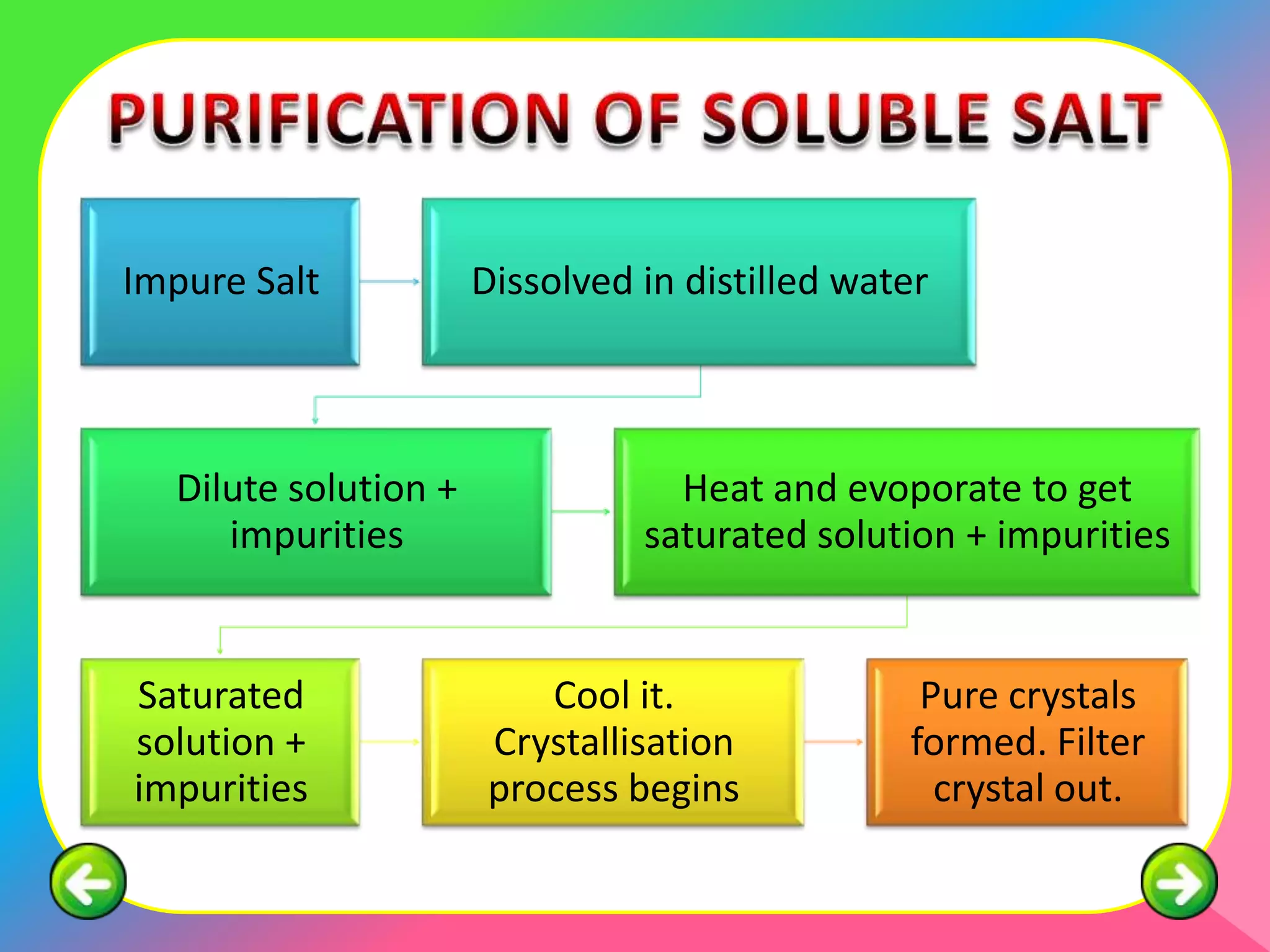
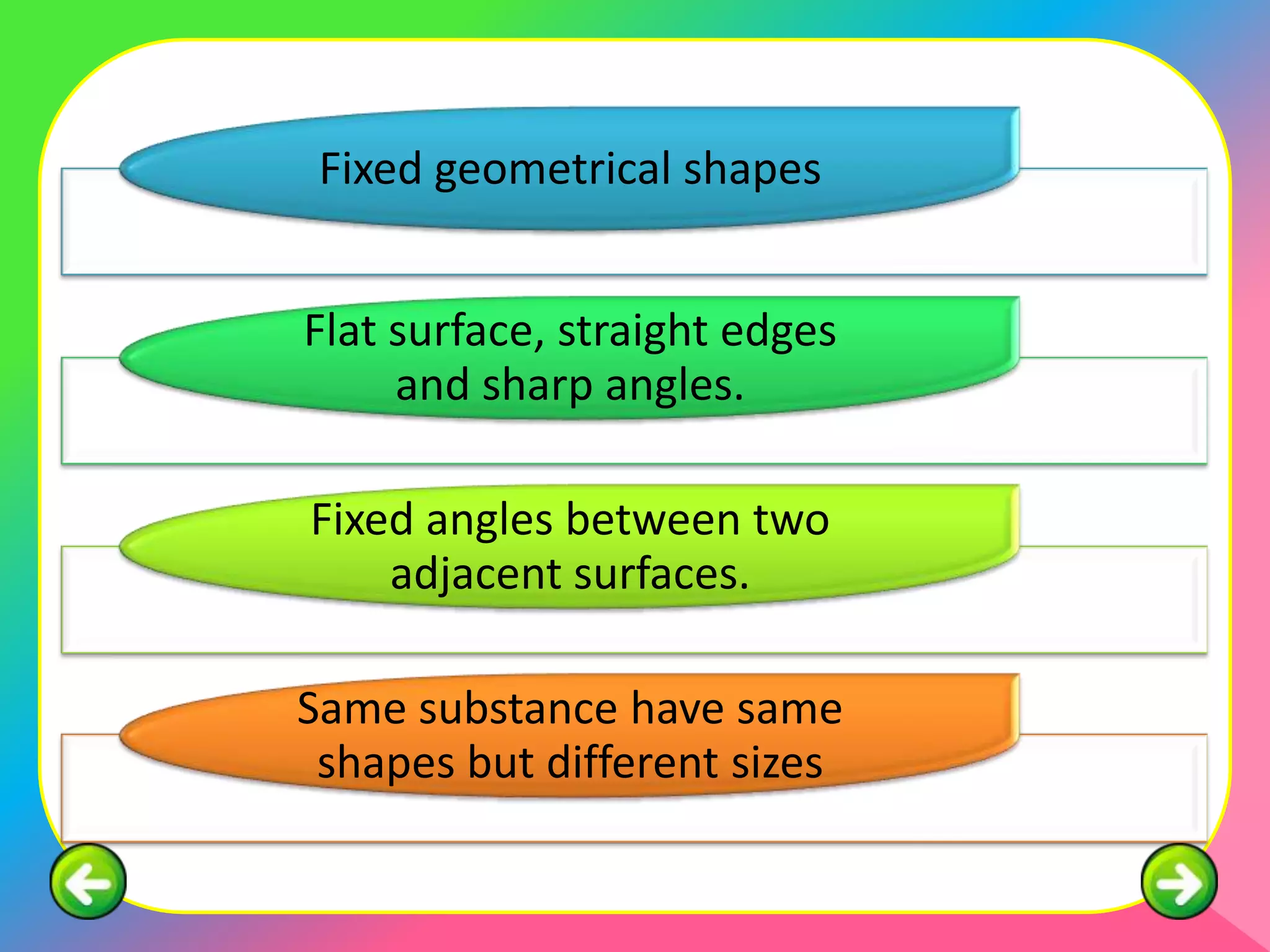
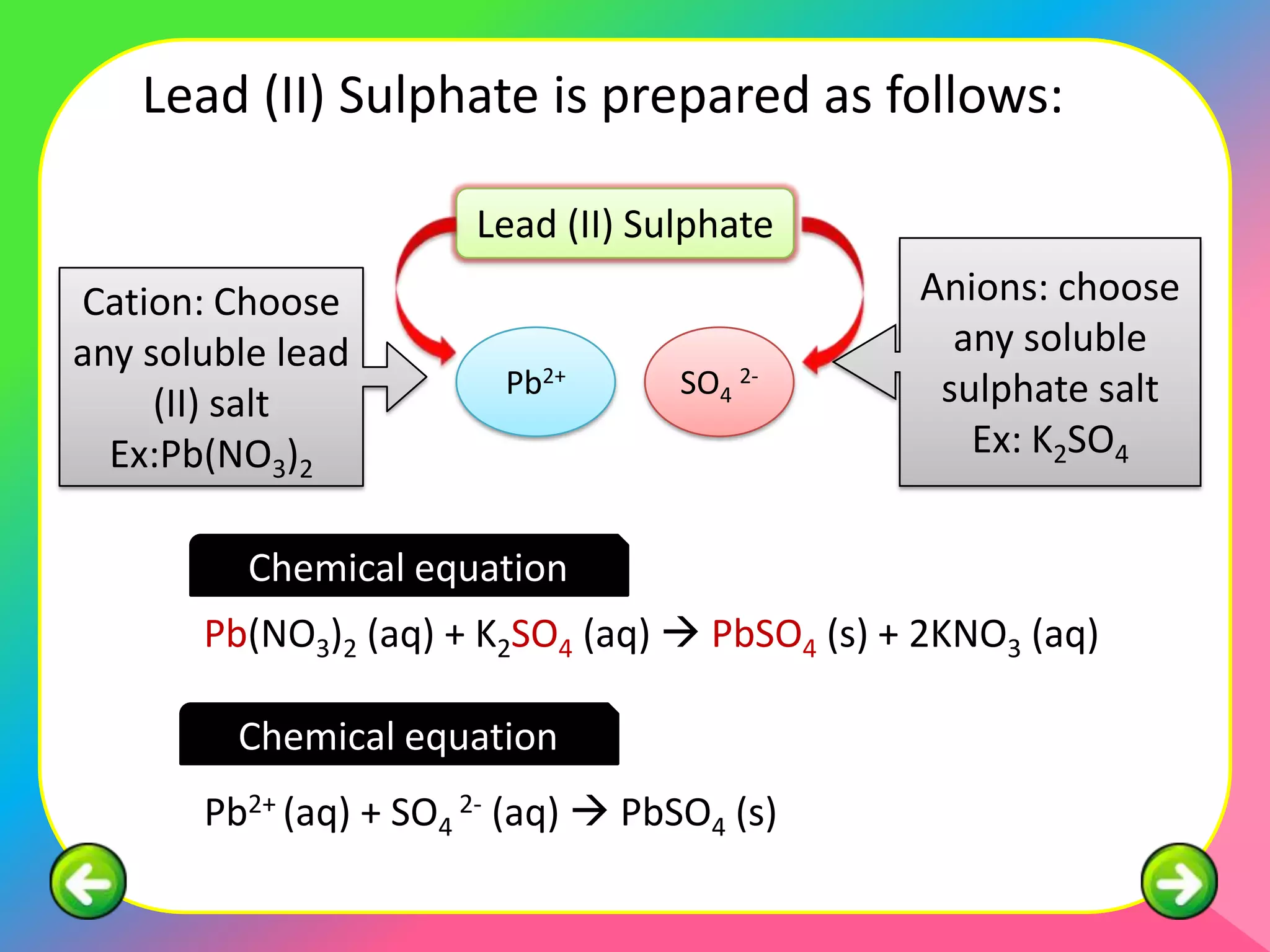
