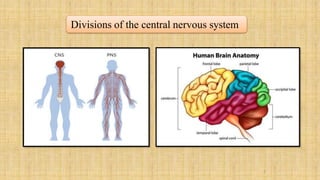
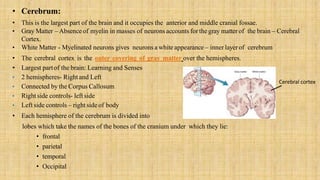
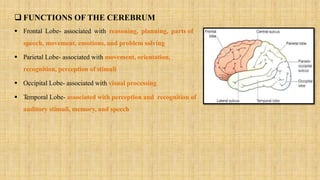
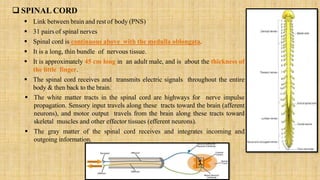
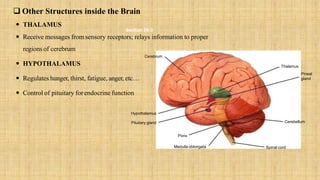
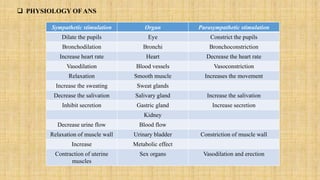
The central nervous system is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. The brain controls bodily functions and awareness through different regions like the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. The cerebrum controls complex brain functions. The cerebellum coordinates movement and balance. The brain stem regulates vital functions like breathing and heart rate. The spinal cord connects the brain to the body and enables reflexes. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves throughout the body. The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary functions through the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.