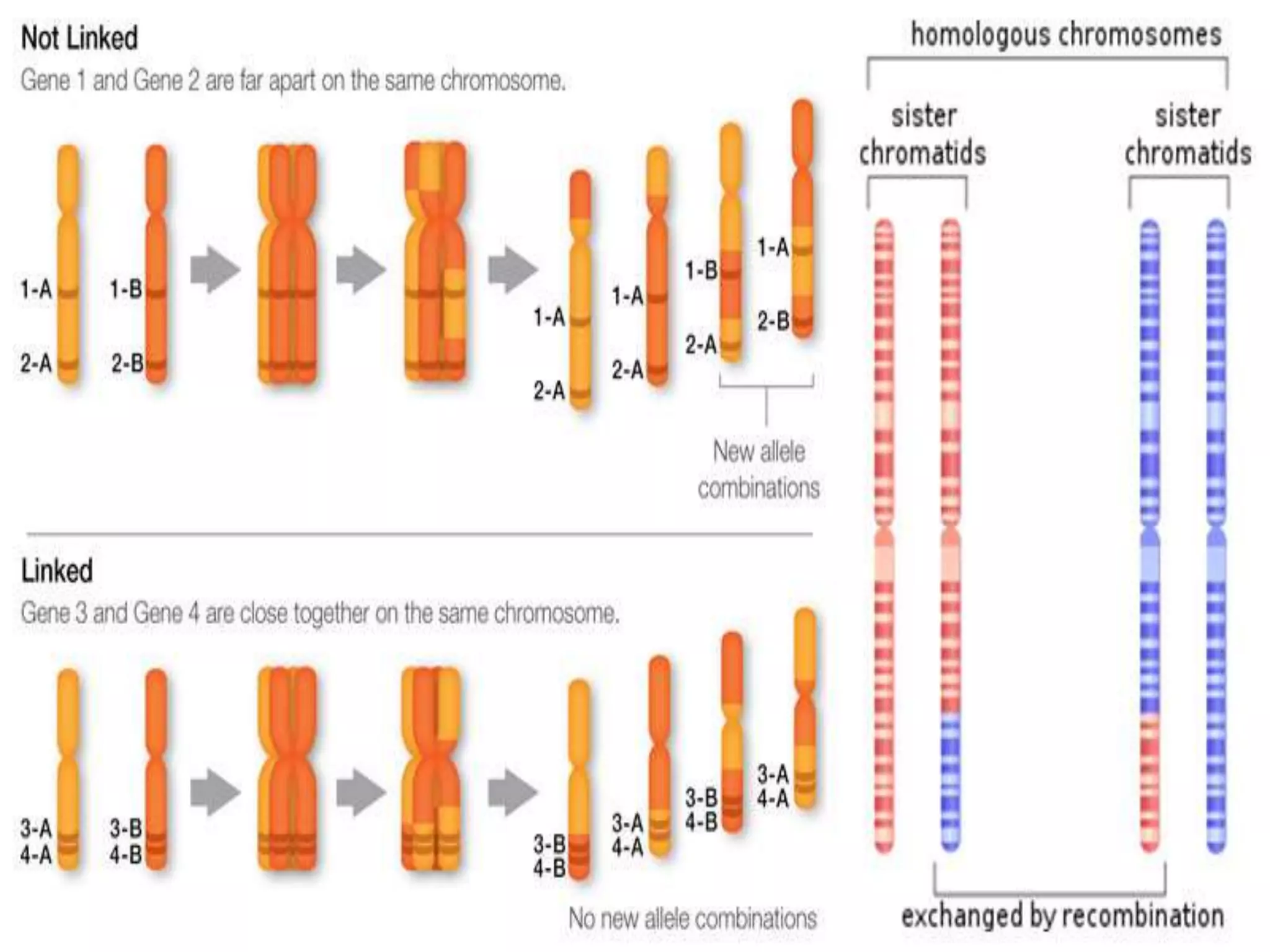
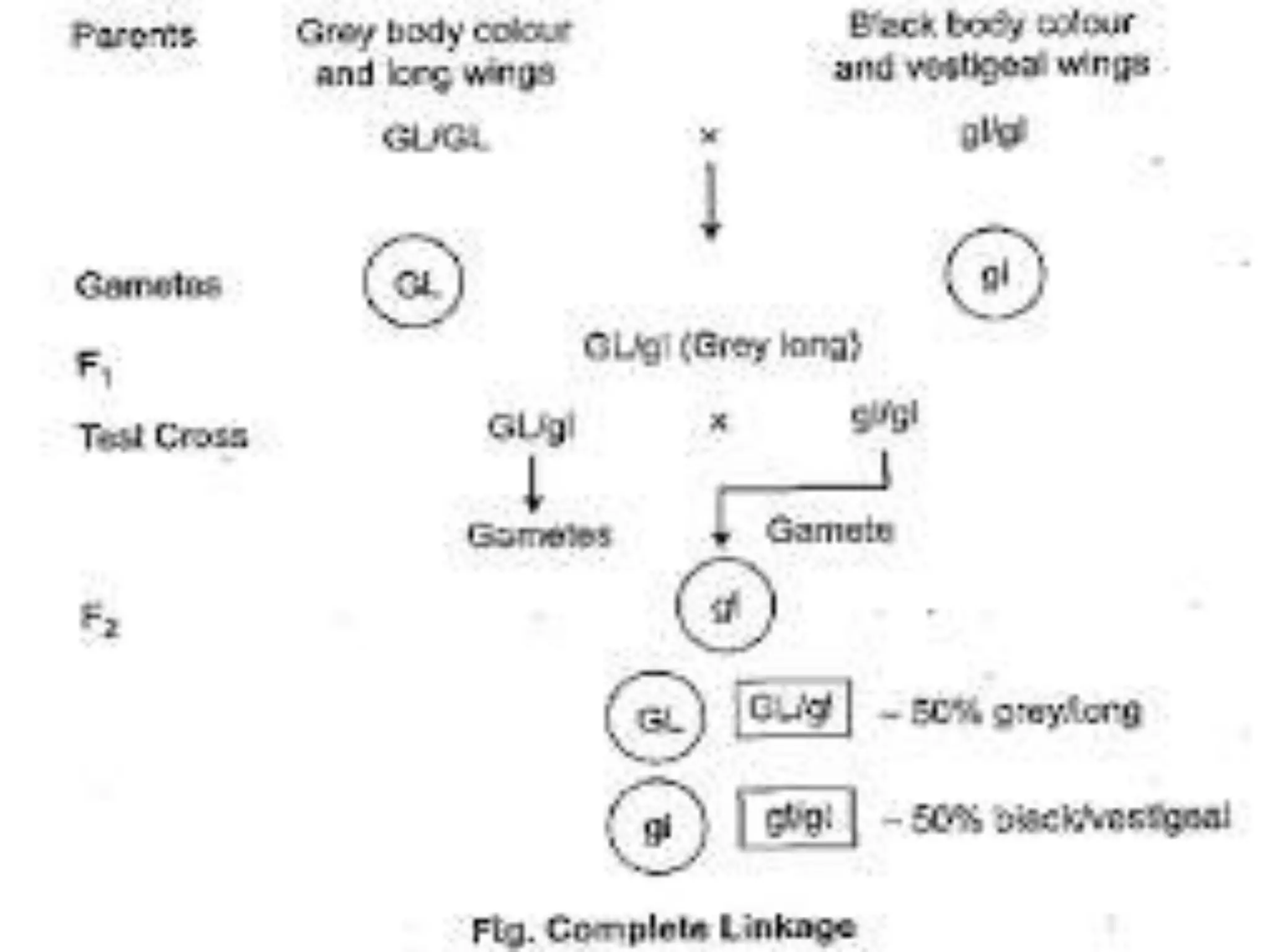
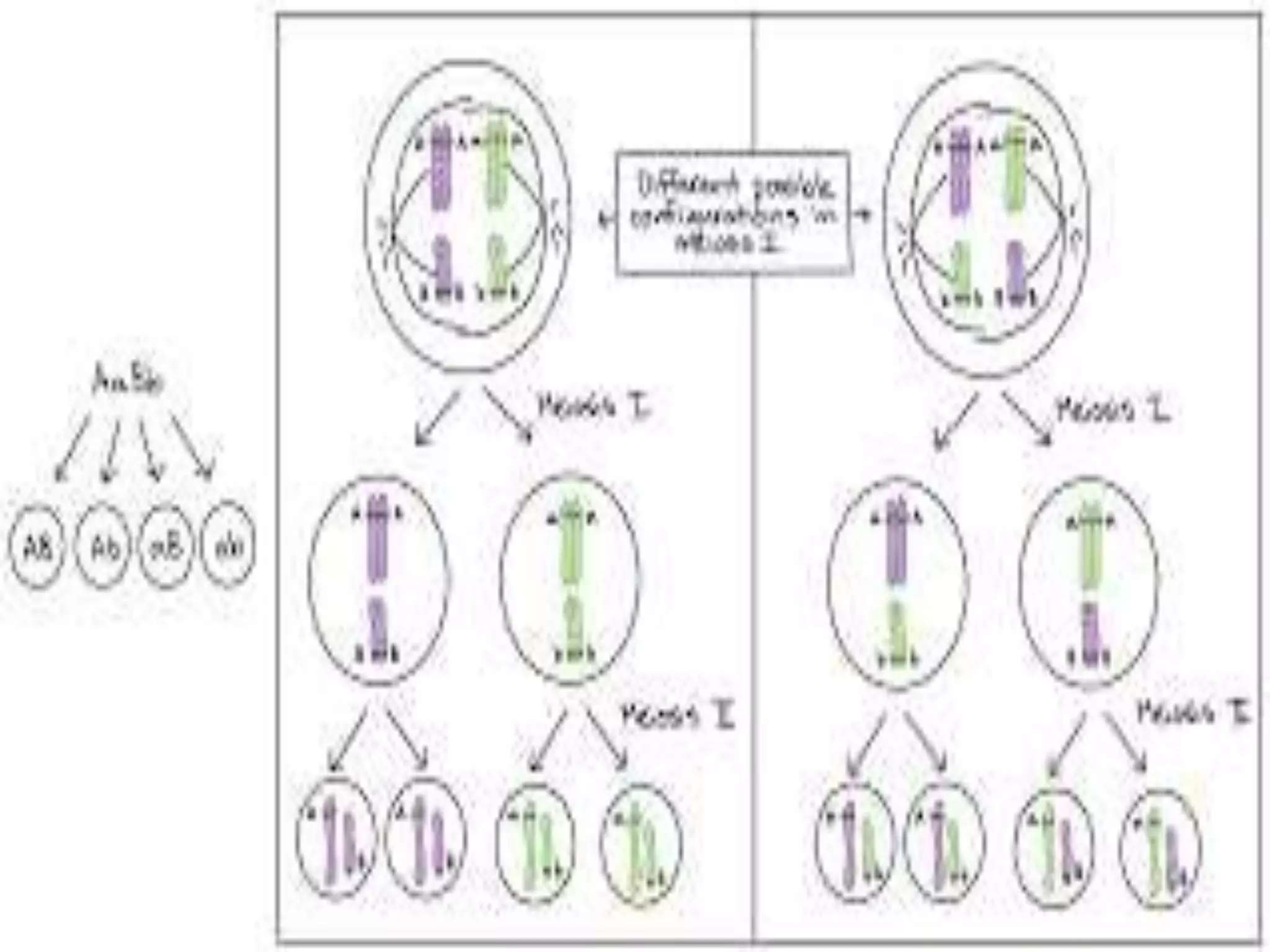
1. Genetic linkage occurs when two genes located near each other on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together during meiosis.
2. Early theories of linkage proposed by Sutton, Boveri, Bateson and Punnett failed to fully explain observed inheritance patterns.
3. Morgan's chromosomal theory of linkage established that genes are linearly arranged on chromosomes and that the closer two genes are, the stronger the tendency for them to be inherited together. This provided an explanation for linkage patterns and laid the foundation for modern genetics.