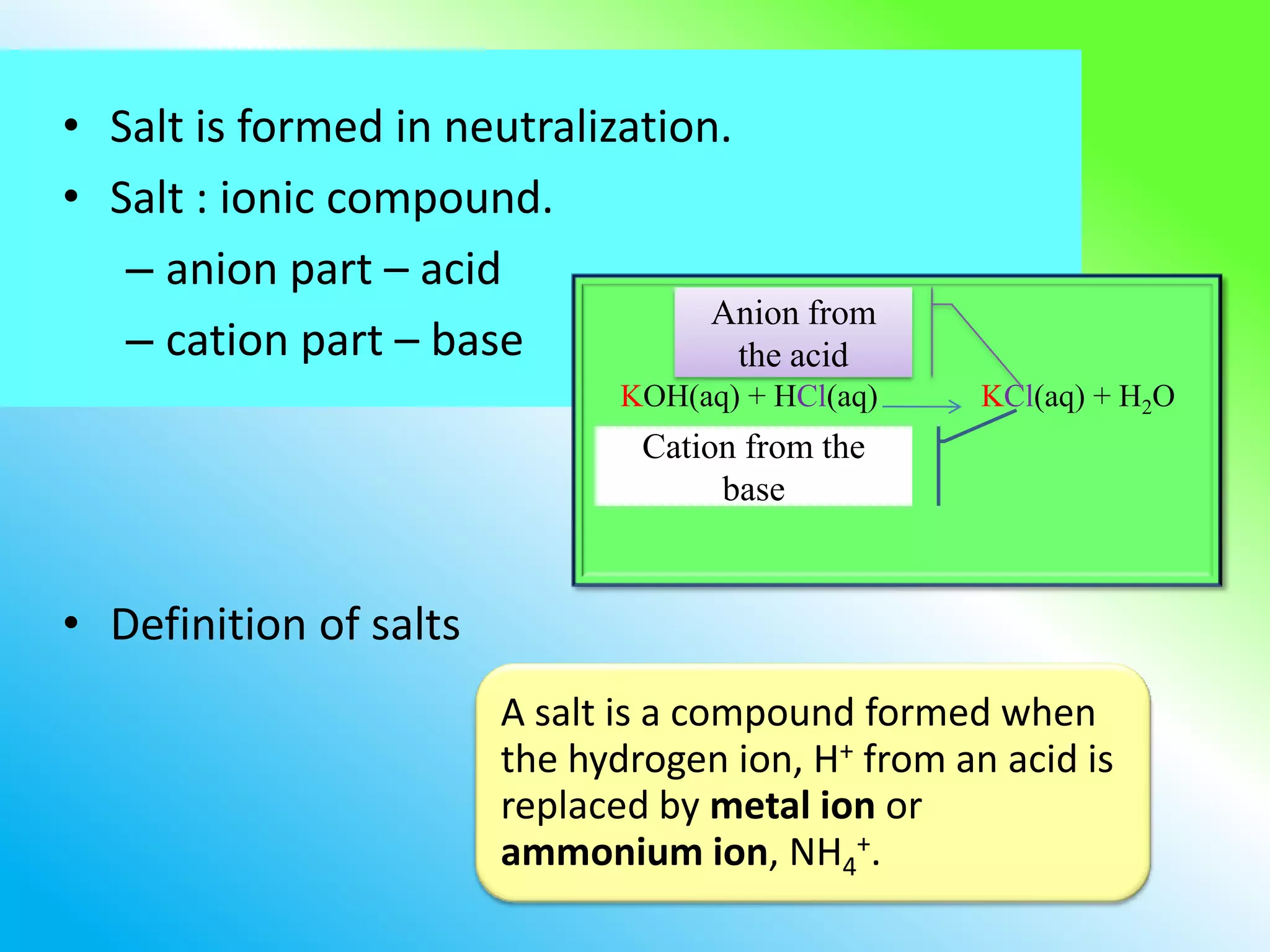
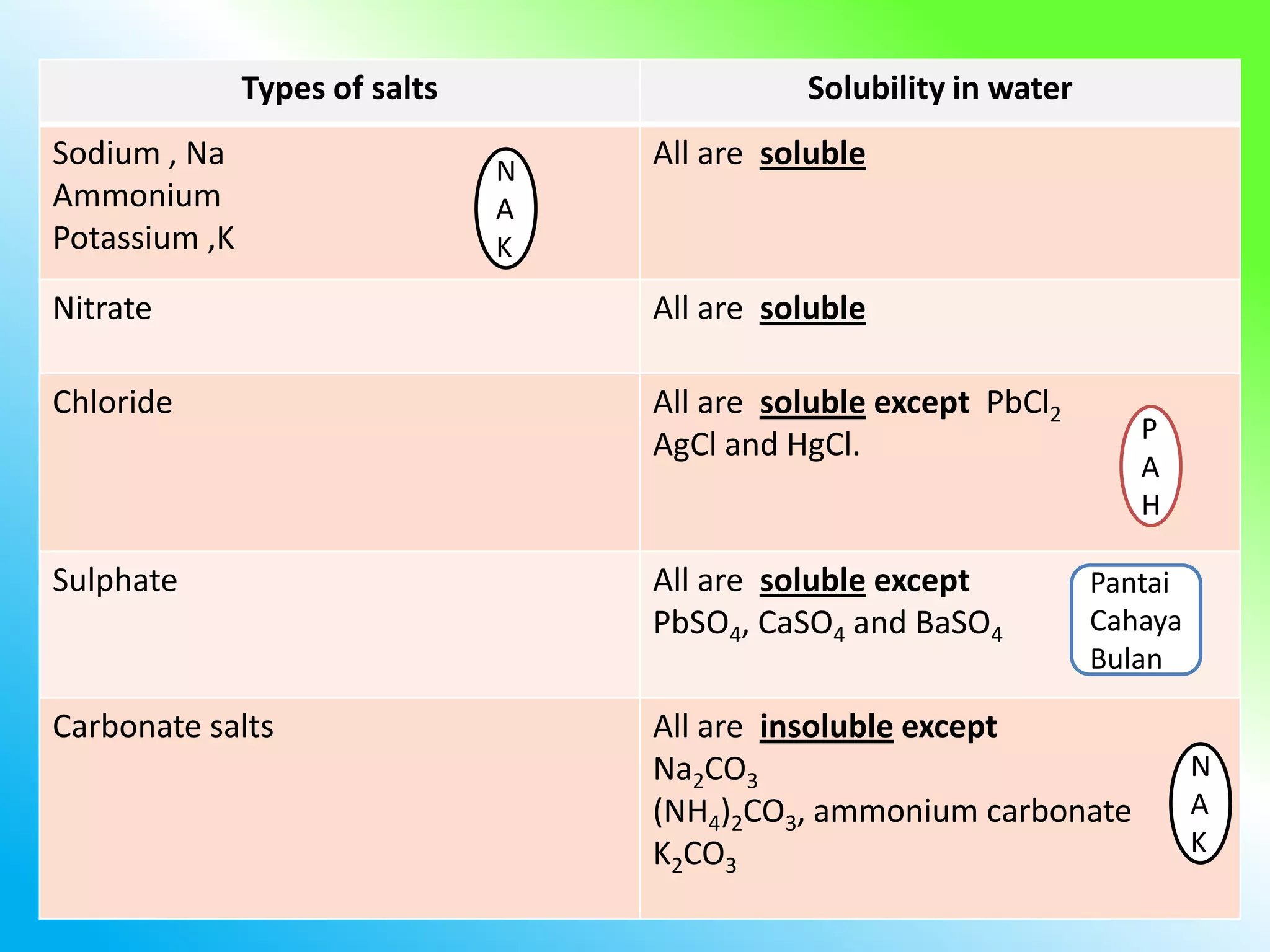
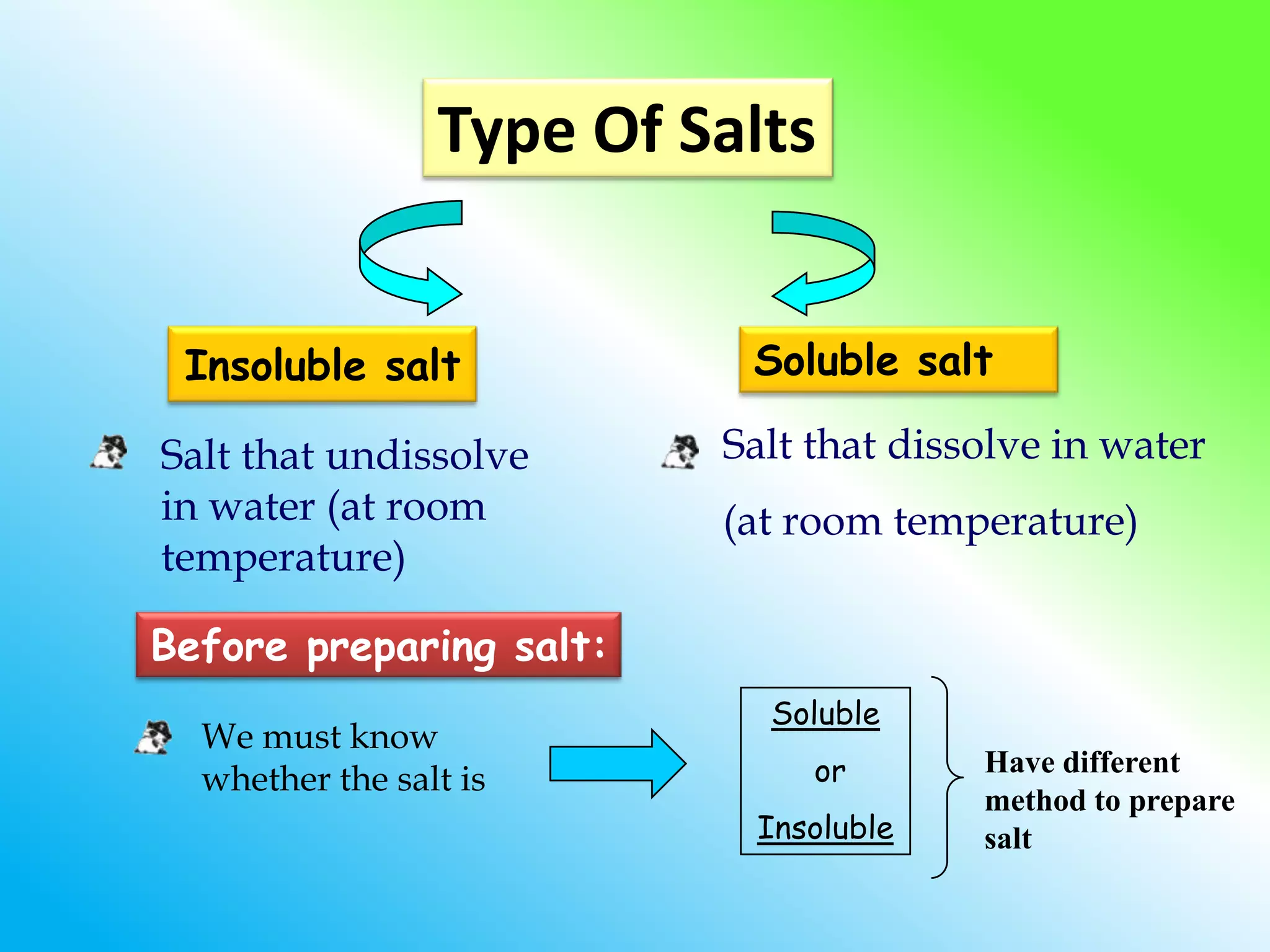
