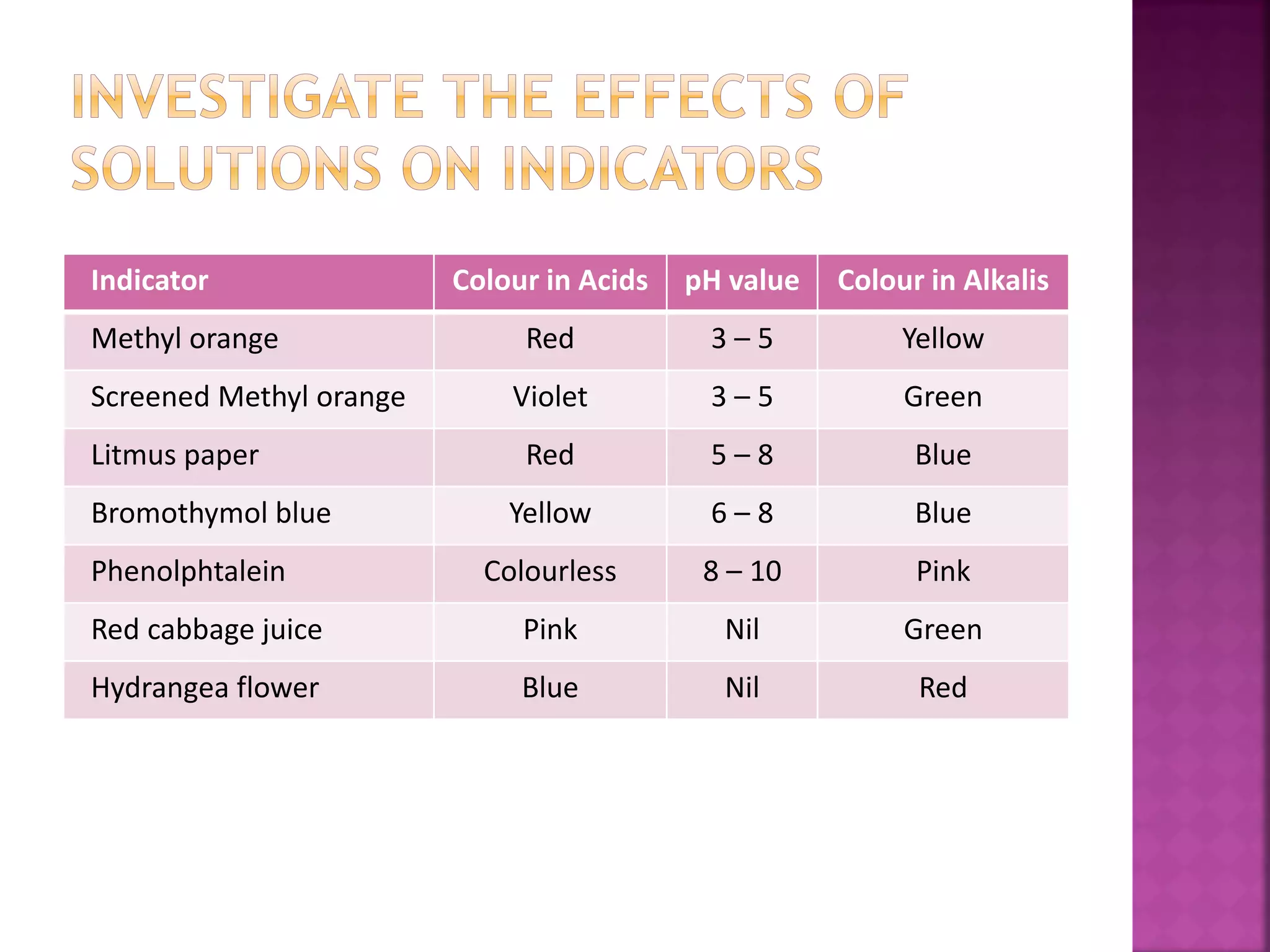
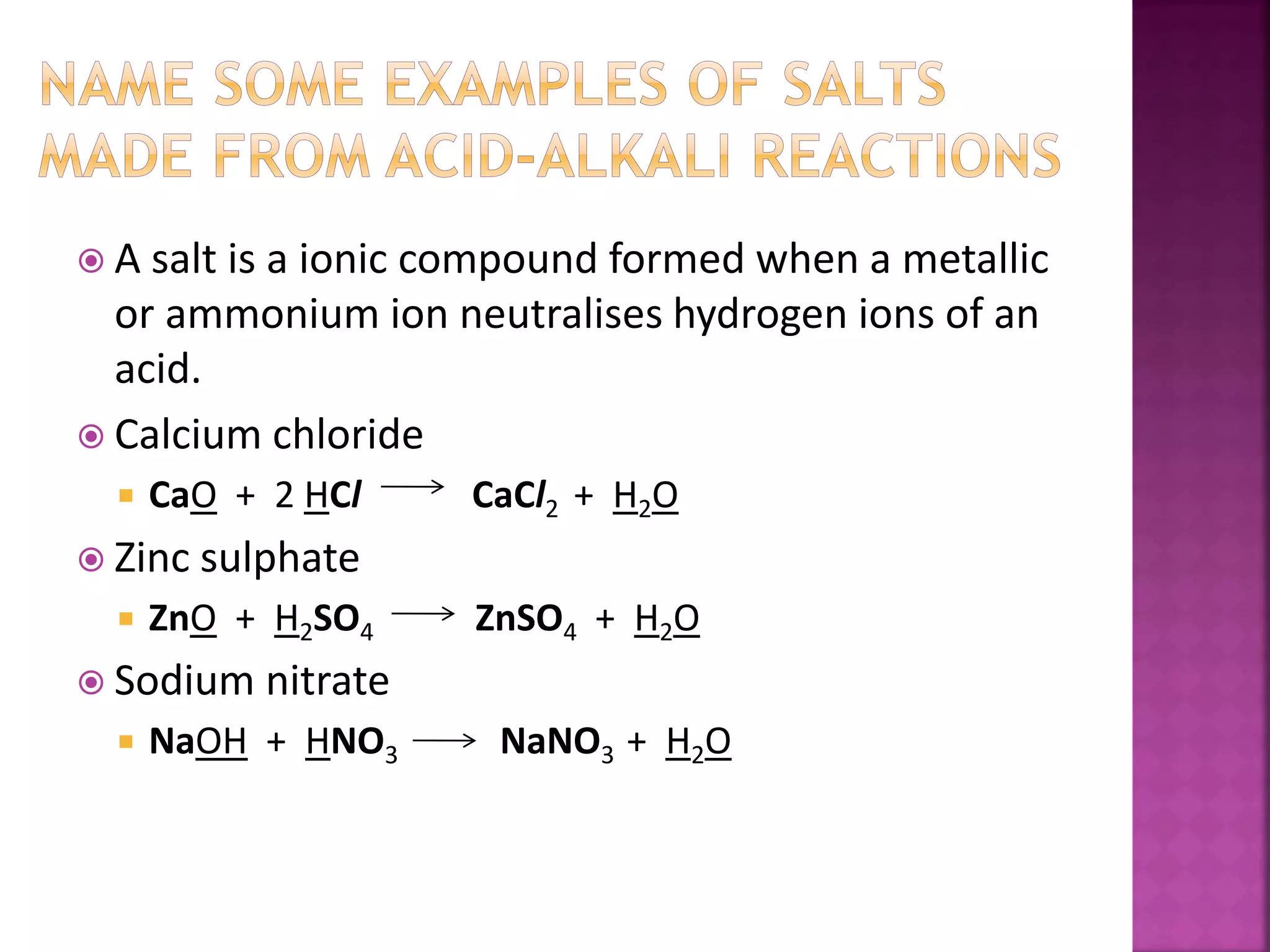
This document discusses acids and alkalis. It defines acids as substances that produce hydrogen ions in water, and provides examples like hydrochloric acid. Acids have properties like a sour taste, turning litmus red, and reacting with metals and carbonates. Alkalis are defined as metal oxides or hydroxides soluble in water, with examples like sodium hydroxide. Alkalis have properties like a bitter taste, turning litmus blue, and reacting with acids. The document also describes how acids and alkalis neutralize each other to form salts and water.





![ An alkali is a metal oxide or hydroxide that is
soluble in water.
Examples :
sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
potassium hydroxide (KOH)
calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2]
barium hydroxide [Ba(OH)2]
aqueous ammonia (NH3).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidsandalkali-090717043707-phpapp01/75/Acids-And-Alkali-6-2048.jpg)