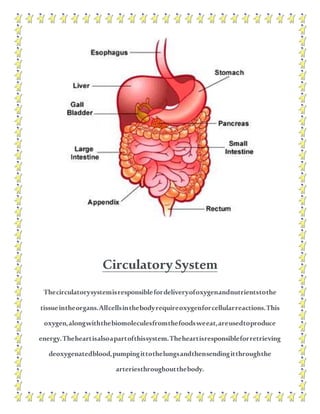
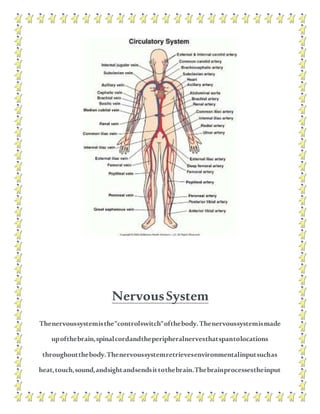
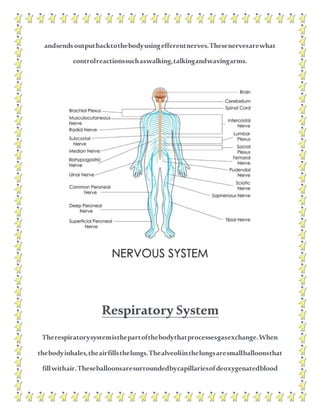
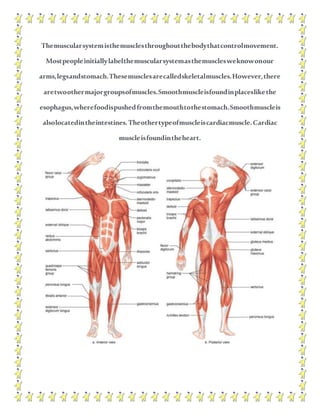
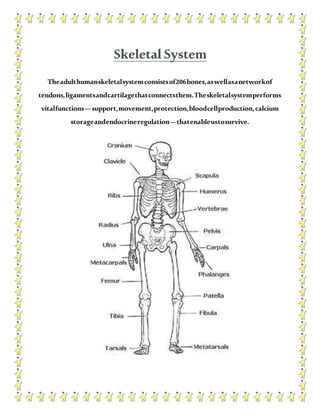
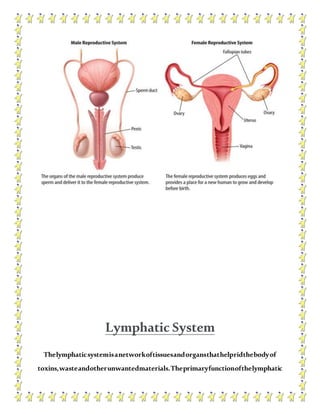
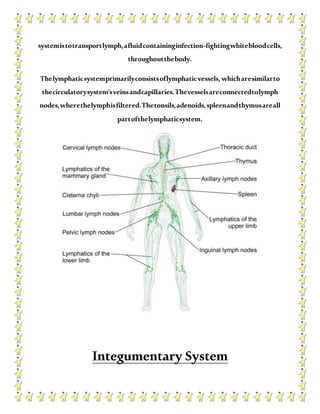
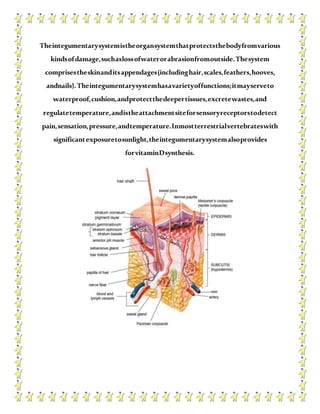
The human body contains multiple systems that work together to sustain life. These systems include the digestive, circulatory, nervous, respiratory, muscular, skeletal, urinary, reproductive, lymphatic, integumentary, and endocrine systems. Each system is comprised of organs and tissues that perform specialized functions to keep the body functioning properly.