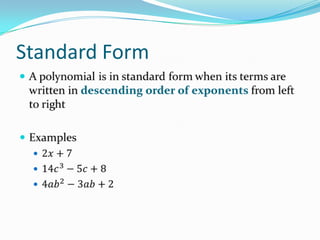
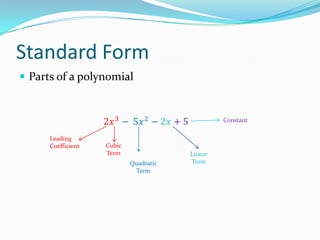
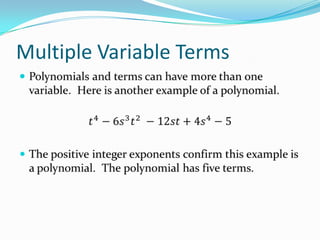
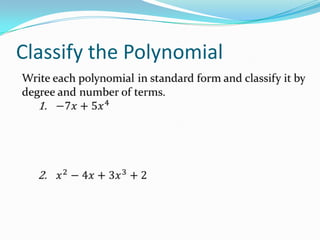
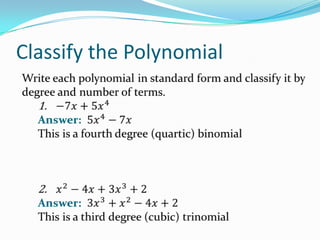
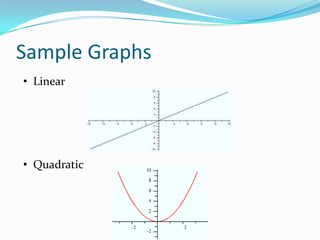
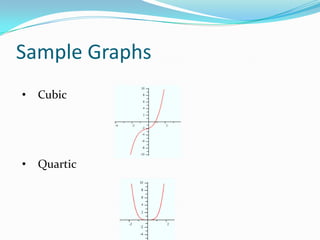
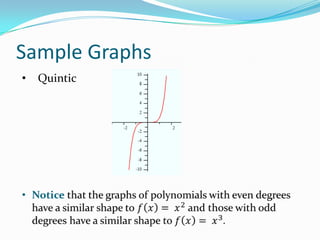
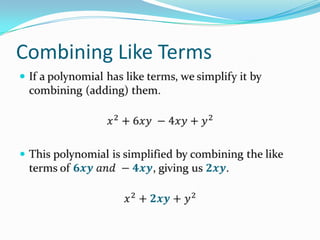
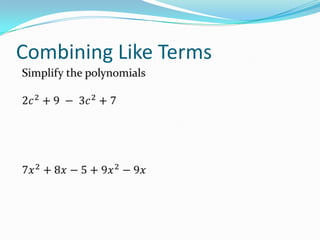
This document provides an introduction to polynomial functions including definitions of key terms like monomial, polynomial, standard form, degree of terms and polynomials, classifying polynomials by number of terms and degree, examples of graphs of low-degree polynomials, and how to combine like terms. It defines a monomial as an expression with variables and numbers, a polynomial as a sum of terms with whole number exponents. Standard form writes polynomials in descending order of exponents. Degree is determined by highest exponent of terms or polynomial. Polynomials are classified by number of terms (monomial, binomial, trinomial, etc.) or degree (linear, quadratic, cubic, etc.). Examples show graphs changing shape with increasing degree. Combining like terms adds coefficients of