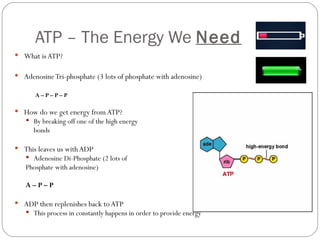
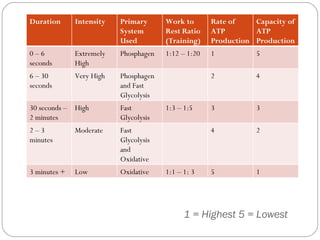
The document describes the three main energy systems the body uses to produce ATP:
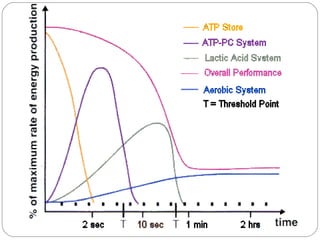
1) The ATP-PC system produces ATP rapidly at the start of intense activity lasting up to 6 seconds through phosphocreatine breakdown.
2) Anaerobic glycolysis produces ATP without oxygen through carbohydrate breakdown, lasting 30-120 seconds but producing lactic acid as a byproduct.
3) The aerobic system produces ATP through carbohydrate and fat breakdown during low to moderate intensity exercise lasting 3 minutes or more.