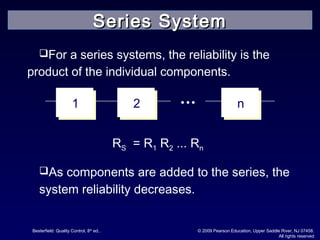
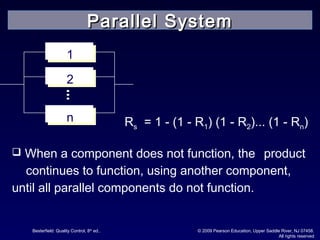
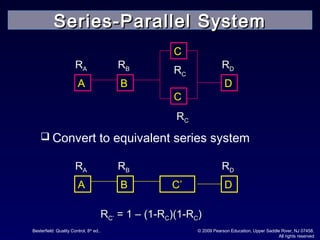
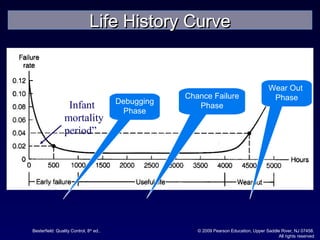
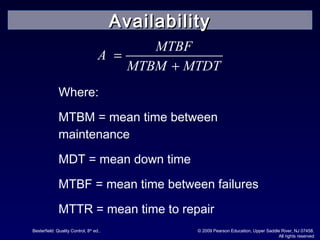
The document discusses reliability and reliability testing. It defines reliability as the probability that a product will perform as expected over a stated period of time under specified operating conditions. Reliability is affected by factors like numerical value, intended function, life, and environmental conditions. Methods to achieve reliability include proper design, production processes, and transportation. Reliability testing involves constructing reliability curves and calculating failure rates using distributions like exponential, normal, and Weibull. Different types of reliability tests are discussed including failure-terminated, time-terminated, and sequential tests.