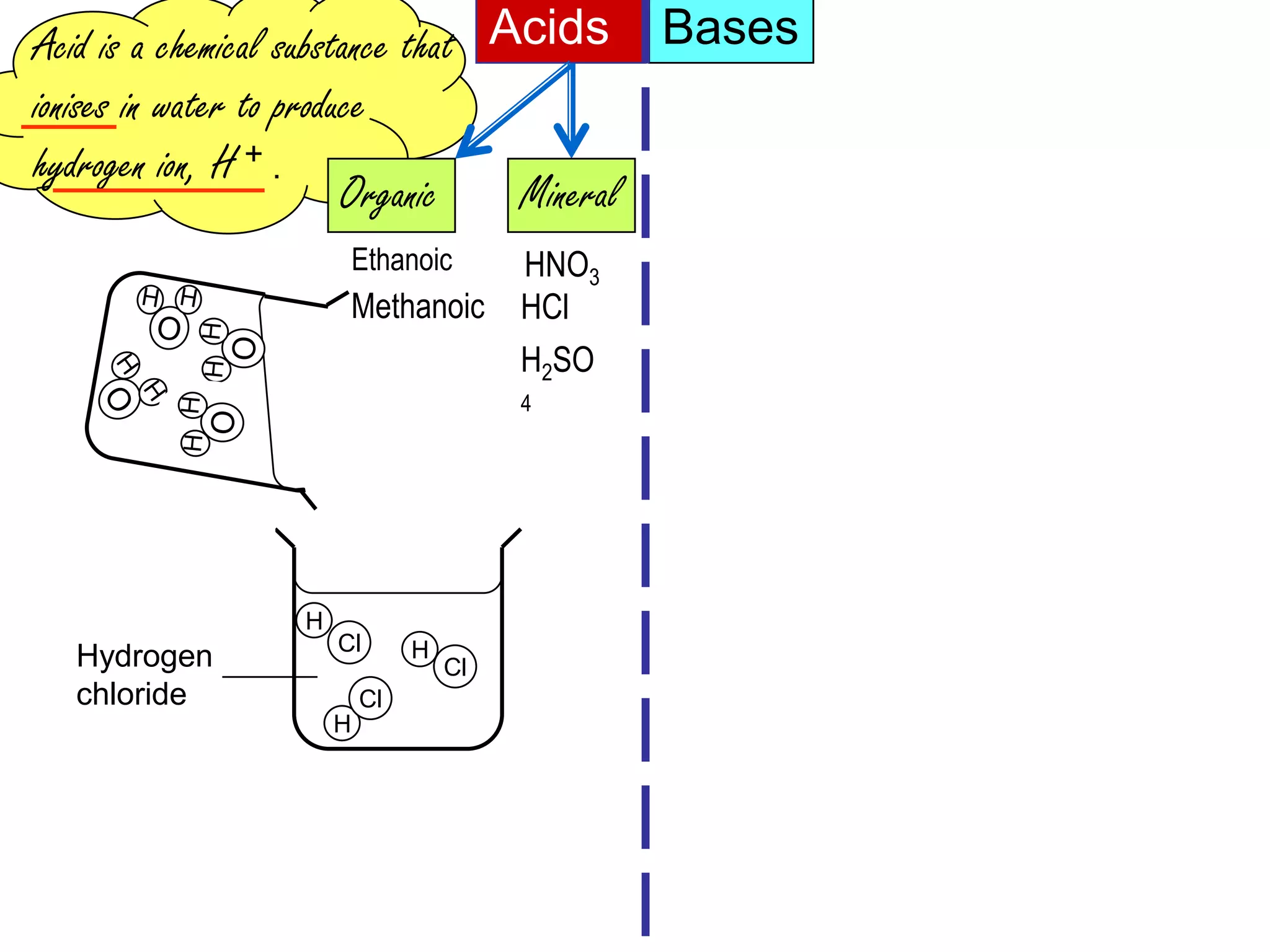
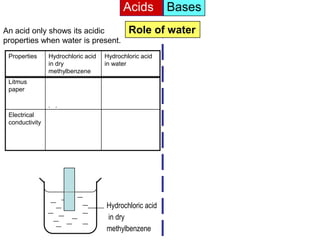
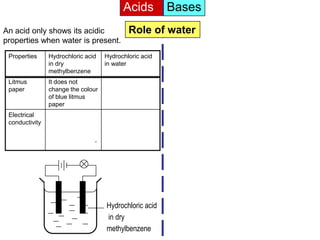
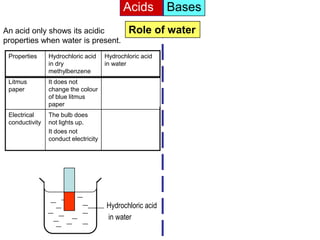
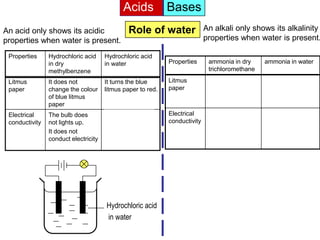
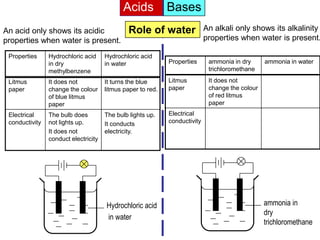
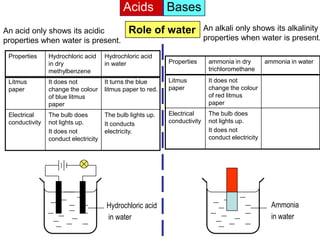
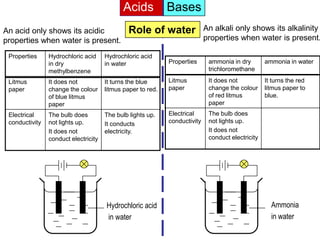
Acid is a chemical substance that ionises in water to produce hydrogen ions (H+). Acids only show their acidic properties when water is present. In water, hydrochloric acid turns litmus paper red and allows electricity to conduct, but in dry methylbenzene it does not change litmus color or allow conductivity. Similarly, alkalis like ammonia only demonstrate their alkaline properties in water, not in dry solvents.
![Standard solution Standard Solution
is a solution which its
concentration is accurately
known.
Acids Bases
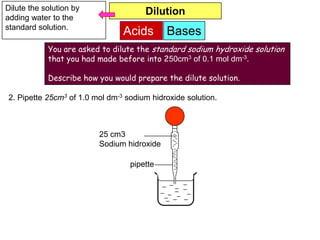
You are given solid sodium hidroxide. Describe the procedure
to prepare 500cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium hidroxide solution.
[Relative atomic mass: H=1; 0=16; Na=23]
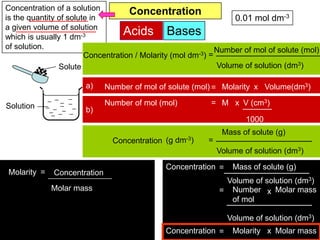
