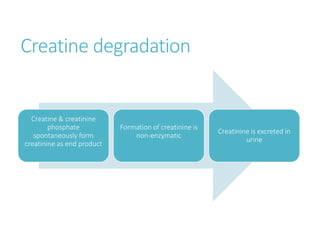
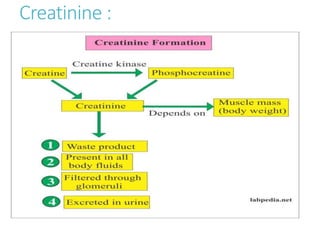
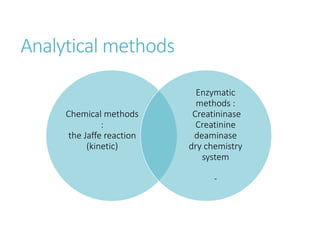
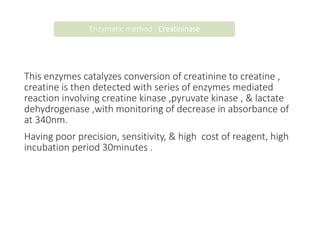
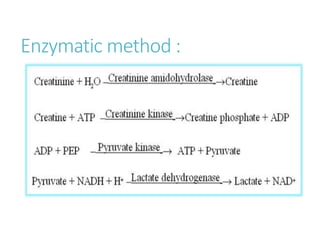
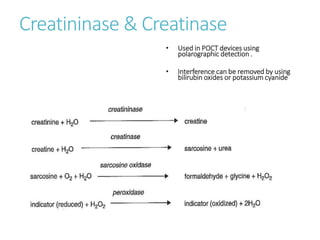
This document outlines the biochemistry and physiology of creatinine and provides details on measuring serum creatinine levels. It discusses how creatinine is formed as a breakdown product of creatine phosphate in muscle and is excreted by the kidneys. The key analytical methods for measuring creatinine are described, including the commonly used Jaffe reaction and enzymatic methods, along with factors that can interfere with the tests. Reference intervals and considerations for sample collection are also presented.