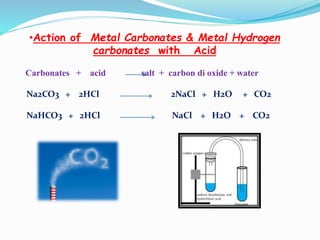
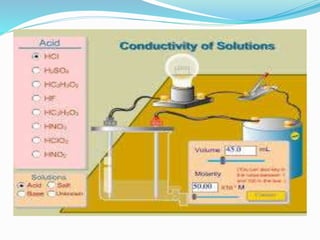
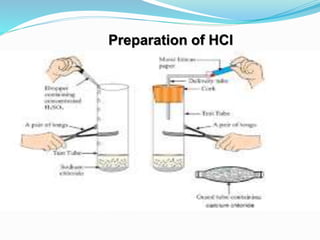
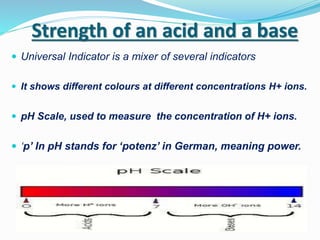
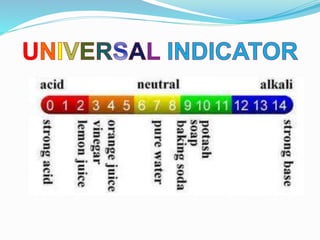
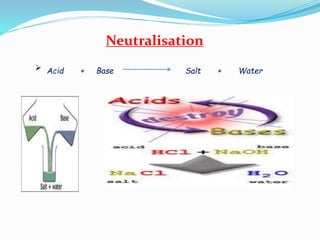
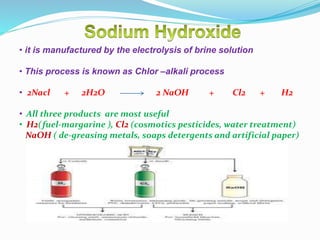
This document discusses indicators, acids, bases, and the reactions between them. It provides examples of natural and synthetic acid-base indicators and how they change color with pH. Acids are defined as sour substances that turn litmus red and donate hydrogen ions in water, while bases are defined as bitter substances that turn litmus blue and accept hydrogen ions in water. Common strong acids and bases are listed. The document also summarizes several acid-base reactions including neutralization and reactions with metals, carbonates, and oxides. It discusses the pH scale and importance of pH in everyday life. In the end, it briefly discusses the preparation and uses of several common salts.