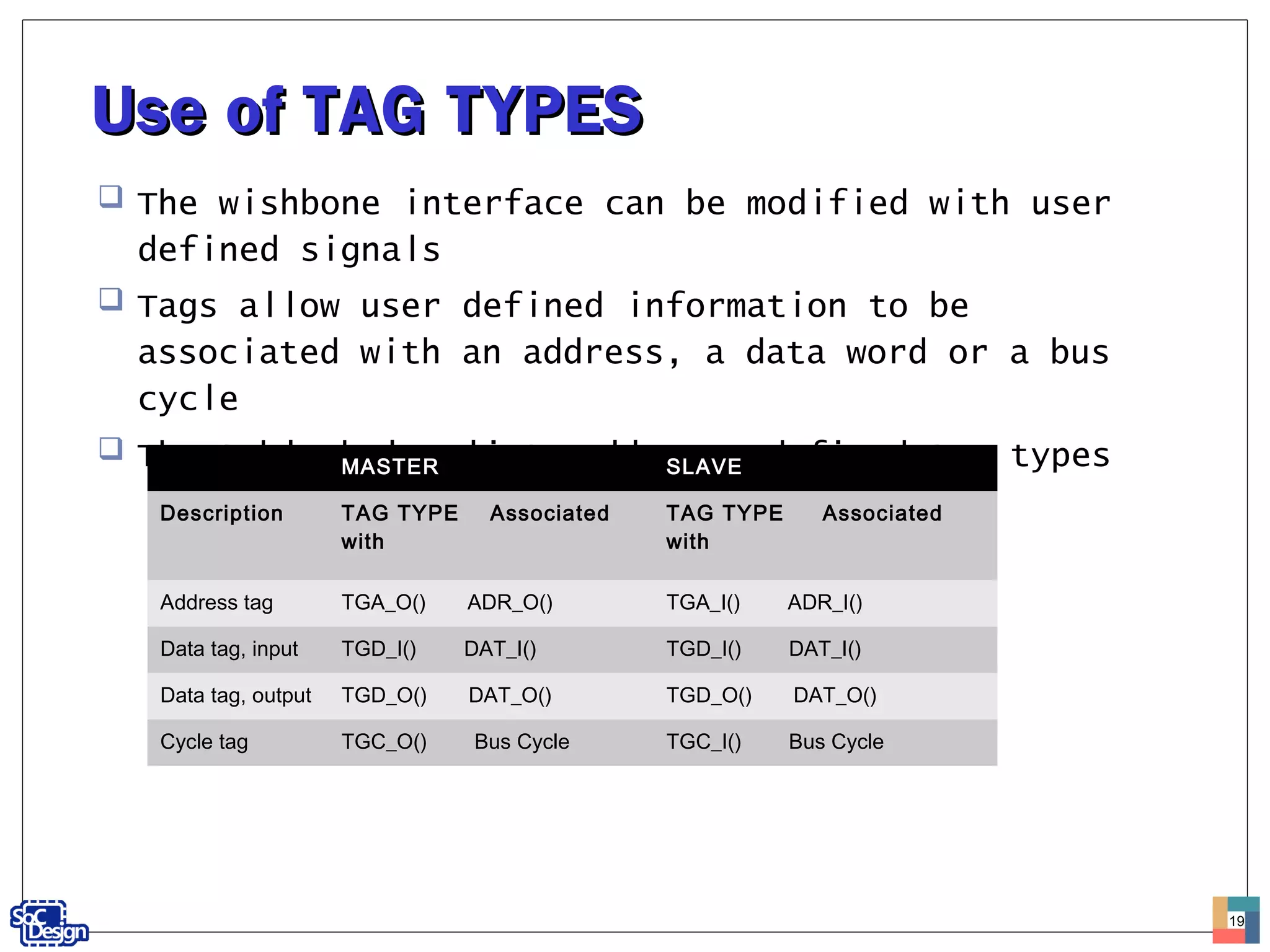
This document provides specifications for a Wishbone interface and describes classic bus cycles. It defines the Wishbone specification, interface signals, and standard handshaking protocols for single and pipelined transfers. Tag types are also described that allow user-defined information to be associated with addresses, data, and bus cycles.





![Logic LevelsLogic Levels
All wishbone interface signals must use active high
logic
Generally, active low signals does not present a
problem
However, some tools do not have a standard way of
indicating an active low signal
Using [#RST_I], [/RST_I] or [N_RST_I] to represent
active low reset may cause confusion among users
and incompatibility between modules
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wishboneinterfaceandbus-140801044732-phpapp01/75/Wishbone-interface-and-bus-cycles-6-2048.jpg)
![Wishbone Signal DescriptionWishbone Signal Description
SYSCON module signals
7
Signal name description
CLK_O It coordinates all activities for
the internal logic within the
WISHBONE interconnect.
