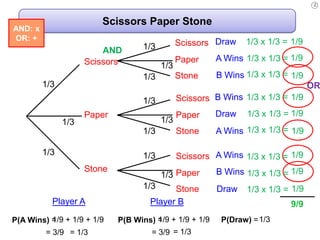
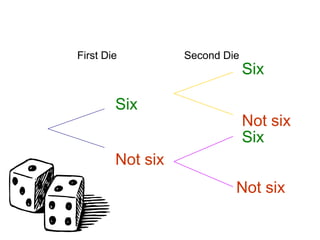
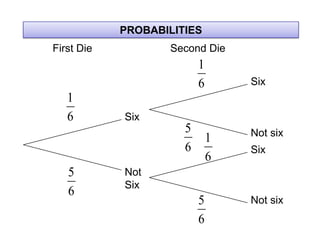
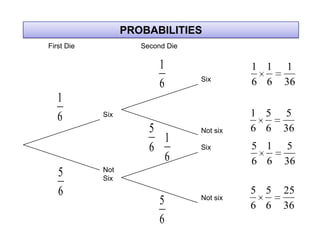
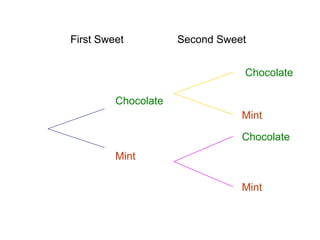
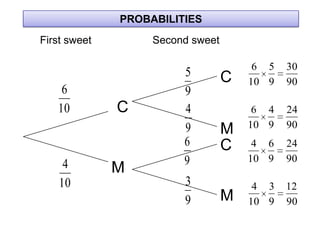
The document describes how to use tree diagrams to calculate conditional probabilities through games like scissors-paper-stone and dice rolls, as well as sweets selection. It provides instructions for playing a game, tabulating results, and converting tallies into probabilities. Additionally, it includes problems involving calculating probabilities of drawing two similar sweets from a tin.