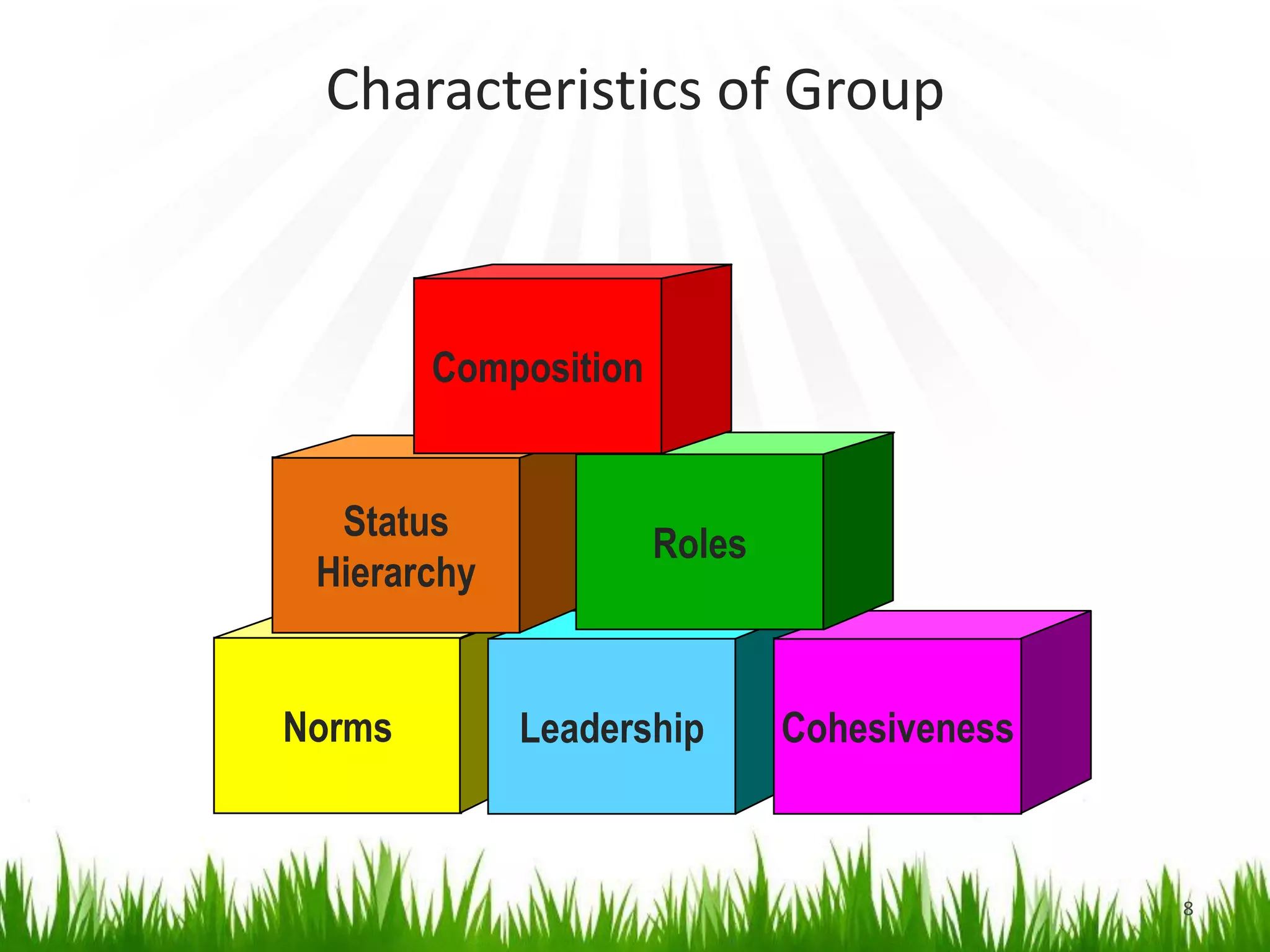
