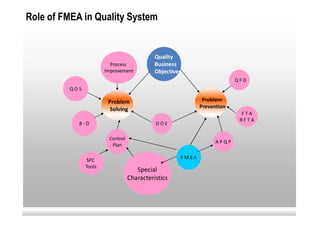
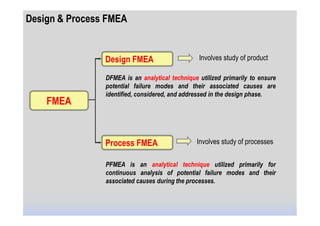
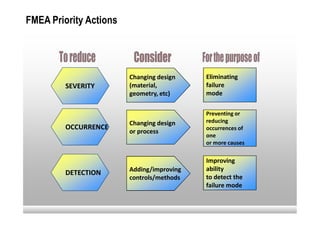
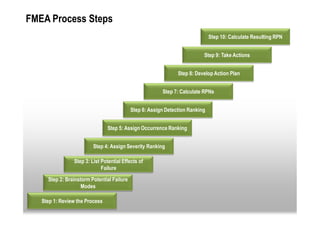
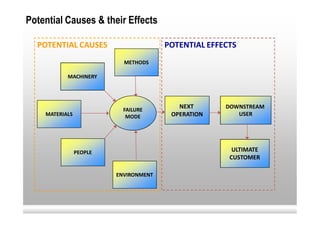
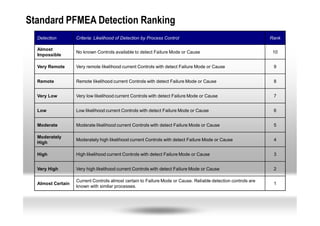
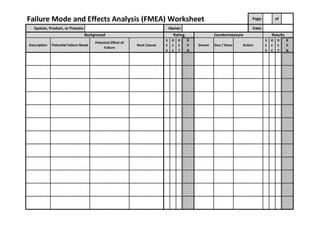
This document provides an overview of Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). FMEA is a systematic method used to evaluate potential failure modes in a design, process or service and their causes and effects. It involves analyzing potential failures, their likelihood and severity, and identifying actions to address potential failures with high risk priority numbers. The document defines key terms in FMEA like severity, occurrence, detection and risk priority number. It also outlines the FMEA process, including steps to identify potential failure modes, effects, causes, current controls and priority actions.