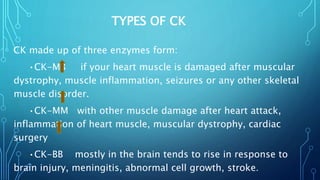
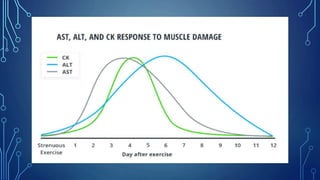
Elevated levels of liver enzymes like ALT, AST, and GGT in the blood can indicate liver damage, but can also occur after strenuous exercise due to muscle injury. While ALT and AST are found in both the liver and muscles, abnormal ALT alone is more indicative of liver injury, whereas abnormal AST with normal ALT likely indicates a muscle problem. Creatine kinase is released from damaged muscles and elevated levels after exercise can persist for over a week as muscles recover. Monitoring enzyme levels can help determine if training loads are allowing for adequate muscle recovery or indicating potential overtraining.