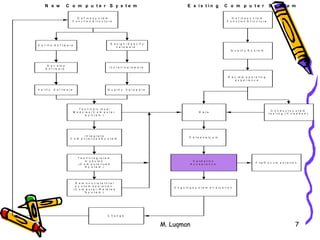
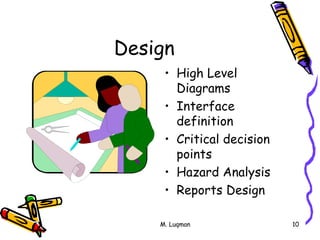
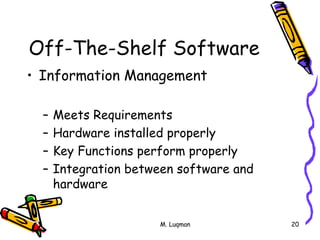
This document discusses expectations for validation of computer systems according to FDA/EC/WHO guidelines. It defines validation as establishing documented evidence that a process will consistently produce products meeting predetermined specifications. For software validation, it means establishing evidence that software conforms to user needs and intended functions. The document outlines key aspects of software validation including requirements analysis, design, testing, integration and maintenance. It provides examples of validation for different types of software like off-the-shelf, custom designed, in-house developed and maintained software. Important elements of an effective validation program include training, procedures, documentation and communication between developers and quality assurance.