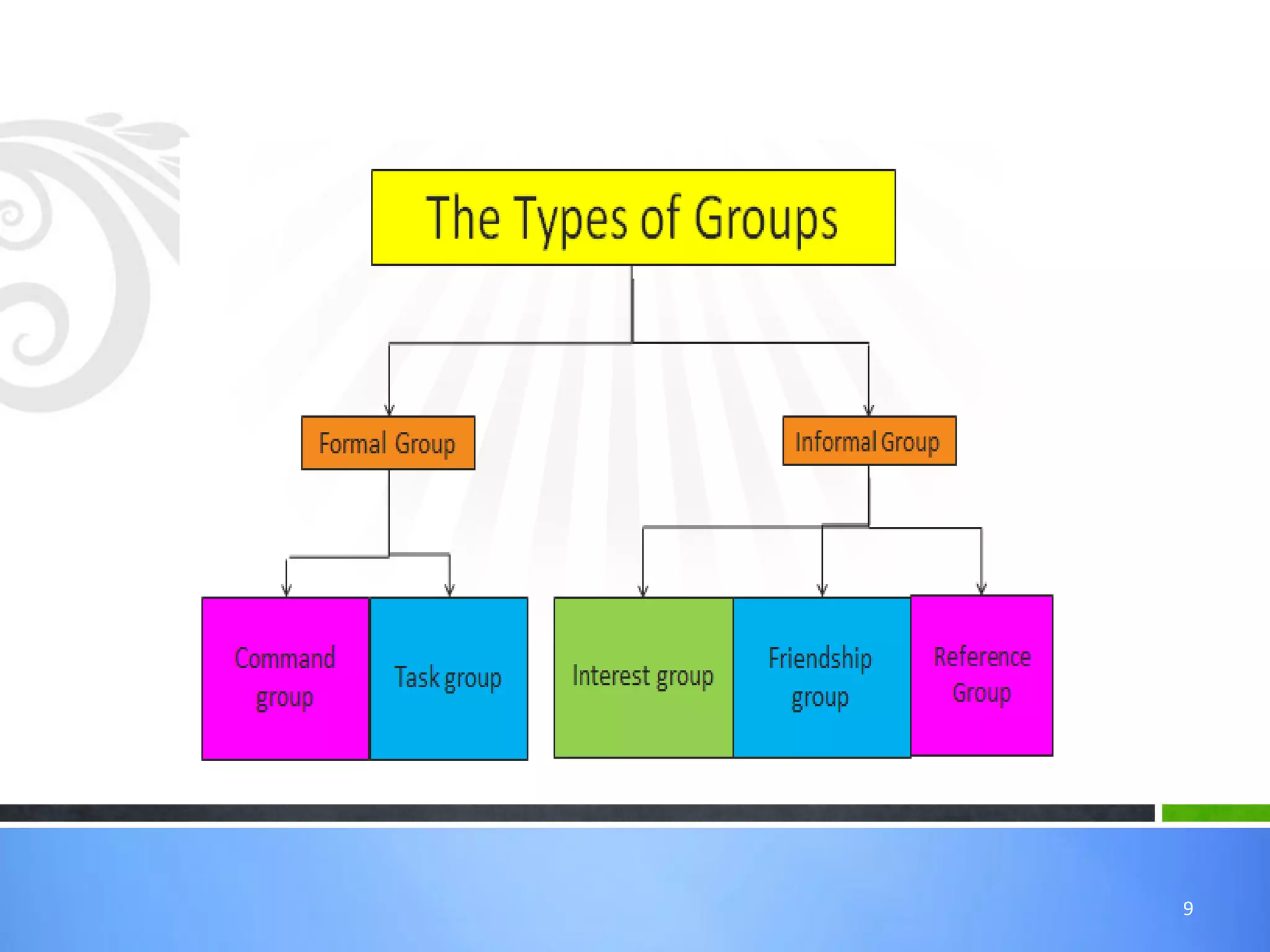
