This document provides an overview of computer validation and compliance with regulatory guidance. It discusses the need for computer validation and outlines key principles from guidance documents such as software validation, use of off-the-shelf software in medical devices, and validation of electronic records and signatures. Validation approaches for different systems and software are covered, including spreadsheets. The document provides references to FDA and international regulatory guidance on these topics.






















![ According to your view point, Why it is necessary to validate
“Computer” ? [ 2 marks ]
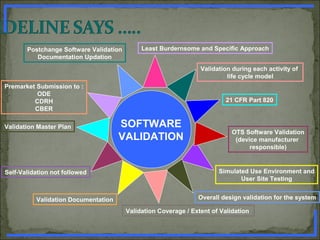
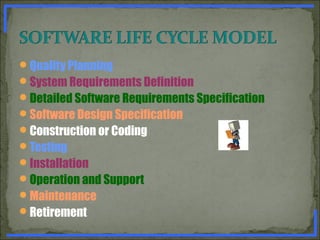
State the general principles of Software Validation. [ 5 marks ]
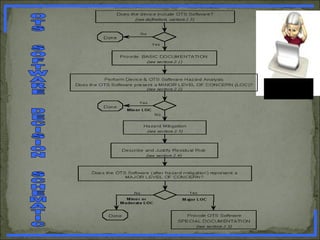
What is OTS Software ? How the level of concern affect the
documentation of OTS software validation ? [ 2 marks ]
State the key principles of validating Electronic Records and Electronic
Signatures. [ 5 marks ]
How will you validate the Electronic Spreadsheet ? [ 2 marks ]
www.PharmInfopedia.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computersystemvalidation-121211043502-phpapp02/85/Computer-system-validation-26-320.jpg)