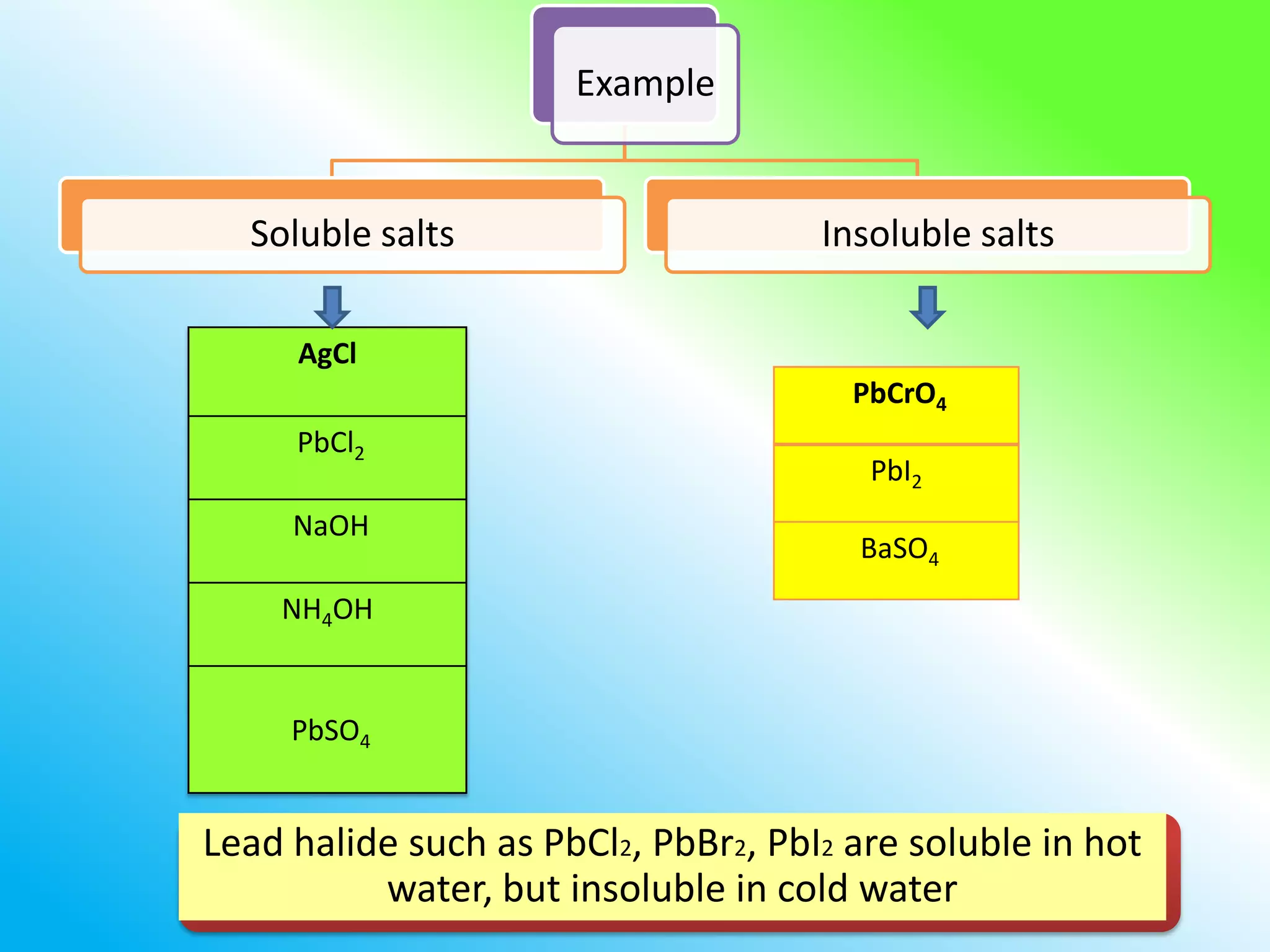
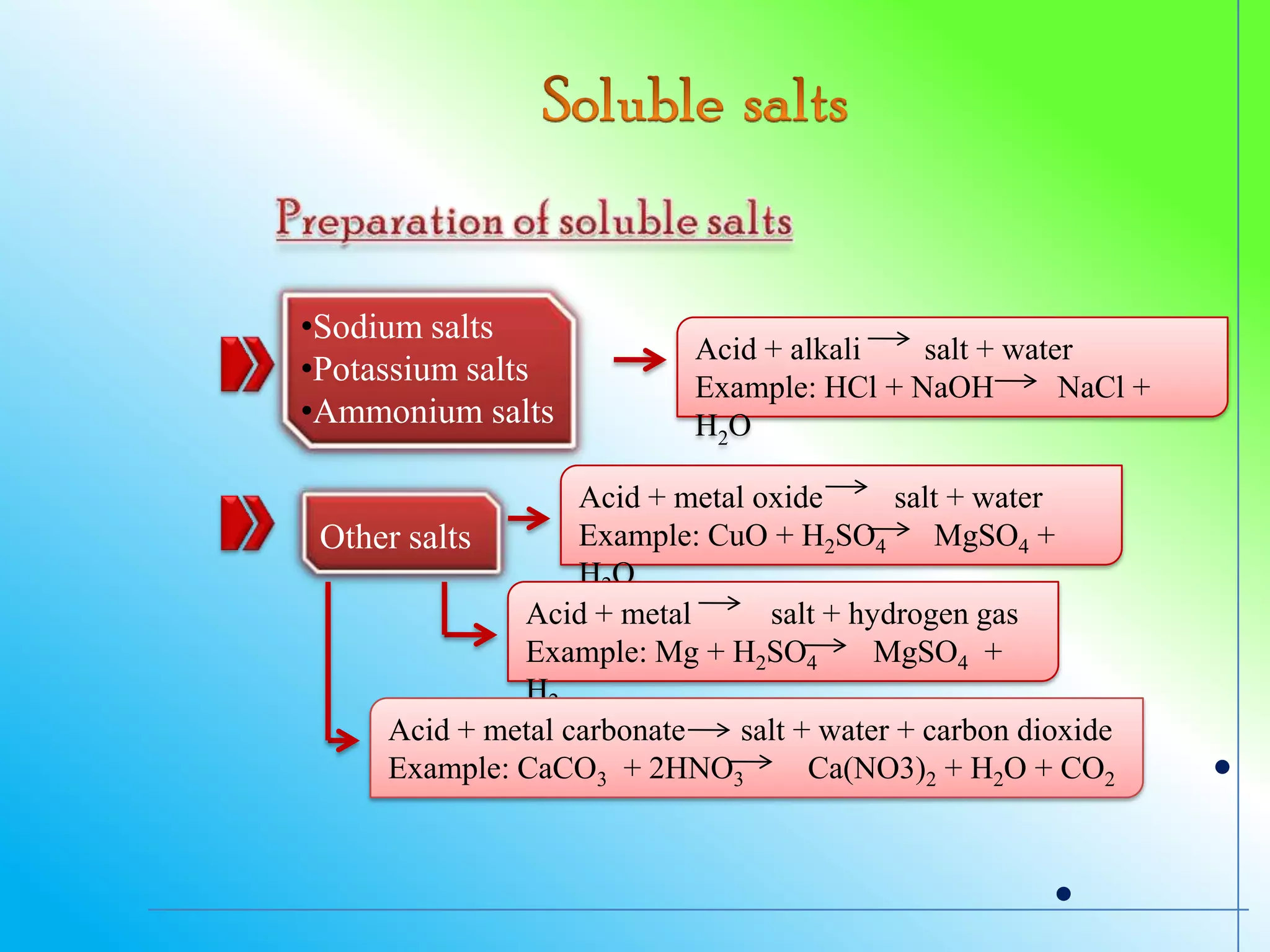