1. Calculate the mass of solute needed to give the required volume and molarity.
Number of mol, = M V (cm3) Number of mol, = Mass, NaOH
NaOH NaOH
1000 Molar mass
= 1.0 mol dm-3 (500cm3
) Mass, = Number of mol x Molar mass
1000 NaOH
= 0.5 mol = 0.5 mol x (23 + 16 +1) g mol-1
= 20.0 g
2. The solute is weighed.
20.0g Electronic Balance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbases-120920031517-phpapp01/85/Acid-bases-14-320.jpg)
![Standard solution Standard Solution
is a solution which its
concentration is accurately
known.
Acids Bases
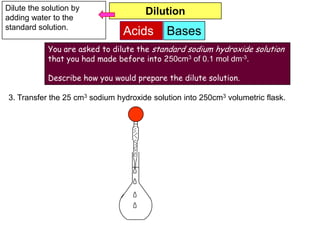
You are given solid sodium hidroxide. Describe the procedure
to prepare 500cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium hidroxide solution.
[Relative atomic mass: H=1; 0=16; Na=23]
3. Dissolve the solute in distilled water in a beaker.
20.0g Sodium hydroxide
glass rod
Sodium hydroxide
Distilled water
solution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbases-120920031517-phpapp01/85/Acid-bases-15-320.jpg)
![Standard solution Standard Solution
is a solution which its
concentration is accurately
known.
