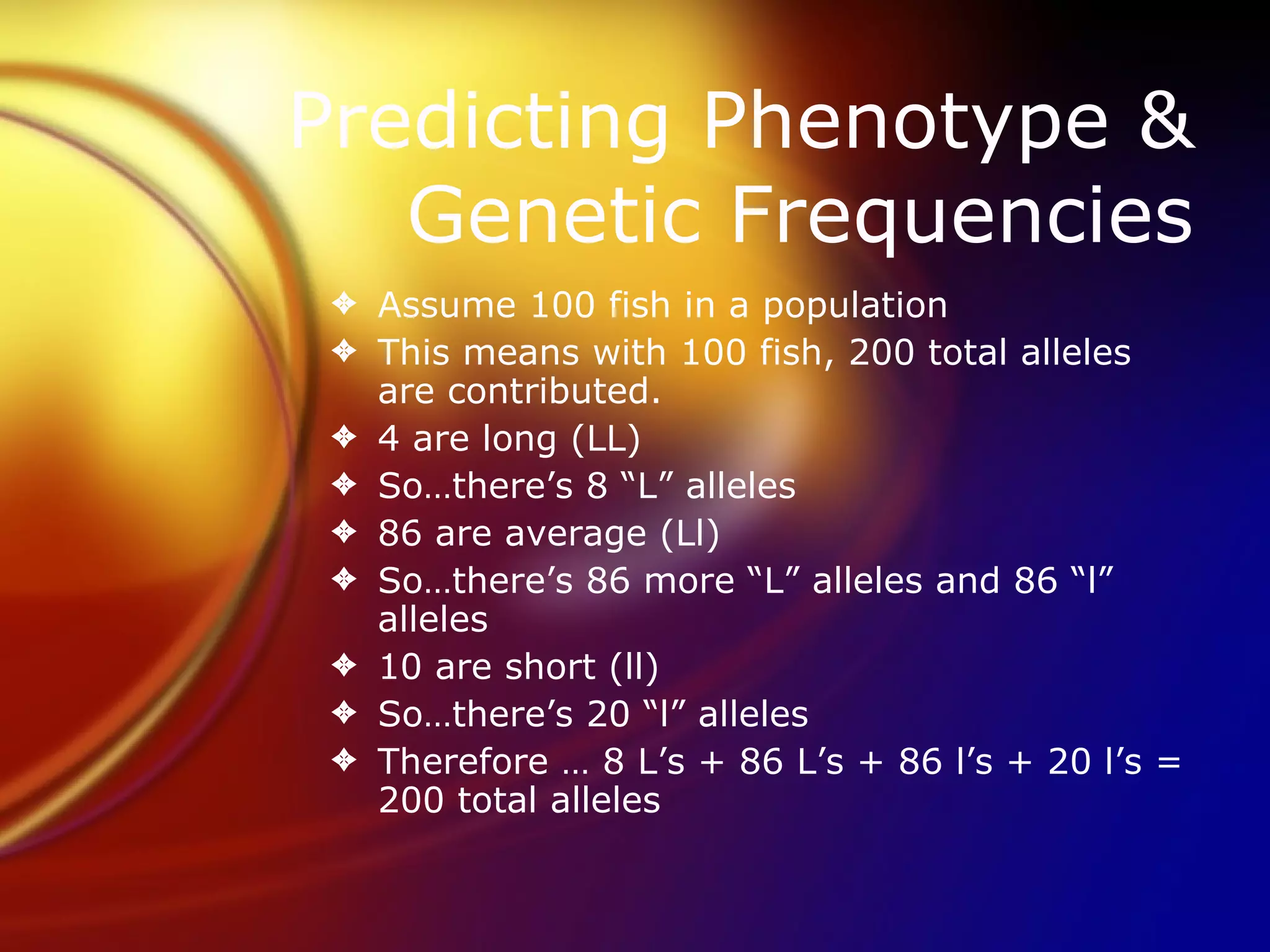
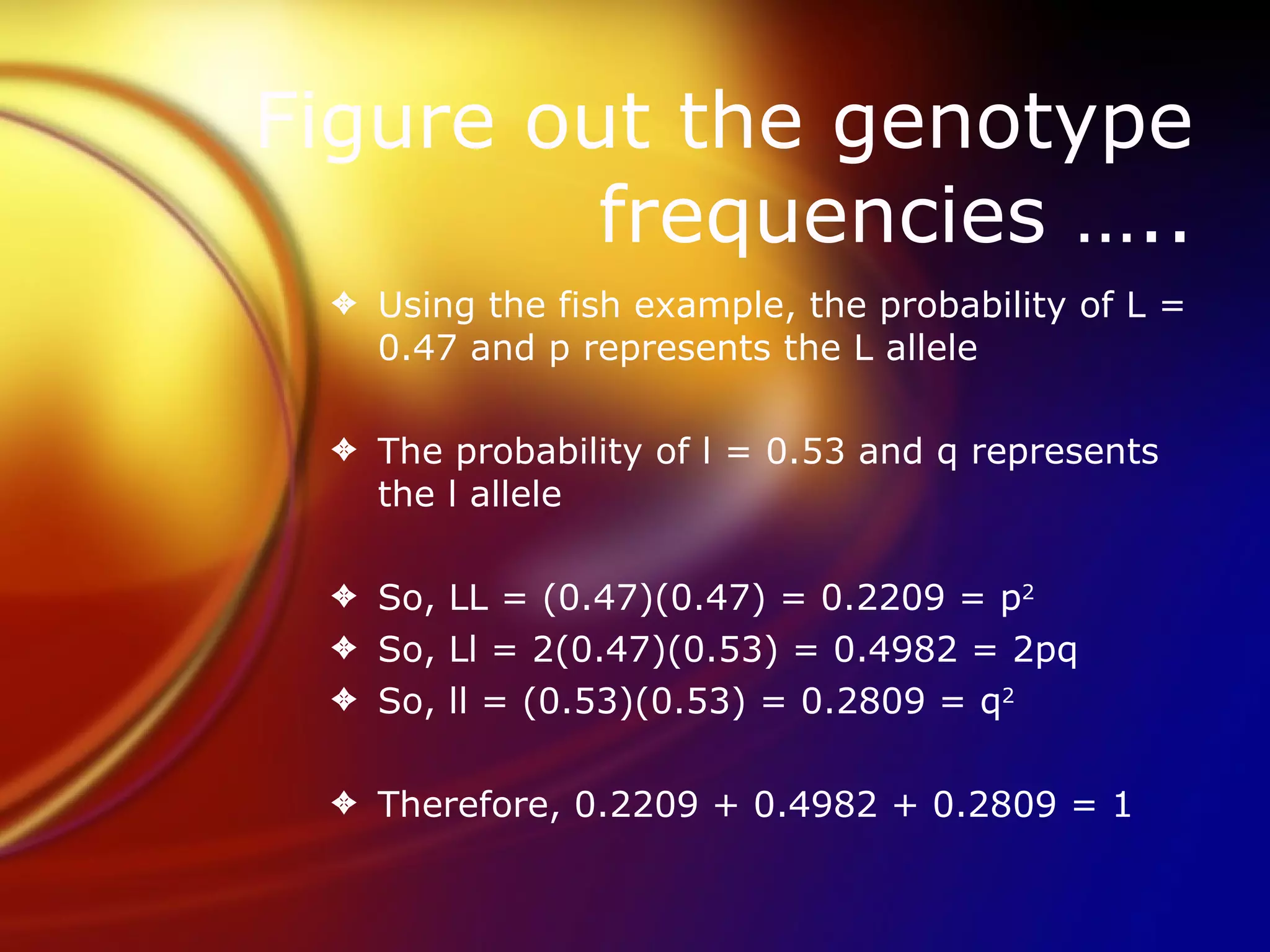
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium allows prediction of allele and genotype frequencies in a population over generations if the population is large, mates randomly, and is unaffected by mutations, migration or selection. It states that the allele frequencies will remain constant and can be used to determine the expected proportions of genotypes such as AA, Aa, and aa based on the allele frequencies p and q where p + q = 1.