The INTERCON module
connects the [CLK_O] output
to the [CLK_I] input on
MASTER and SLAVE
interfaces.
RST_O It forces all WISHBONE
interfaces to restart. All
internal self-starting state
machines are forced into an
initial state. The INTERCON
connects the [RST_O] output
to the [RST_I] input on
MASTER and SLAVE
interfaces
RST_I
CLK_I CLK_I
DAT_IO DAT_IO
WE_O WE_I
STB_O STB_O
ACK_I ACK_O
CYC_O CYC_I
TG_IO TG_IO
SYSCON
WISHBONEMASTER
WISHBONESLAVE
CLK_ORST_O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wishboneinterfaceandbus-140801044732-phpapp01/75/Wishbone-interface-and-bus-cycles-7-2048.jpg)
![Wishbone Signal DescriptionWishbone Signal Description
Signals common to MASTER and SLAVE interfaces
8
Signal
name
Description
CLK_I All WISHBONE output signals are registered at the rising edge
of [CLK_I]. All WISHBONE input signals are stable before the rising
edge of [CLK_I].
DAT_I() The data input array [DAT_I()] is used to pass binary data. The array
boundaries are determined by the port size, with a maximum port
size of 64-bits (e.g. [DAT_I(63..0)]).
DAT_O() The data output array [DAT_O()] is used to pass binary data. The
array boundaries are determined by the port size, with a maximum
port size of 64-bits (e.g. [DAT_I(63..0)]).
RST_I() The reset input [RST_I] forces the WISHBONE interface to restart
TGD_I() Data tag type [TGD_I()] is used on MASTER and SLAVE interfaces.
It contains information that is associated with the data input array
[DAT_I()], and is qualified by
signal [STB_I].
TGD_O(
)
Data tag type [TGD_O()] is used on MASTER and SLAVE
interfaces. It contains information that is associated with the data
output array [DAT_O()], and is qualified by signal [STB_O]
88
RST_I
CLK_I CLK_I
DAT_IO DAT_IO
WE_O WE_I
STB_O STB_O
ACK_I ACK_O
CYC_O CYC_I
TG_IO TG_IO
SYSCON
WISHBONEMASTER
WISHBONESLAVE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wishboneinterfaceandbus-140801044732-phpapp01/75/Wishbone-interface-and-bus-cycles-8-2048.jpg)