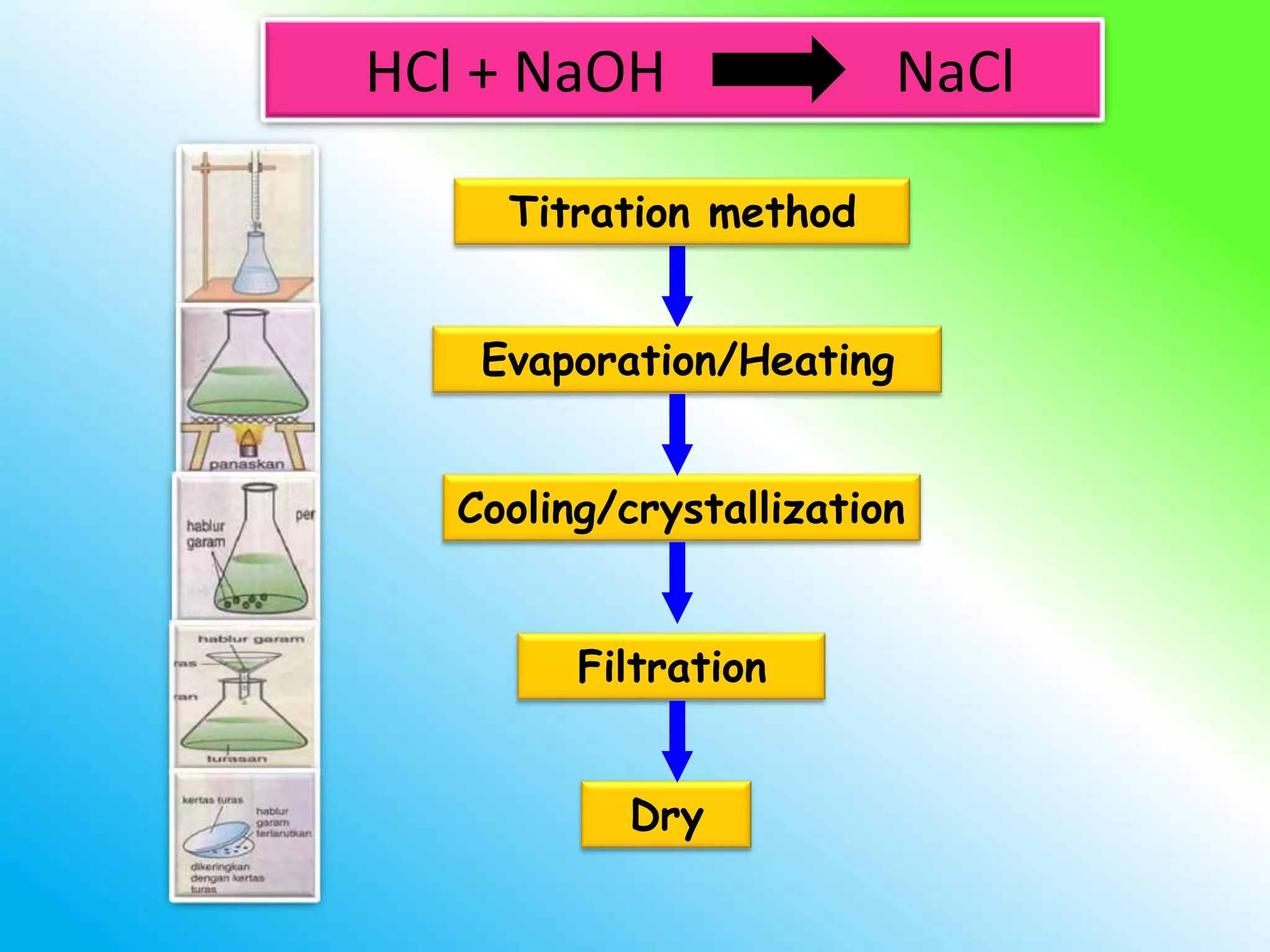
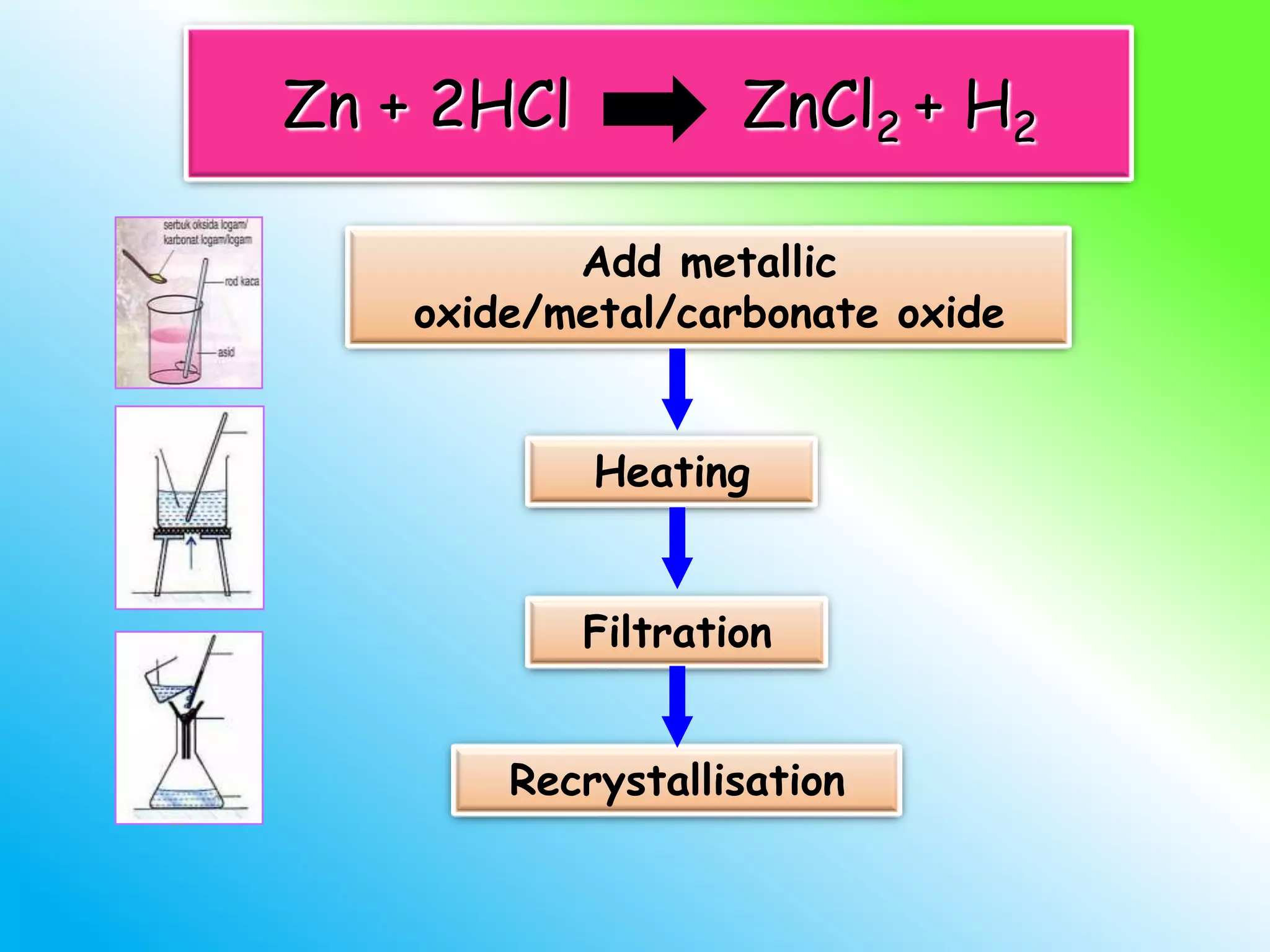
The document discusses learning outcomes about salts. It defines a salt as a compound formed when a hydrogen ion from an acid is replaced by a metal ion or ammonium ion. Examples of commonly used salts include NaCl, MSG, and CaCO3. Salts can be soluble or insoluble depending on their cation and anion. The document also describes different methods for preparing soluble and insoluble salts, such as titration, evaporation/heating, cooling/crystallization, filtration, and drying.