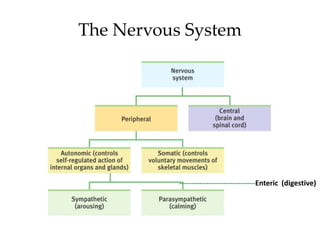
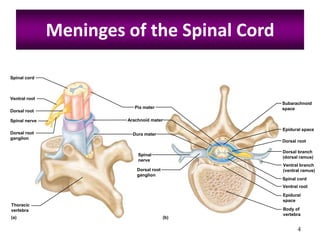
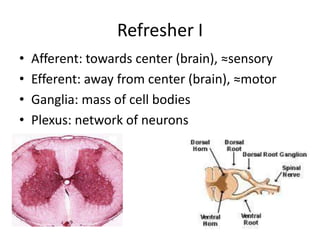
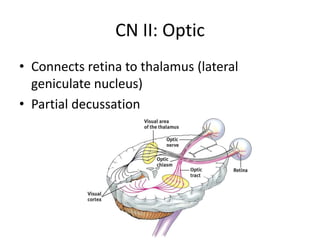
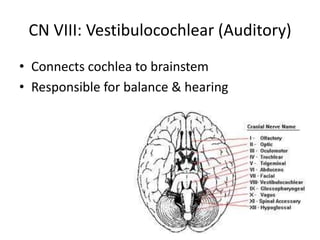
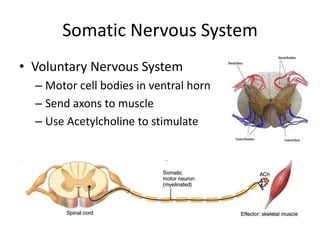
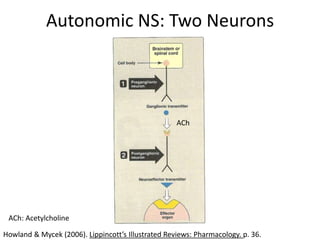
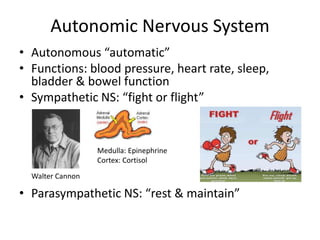
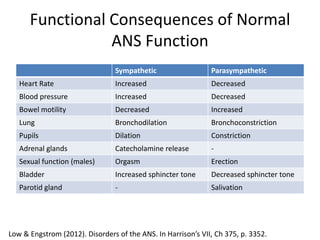
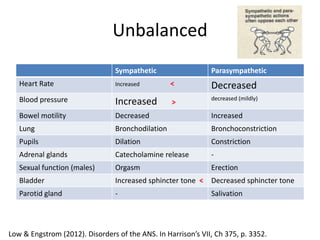
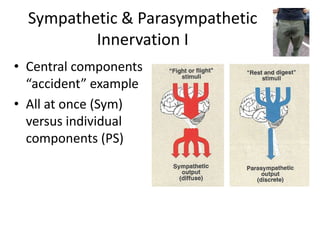
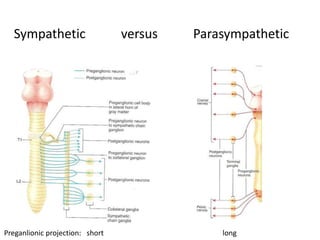
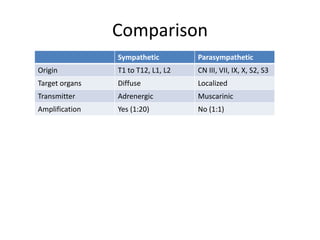
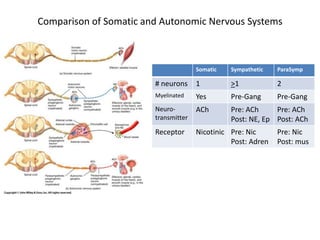
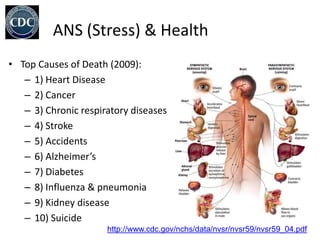
The document outlines the anatomy and physiology of the peripheral nervous system, detailing the somatic and autonomic systems, including specific cranial nerves and their functions. It compares sympathetic and parasympathetic systems in terms of organization, function, and neurotransmitters. Furthermore, it addresses the implications of the autonomic nervous system on health and outlines major causes of death.