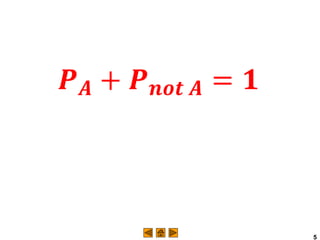Embed presentation
Downloaded 99 times



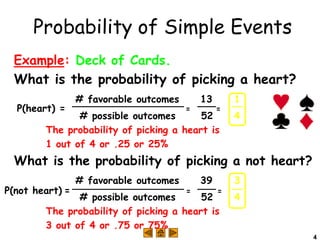
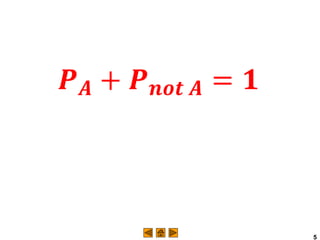


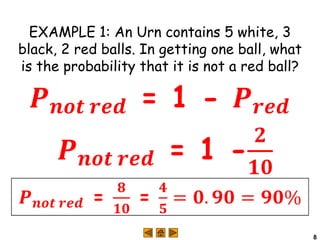



Complementary events are two events where the probability of one happening plus the probability of the other not happening equals 1. For example, with a standard six-sided die, the probability of rolling greater than 4 is 1/3, and the probability of rolling less than or equal to 4 (the complement) is 2/3, which sums to 1. The probability of an event can also be found by subtracting the probability of its complement from 1. For example, in drawing a ball from an urn with 5 white, 3 black, and 2 red balls, the probability of not drawing a red ball is 10/10, which is 1 minus the probability of drawing a red ball, 2/10.