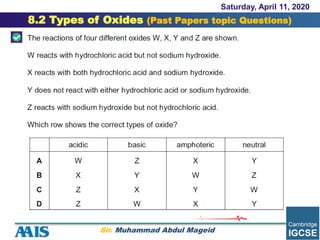
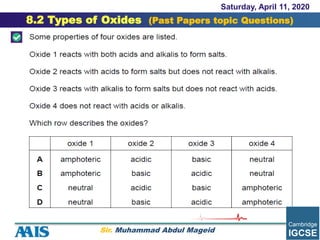
This document discusses different types of oxides:
- Acidic oxides are formed from nonmetals and produce acidic solutions. Basic oxides are formed from metals and produce basic solutions.
- Neutral oxides do not react with acids or bases. Amphoteric oxides can behave as either acids or bases depending on the other reactants.
- Common acidic oxides include SO2 and SiO2. Sodium oxide (Na2O) and calcium oxide (CaO) are examples of basic oxides. Zinc oxide and aluminum oxide are amphoteric oxides that can react as either acids or bases.