Acids Bases
You are given solid sodium hidroxide. Describe the procedure
to prepare 500cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium hidroxide solution.
[Relative atomic mass: H=1; 0=16; Na=23]
4. Transfer the content into a 500cm3 volumetric flask.
Calibration mark
Volumetric flask
500cm3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbases-120920031517-phpapp01/85/Acid-bases-16-320.jpg)
![Standard solution Standard Solution
is a solution which its
concentration is accurately
known.
Acids Bases
You are given solid sodium hidroxide. Describe the procedure
to prepare 500cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium hidroxide solution.
[Relative atomic mass: H=1; 0=16; Na=23]
5. Rinse the beaker with distilled water and transfer all the content into the
volumetric flask.
Wash bottle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbases-120920031517-phpapp01/85/Acid-bases-17-320.jpg)
![Standard solution Standard Solution
is a solution which its
concentration is accurately
known.
Acids Bases
You are given solid sodium hidroxide. Describe the procedure
to prepare 500cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium hidroxide solution.
[Relative atomic mass: H=1; 0=16; Na=23]
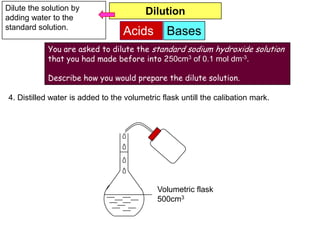
6. Distilled water is added to the volumetric flask untill the calibration mark.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbases-120920031517-phpapp01/85/Acid-bases-18-320.jpg)
![Standard solution Standard Solution
is a solution which its
concentration is accurately
known.
Acids Bases
You are given solid sodium hidroxide. Describe the procedure
to prepare 500cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium hidroxide solution.
[Relative atomic mass: H=1; 0=16; Na=23]
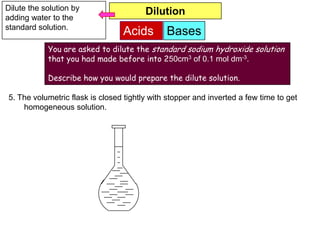
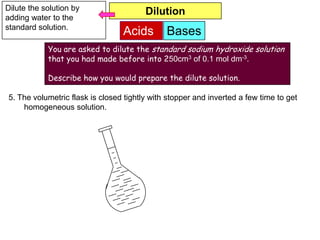
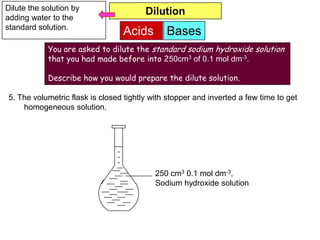
7. The volumetric flask is closed tightly with stopper and inverted a few time to get
homogeneous solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbases-120920031517-phpapp01/85/Acid-bases-19-320.jpg)
![Standard solution Standard Solution
is a solution which its
concentration is accurately
known.
Acids Bases
You are given solid sodium hidroxide. Describe the procedure
to prepare 500cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium hidroxide solution.
[Relative atomic mass: H=1; 0=16; Na=23]
7. The volumetric flask is closed tightly with stopper and inverted a few time to get
homogeneous solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbases-120920031517-phpapp01/85/Acid-bases-20-320.jpg)
![Standard solution Standard Solution
is a solution which its
concentration is accurately
known.
Acids Bases
You are given solid sodium hidroxide. Describe the procedure
to prepare 500cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium hidroxide solution.
[Relative atomic mass: H=1; 0=16; Na=23]
7. The volumetric flask is closed tightly with stopper and inverted a few time to get
homogeneous solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbases-120920031517-phpapp01/85/Acid-bases-21-320.jpg)
![Standard solution Standard Solution
is a solution which its
concentration is accurately
known.
Acids Bases
You are given solid sodium hidroxide. Describe the procedure
to prepare 500cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium hidroxide solution.
[Relative atomic mass: H=1; 0=16; Na=23]
7. The volumetric flask is closed tightly with stopper and inverted a few time to get
homogeneous solution.
500 cm3 1.0 mol dm-3,
Sodium hydroxide solution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbases-120920031517-phpapp01/85/Acid-bases-22-320.jpg)