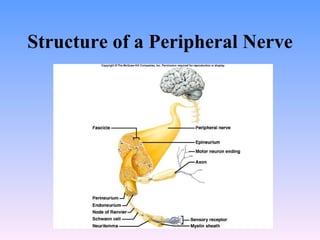
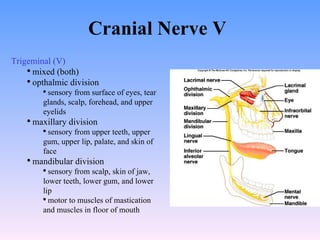
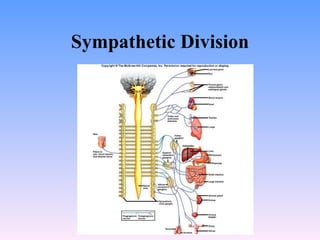
The peripheral nervous system has both cranial and spinal nerves. Cranial nerves arise from the brain and connect to organs, muscles, and skin. Spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord and also connect to organs, muscles, and skin. Peripheral nerves can be sensory, motor, or mixed. Examples of cranial nerves include the trigeminal nerve which is mixed and innervates parts of the face, and the facial nerve which is also mixed and innervates muscles of facial expression. Spinal nerves form plexuses like the brachial plexus which innervates the arm. The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary functions and has sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.