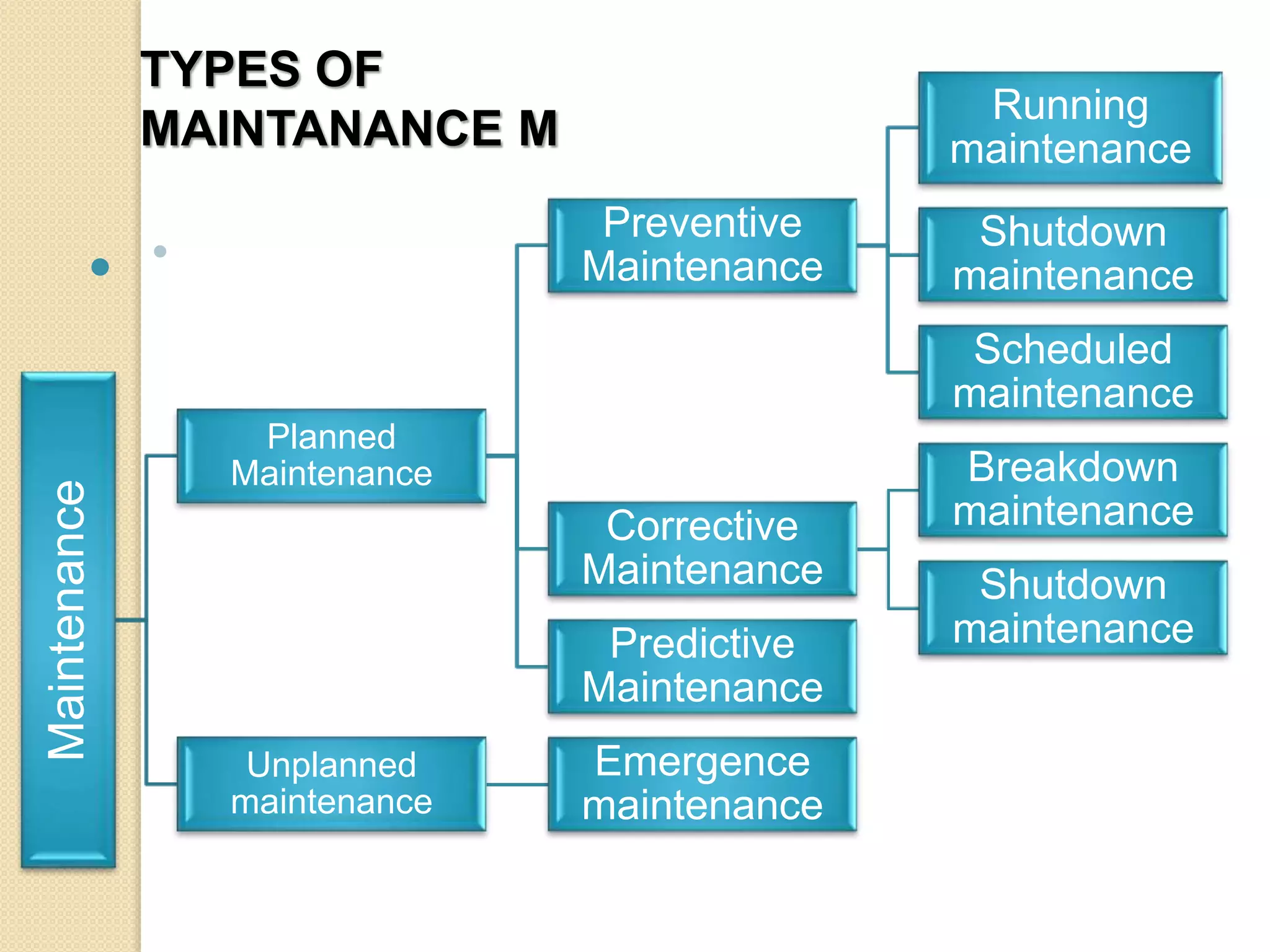
Maintenance management involves keeping equipment running at high capacity and low cost through a set of organized activities. The objectives of maintenance include efficient use of personnel, maximizing equipment life, reliability, quality, safety and minimizing costs and interruptions. There are various types of maintenance like preventive, corrective, and predictive. Preventive maintenance involves scheduled, running and shutdown maintenance to prevent failures. Corrective maintenance repairs equipment after failure through breakdown or shutdown maintenance. Predictive maintenance predicts failures through condition monitoring.