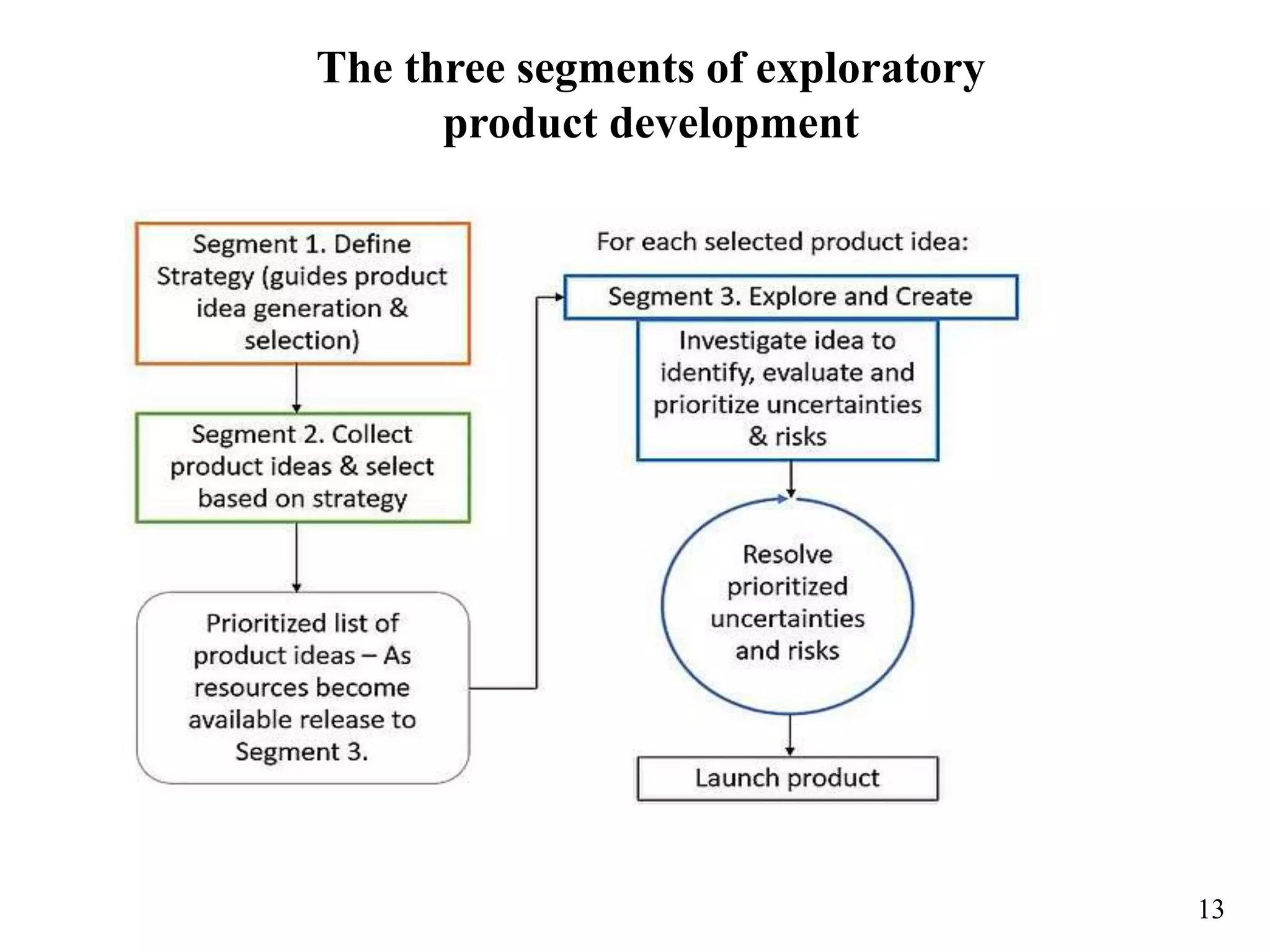
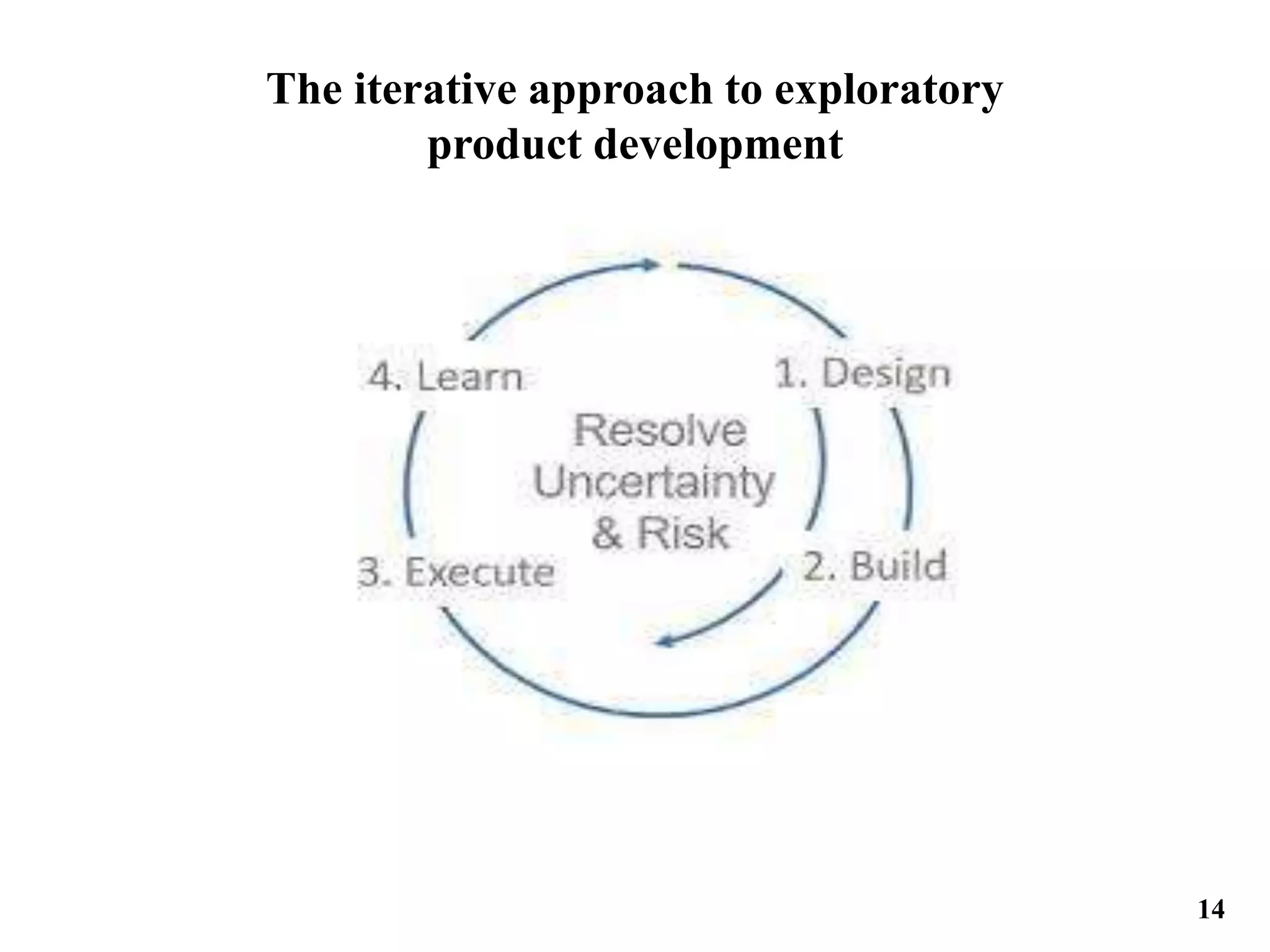
The document outlines the importance of documentation in the pharmaceutical industry, emphasizing good documentation practices to ensure accuracy, traceability, and compliance with regulatory standards. It discusses the definitions of drug substance and drug product, and critiques traditional phased-and-gated product development processes for being slow and inflexible. The document proposes an exploratory product development approach aimed at reducing uncertainty and risk through an adaptive system that responds to changing market and technology conditions.