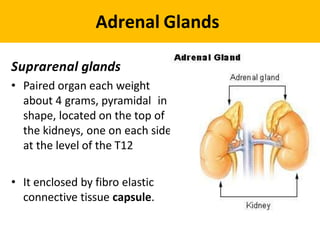
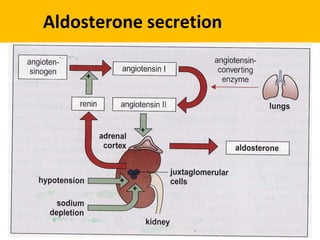
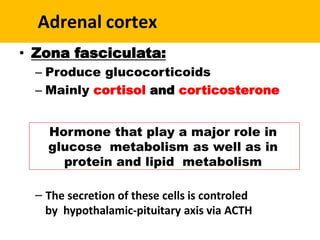
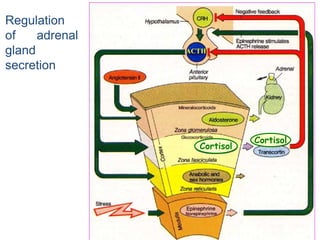
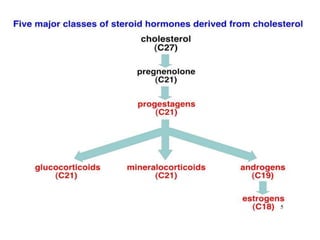
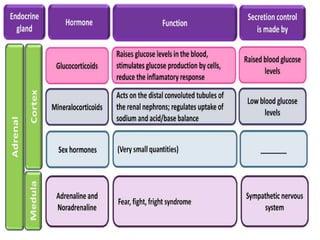
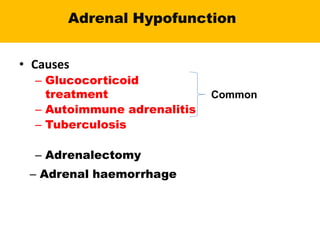
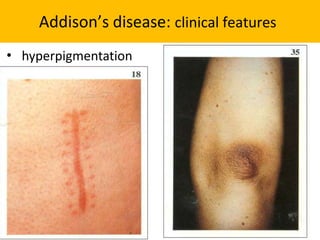
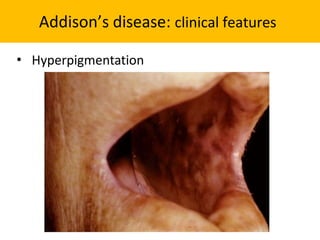
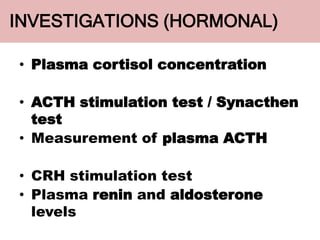
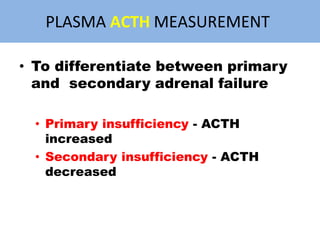
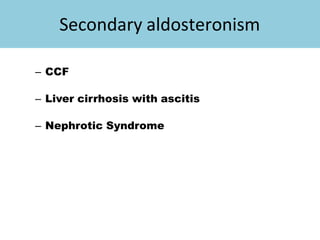
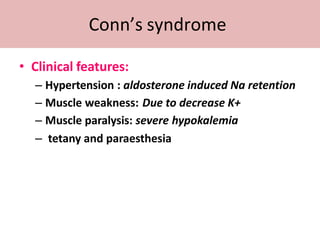
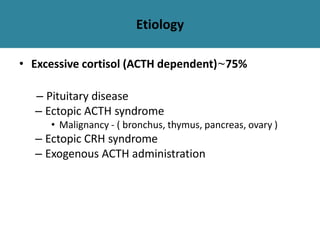
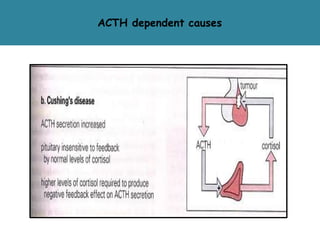
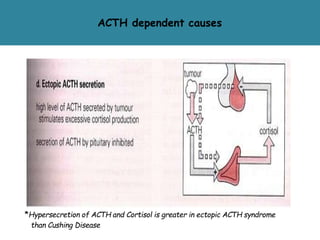
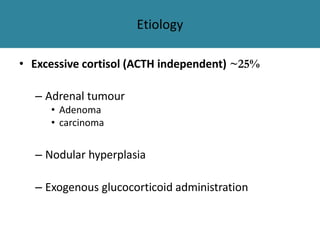
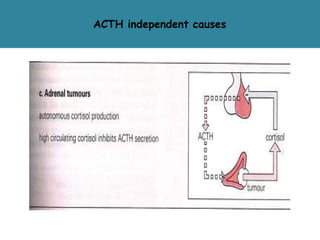
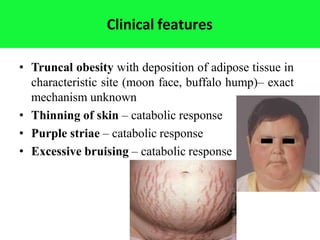
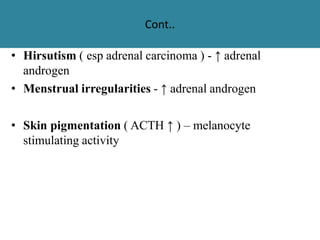
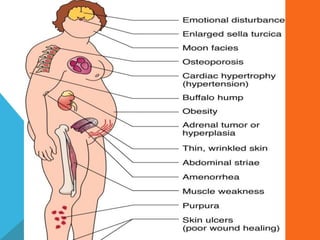
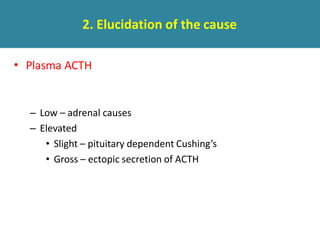
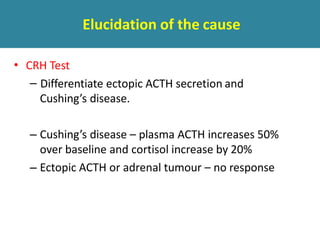
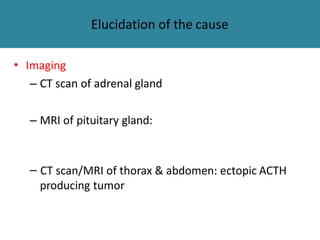
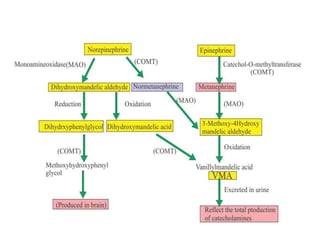
The adrenal glands are located above the kidneys and are divided into an outer cortex and inner medulla. The cortex secretes steroid hormones like cortisol and aldosterone which are involved in glucose metabolism, mineral balance, and sexual development. The medulla secretes catecholamines which increase heart rate and blood pressure. Diseases can result from hypo- or hyperfunction of the adrenal cortex or medulla. Tests are used to identify the cause and guide treatment options such as surgery or medication.