![Wishbone Signal DescriptionWishbone Signal Description
MASTER signals
9
Signal
name
Description
ACK_I The acknowledge input [ACK_I], when
asserted, indicates the normal termination
of a bus cycle
CYC_O The cycle output [CYC_O], when asserted,
indicates that a valid bus cycle is in
progress
STALL_I The pipeline stall input [STALL_I] indicates
that current slave is not able to accept the
transfer in the transaction queue
ERR_I The error input [ERR_I] indicates an
abnormal cycle termination
RTY_I The retry input [RTY_I] indicates that the
interface is not ready to accept or send
data, and that the cycle should be retried
STB_O The strobe output [STB_O] indicates a
valid data transfer cycle
WE_O The write enable output [WE_O] indicates
whether the current local bus cycle is a
READ or WRITE cycle
RST_I
CLK_I CLK_I
DAT_IO DAT_IO
WE_O WE_I
STB_O STB_O
ACK_I ACK_O
CYC_O CYC_I
TG_IO TG_IO
SYSCON
WISHBONEMASTER
WISHBONESLAVE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wishboneinterfaceandbus-140801044732-phpapp01/75/Wishbone-interface-and-bus-cycles-9-2048.jpg)
![Wishbone Signal DescriptionWishbone Signal Description
SLAVE signals
10
Signal name Description
ACK_O The acknowledge output [ACK_O], when
asserted, indicates the termination of a normal
bus cycle
CYC_I The cycle input [CYC_I], when asserted,
indicates that a valid bus cycle is in progress
STALL_O The pipeline stall signal [STALL_O] indicates
that the slave can not accept additional
transactions in its queue
ERR_O The error output [ERR_O] indicates an abnormal
cycle termination
RTY_O The retry output [RTY_O] indicates that the
indicates that the interface is not ready to
accept or send data, and that the cycle should
be retried
STB_I The strobe input [STB_I], when asserted,
indicates that the SLAVE is selected. A SLAVE
shall respond to other WISHBONE signals only
when this [STB_I] is asserted
WE_I The write enable input [WE_I] indicates whether
the current local bus cycle is a READ or