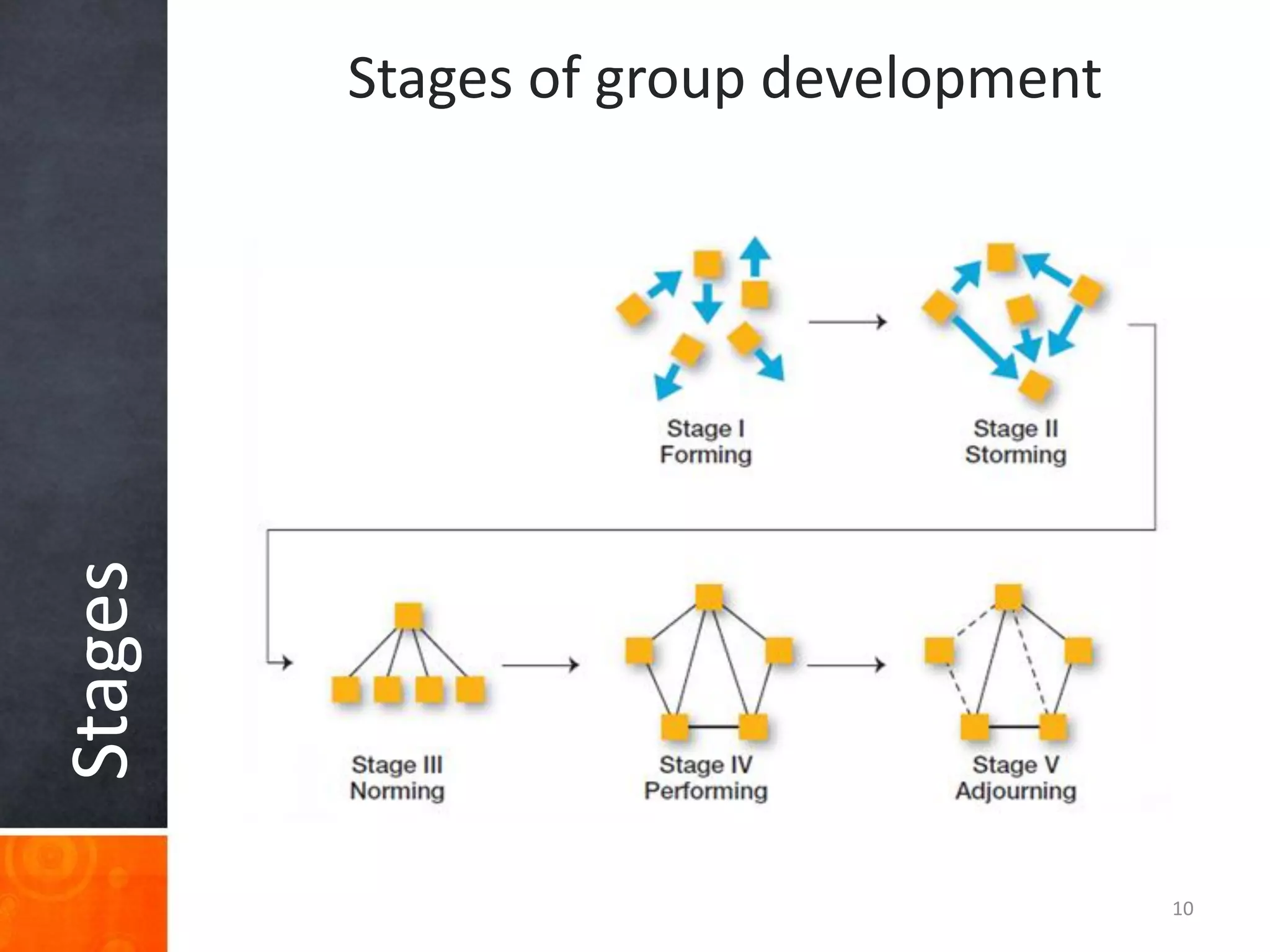