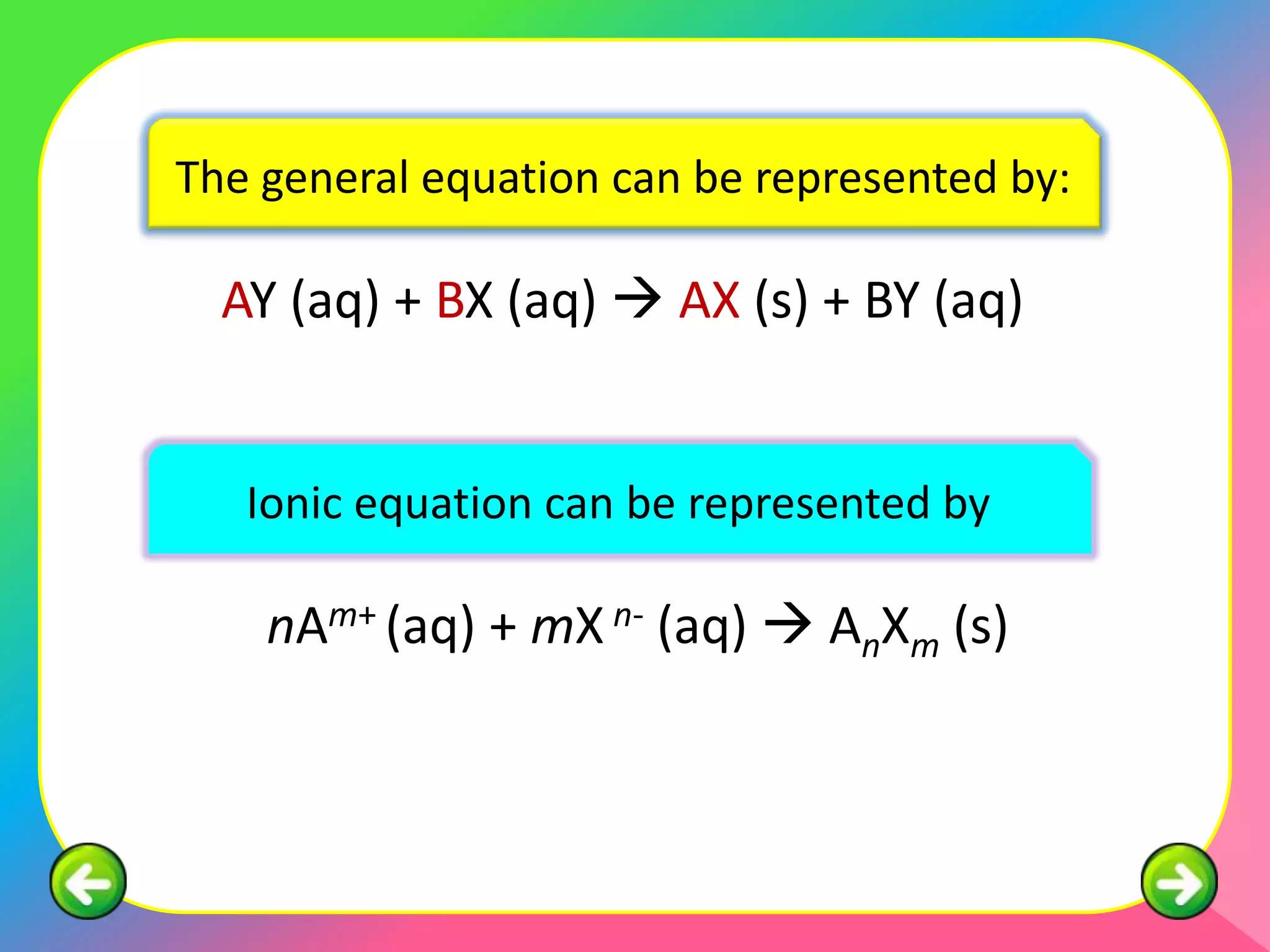
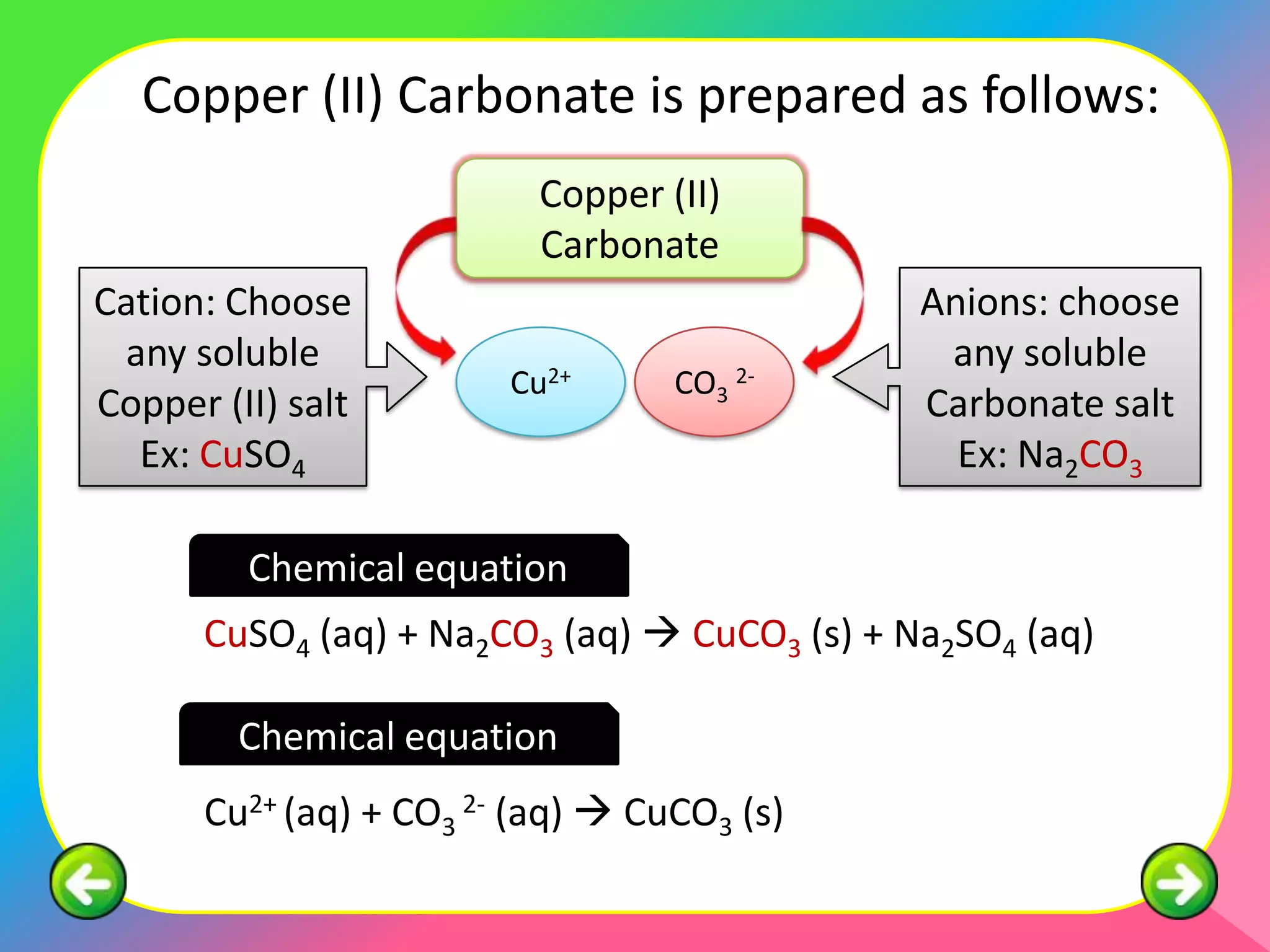
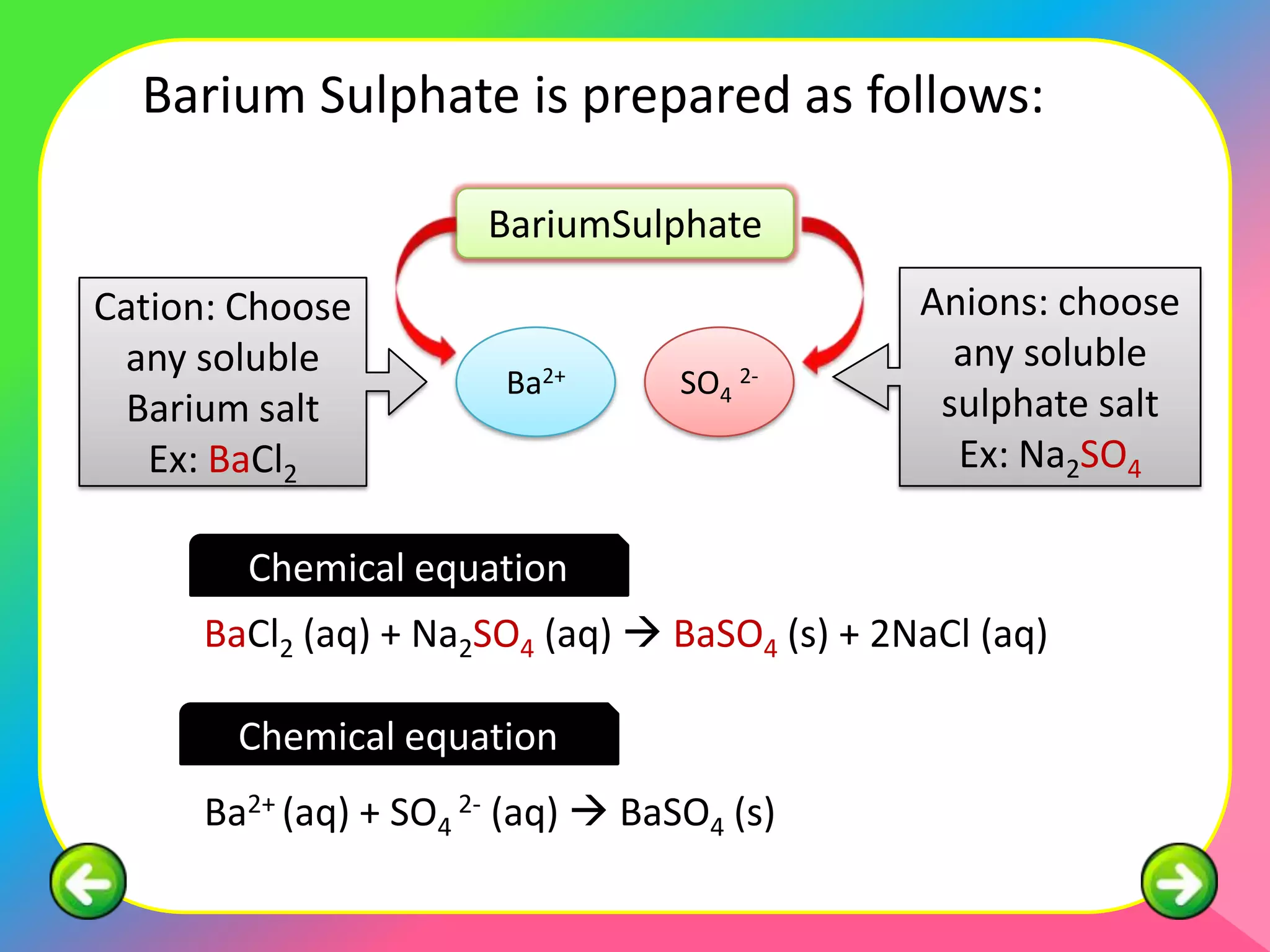
This document describes the purification of soluble salts through recrystallization and the preparation of insoluble salts through precipitation reactions. It discusses physical characteristics of salt crystals such as their geometric shape and fixed angles. It then provides examples of precipitation reactions used to prepare specific insoluble salts like lead (II) sulfate, copper (II) carbonate, and barium sulfate through a double decomposition reaction between aqueous solutions of their ions. General and ionic chemical equations are given to represent these precipitation reactions.