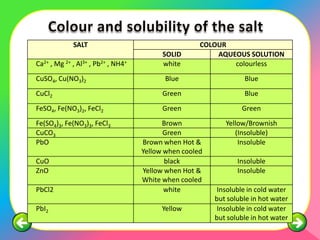
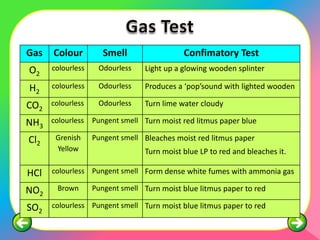
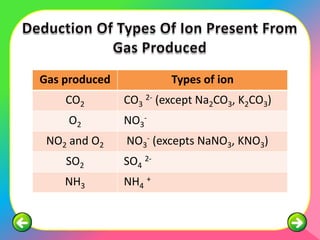
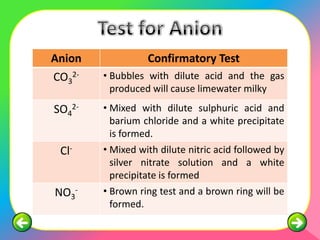
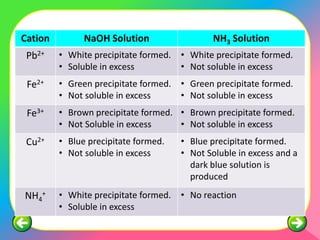
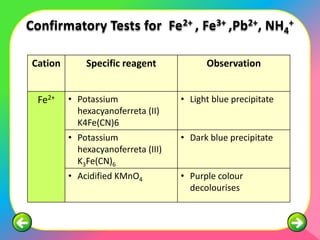
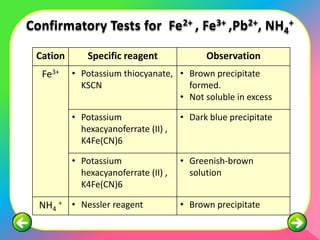
The document describes the process and tests used in qualitative analysis to identify salts based on their physical properties, reaction to heat, and tests to detect specific cations and anions. It provides details on observing the color and solubility of salts, conducting gas tests, and using confirmatory tests to identify ions like Fe2+, Fe3+, Pb2+, and NH4+. The qualitative analysis plan involves examining the salt's physical properties, heating it, testing for cations and anions, and then confirming the identities of ions present.