WRITE cycle
RST_I
CLK_I CLK_I
DAT_IO DAT_IO
WE_O WE_I
STB_O STB_O
ACK_I ACK_O
CYC_O CYC_I
TG_IO TG_IO
SYSCON
WISHBONEMASTER
WISHBONESLAVE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wishboneinterfaceandbus-140801044732-phpapp01/75/Wishbone-interface-and-bus-cycles-10-2048.jpg)

![Reset operationReset operation
[RST_O] is used to initialize all hardware
interfaces to a pre-defined state
It can be asserted anytime and it is used for test
simulation purposes
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wishboneinterfaceandbus-140801044732-phpapp01/75/Wishbone-interface-and-bus-cycles-12-2048.jpg)
![Transfer Cycle InitializationTransfer Cycle Initialization
MASTER interfaces initiate a transfer cycle by
asserting [CYC_O]
SLAVE interfaces respond to other slave signals
only when [CYC_I] is asserted
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wishboneinterfaceandbus-140801044732-phpapp01/75/Wishbone-interface-and-bus-cycles-13-2048.jpg)

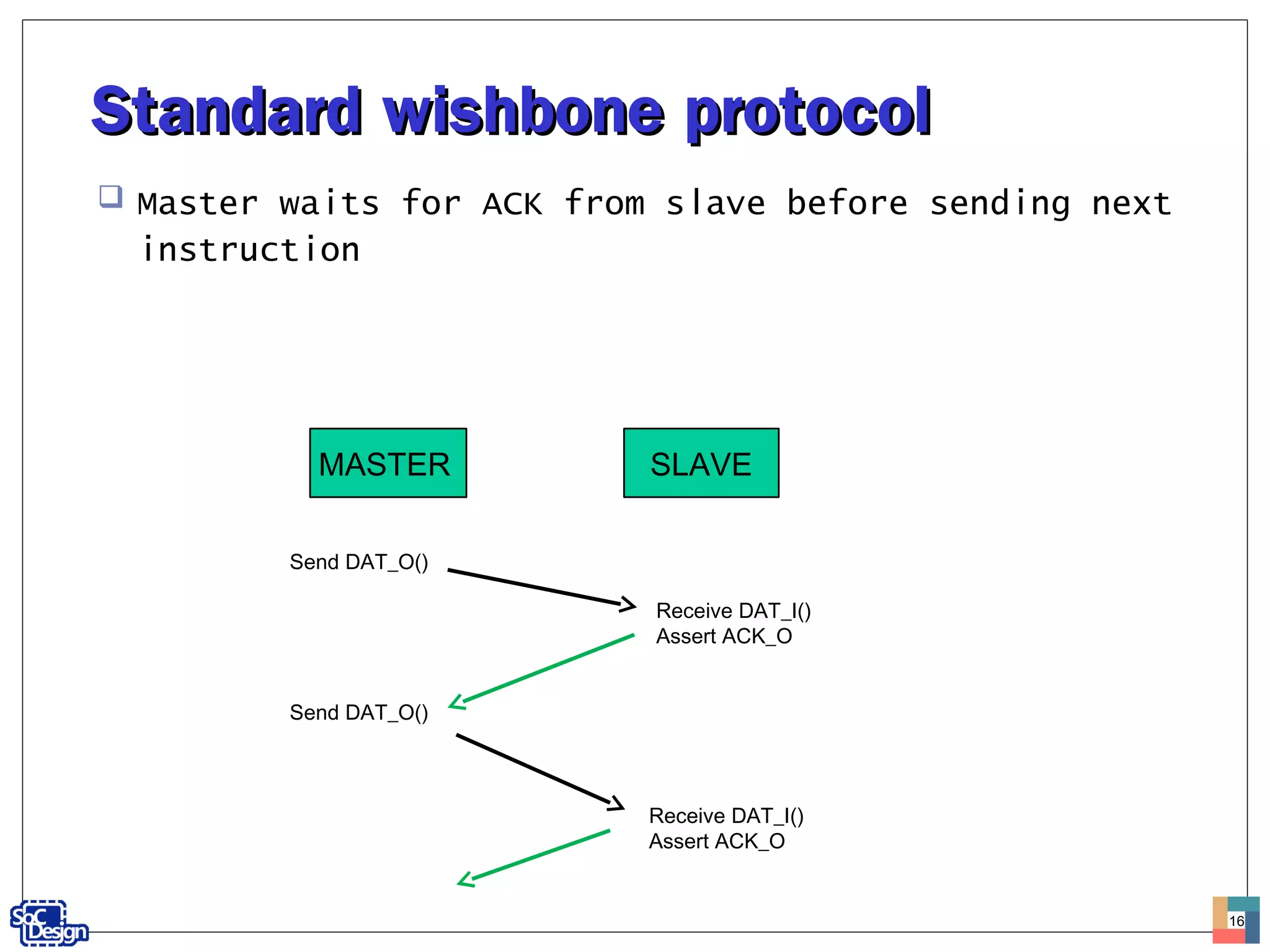
![Standard wishbone protocolStandard wishbone protocol
MASTER asserts [STB_O] when it is ready to transfer
data
[STB_O] remains asserted until the SLAVE asserts
one of the cycle terminating signals: [ACK_I],
[ERR_I] or [RTY_I]
Standard bus handshaking protocol with asynchronous
slave:
15
CLK_I
CYC_O
STB_O
ACK_I](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wishboneinterfaceandbus-140801044732-phpapp01/75/Wishbone-interface-and-bus-cycles-15-2048.jpg)
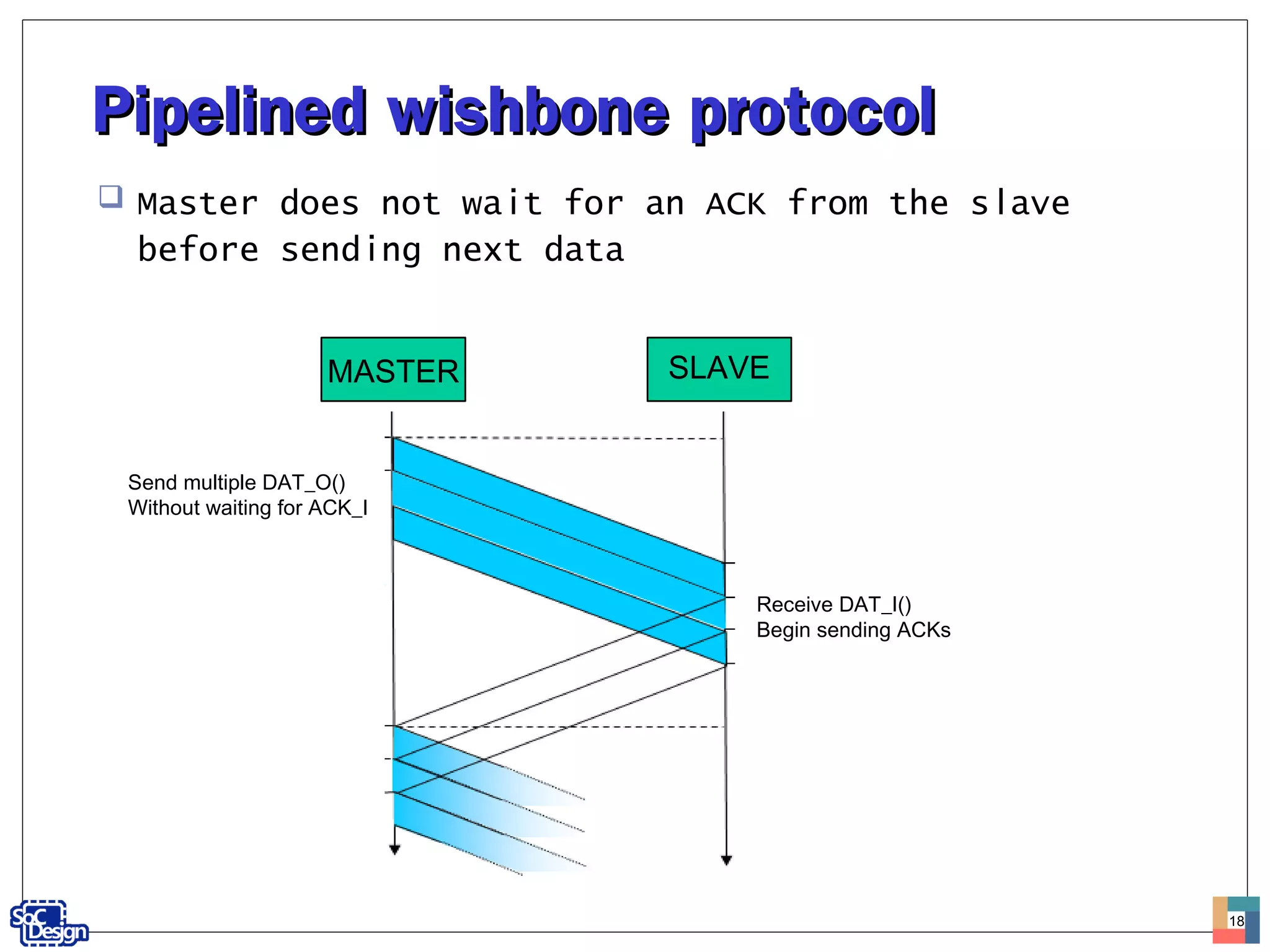
![Pipelined wishbone protocolPipelined wishbone protocol
The MASTER does not wait for [ACK_I] before putting
the next address/data word on the bus
[STALL_I] asserted indicates slave can no longer
accept another request
MASTER outputs requests as long as [STALL_I] is low
17
CLK_I
CYC_O
STB_O
ACK_I
STALL_I](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wishboneinterfaceandbus-140801044732-phpapp01/75/Wishbone-interface-and-bus-cycles-17-2048.jpg)