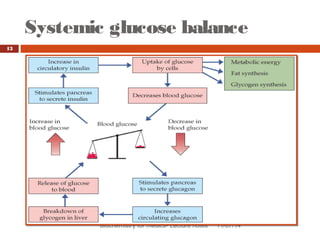
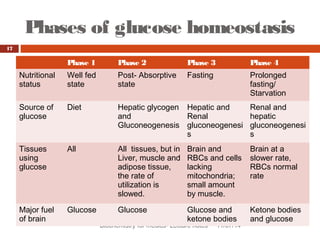
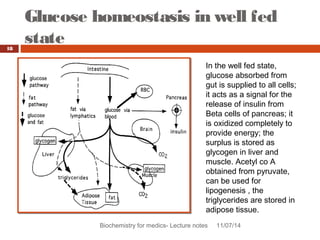
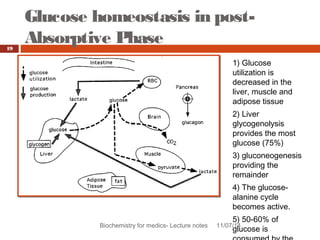
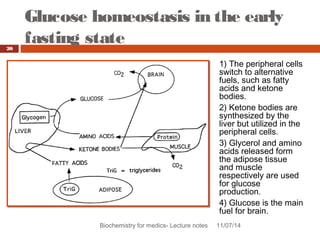
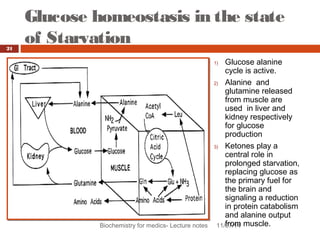
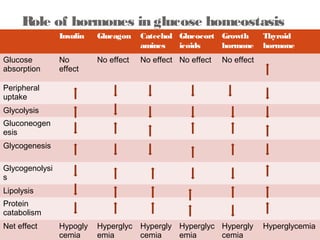
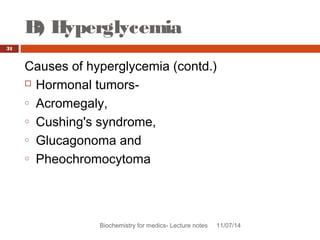
This document discusses glucose homeostasis and the maintenance of blood glucose levels. It explains that glucose homeostasis relies on a balance between glucose production in the liver and uptake by tissues. Insulin is a key regulator that promotes glucose uptake after meals and inhibits production during fasting. Other hormones like glucagon stimulate production when glucose levels drop. The document outlines the complex mechanisms that keep blood glucose within a narrow range to ensure the brain has a continuous supply while allowing for variations from meals and activity.