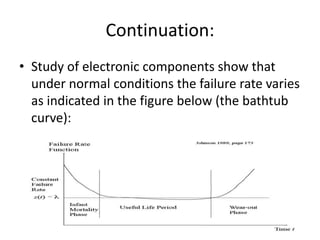
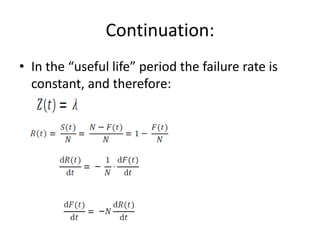
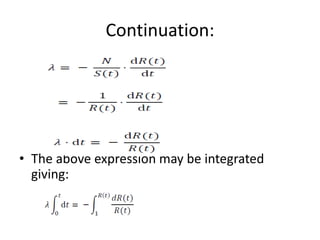
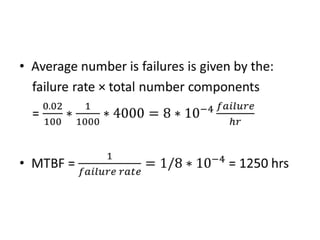
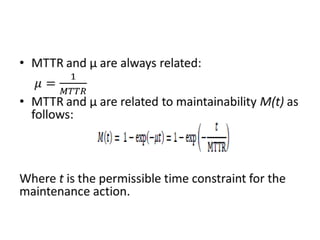
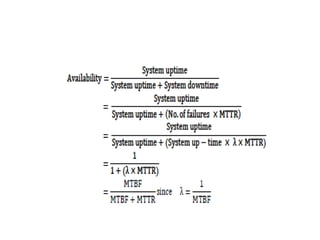
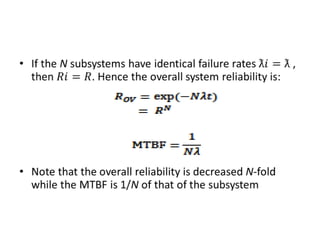
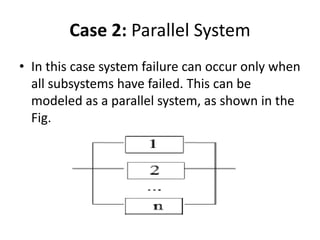
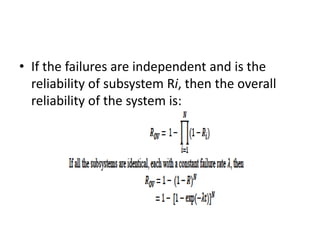
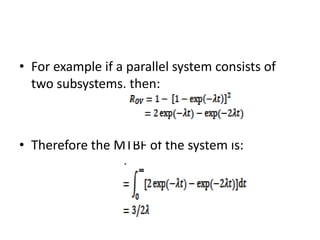
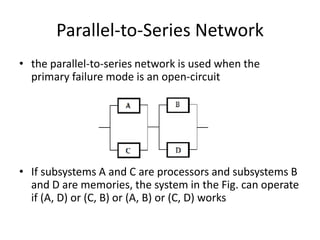
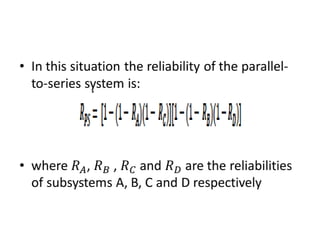
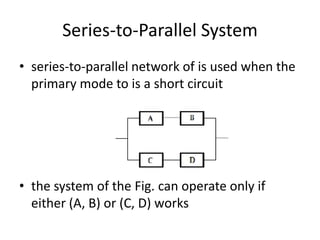
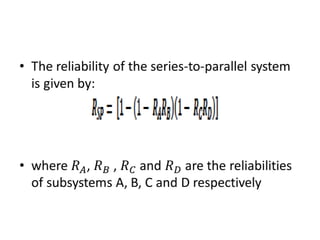
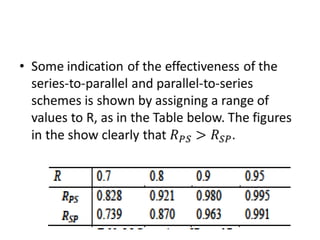
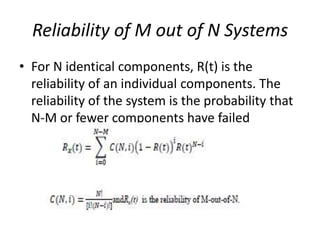
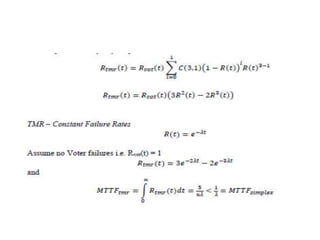
Fault tolerance refers to a system's ability to continue operating correctly even if some components fail. There are three categories of faults: transient, intermittent, and permanent. Fault tolerance is achieved through redundancy, including information, time, and physical redundancy. Reliability is the probability a system will function as intended for a given time. It depends on design, components, and environment. Reliability increases through quality control and redundancy. Maintainability is the probability a failed system can be repaired within a time limit. Availability is the probability a system will be operational when needed. Series systems fail if any component fails, while parallel systems fail only if all components fail.