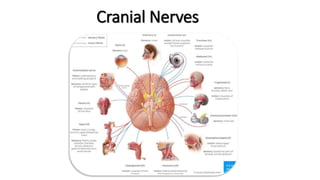
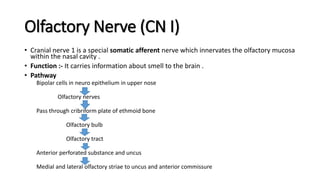
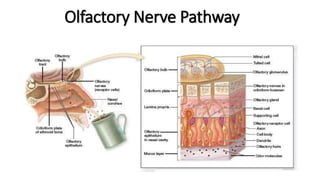
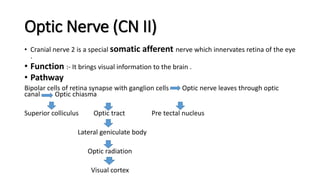
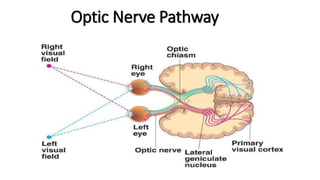
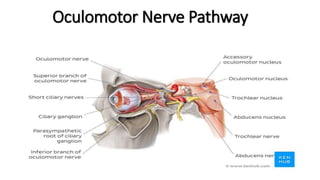
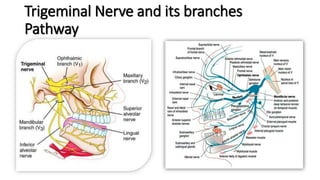
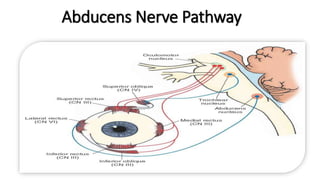
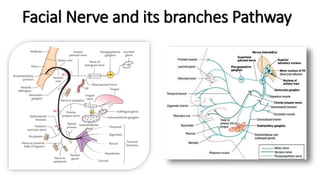
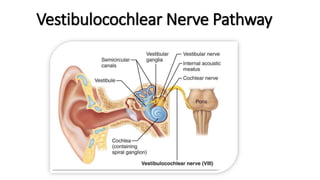
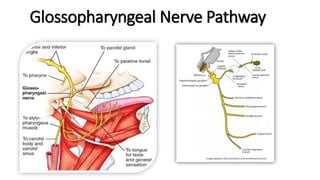
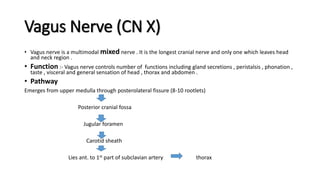
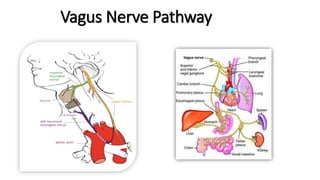
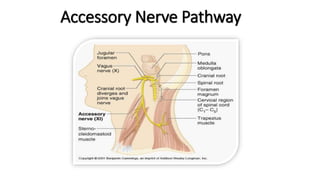
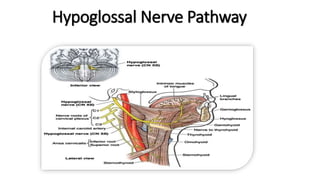
The document provides an overview of cranial nerves, detailing their functions, pathways, and classifications. It lists all 12 cranial nerves, highlighting their origins from brain nuclei and their specific roles, such as sensory functions or motor innervation. Each nerve is briefly described in terms of its structure, function, and pathway through the skull and body.