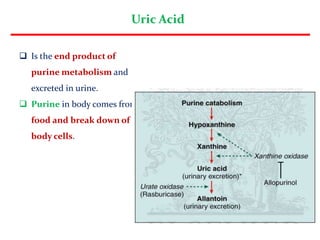
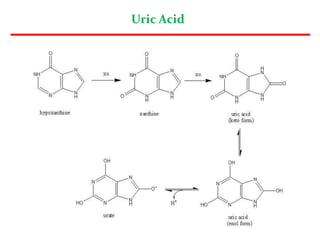
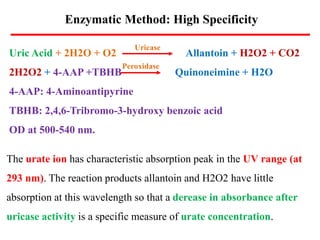
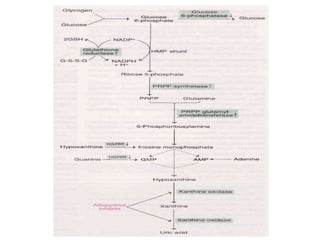
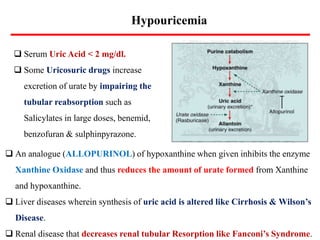
Uric acid is the end product of purine metabolism and is excreted in urine. It is produced from the breakdown of purines from food and cells. There are two main methods for determining serum uric acid levels - the Caraway method which uses phosphotungstic acid and measures absorbance at 700nm, and the enzymatic method using uricase and peroxidase to produce a colored product measured at 500-540nm. Normal serum uric acid levels are 3.5-7.2 mg/dl for males and 2.5-6.2 mg/dl for females. Hyperuricemia can be caused by reduced excretion due to renal disorders or increased production from metabolic disorders and diseases