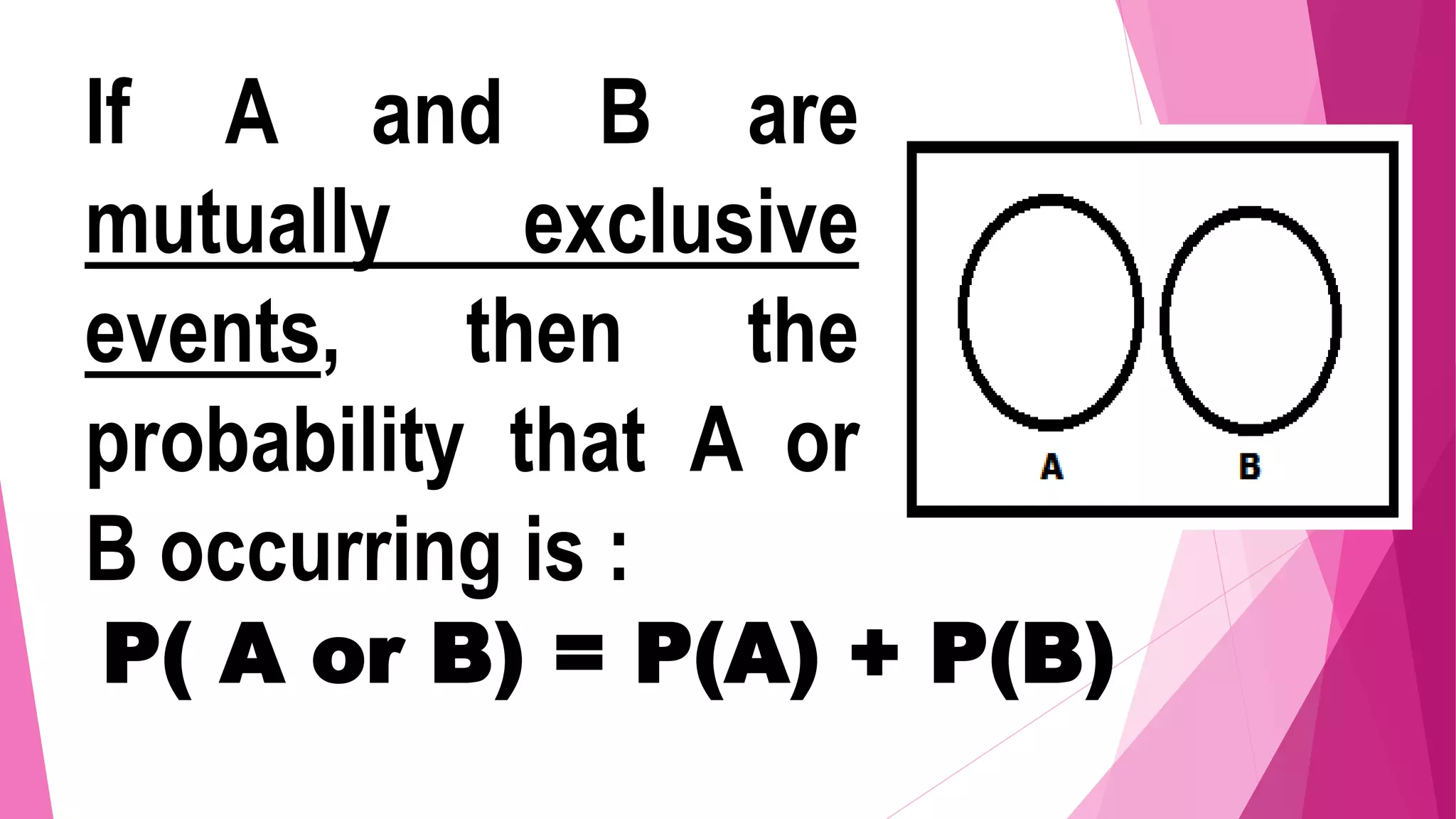
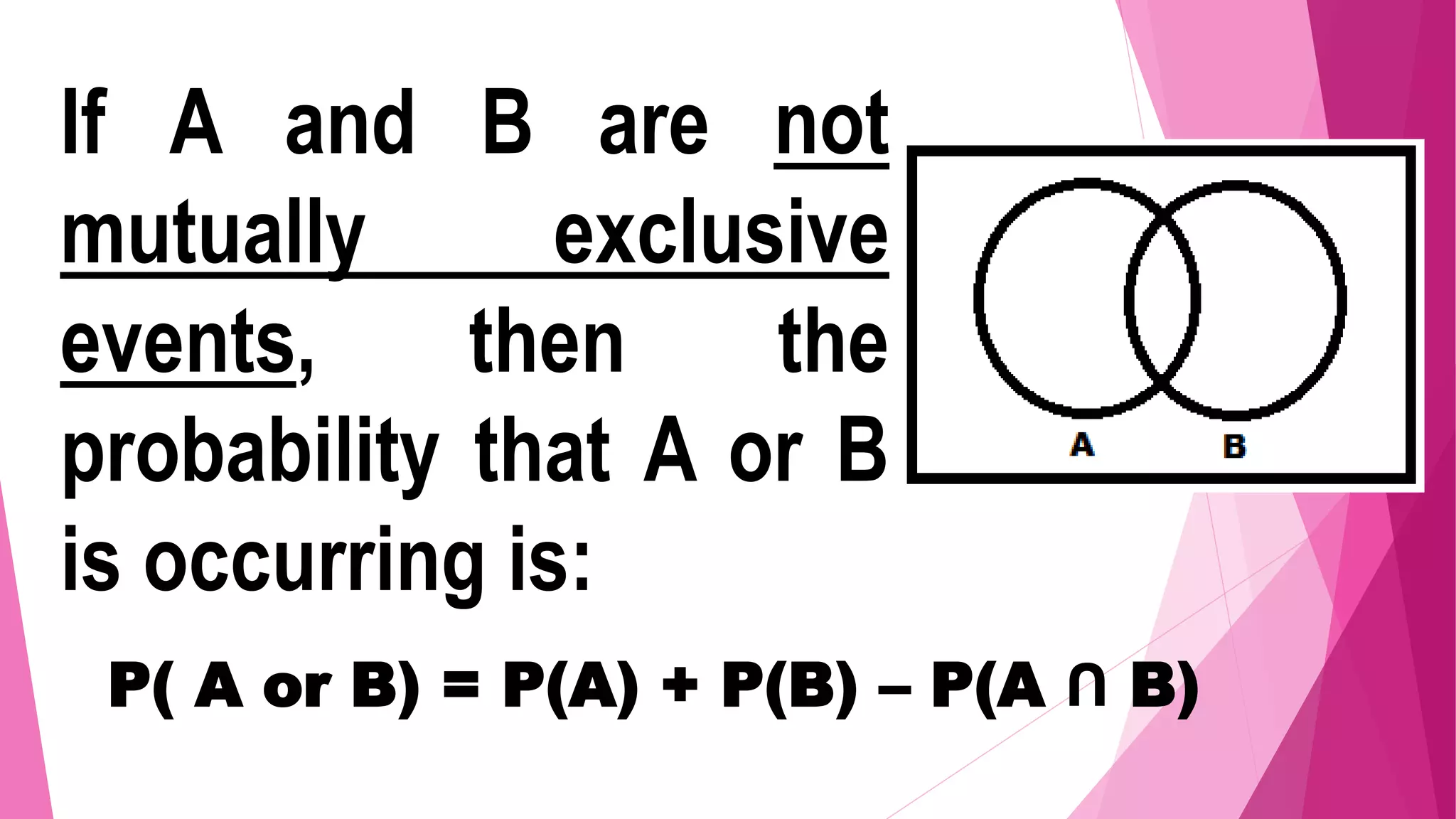
The document discusses mutually exclusive and non-mutually exclusive events. It provides examples to illustrate the difference, including examples involving drawing balls from a jar numbered 1-15 and rolling a die. It discusses how to calculate the probability of unions of events depending on whether they are mutually exclusive or not. Key points are that for mutually exclusive events, the probability of their union is the sum of their individual probabilities, while for non-mutually exclusive events it is the sum of their probabilities minus their intersection.