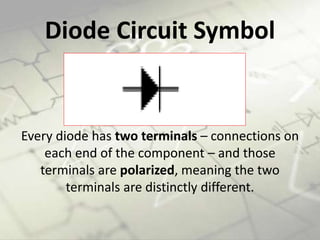
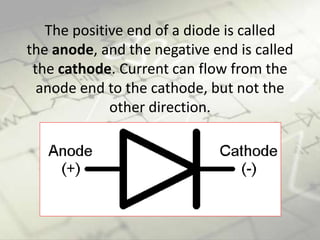
Diodes are semiconductor components that allow current to flow in only one direction. They have two terminals called the anode and cathode. Current can flow from the anode to the cathode but not in the reverse direction. When a forward bias is applied, the depletion region collapses and current can flow through the diode. When a reverse bias is applied, the depletion region expands and blocks current flow. Diodes are used in applications such as rectifiers, reverse current protection, logic gates, and voltage spike suppression.