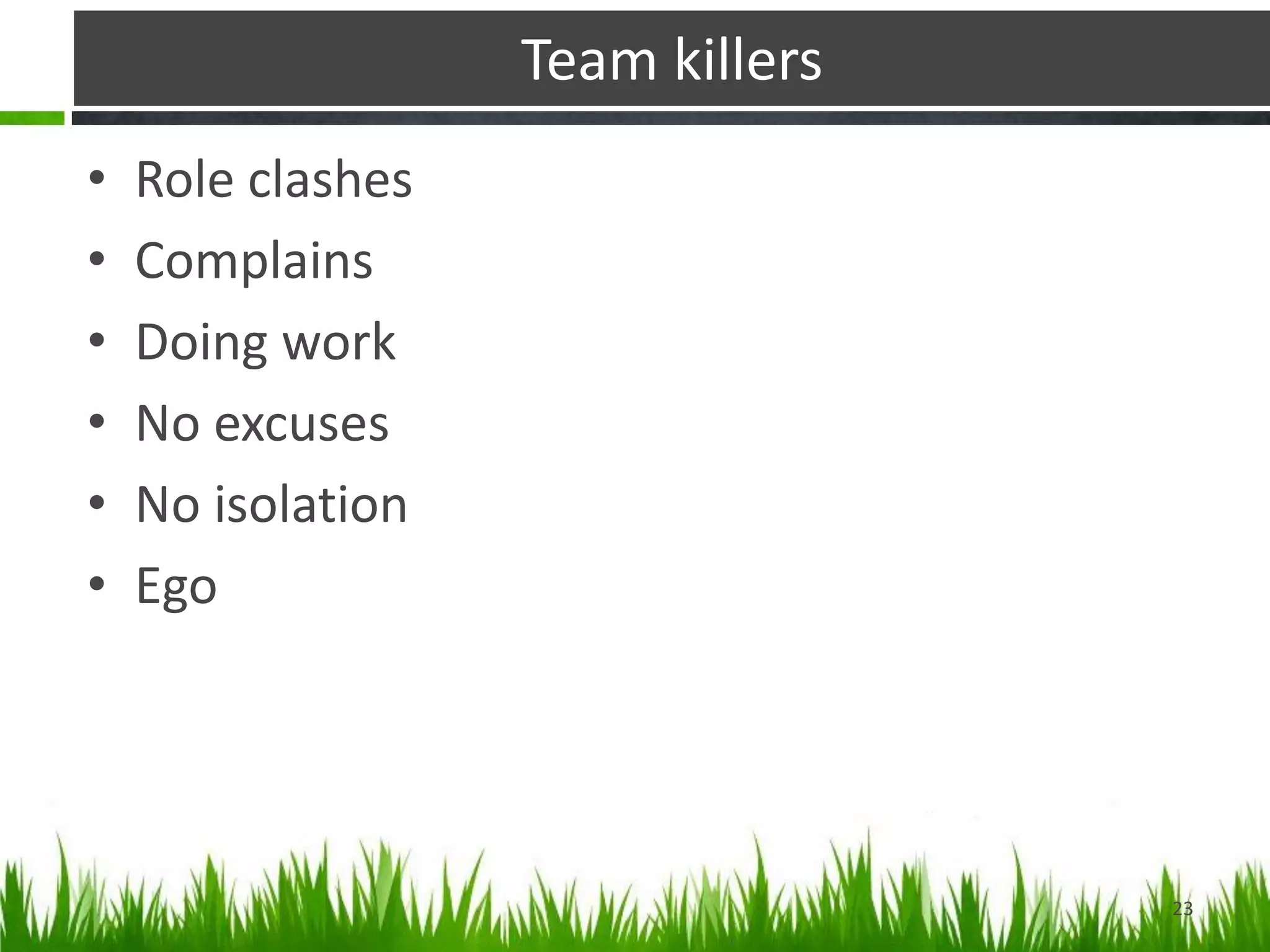
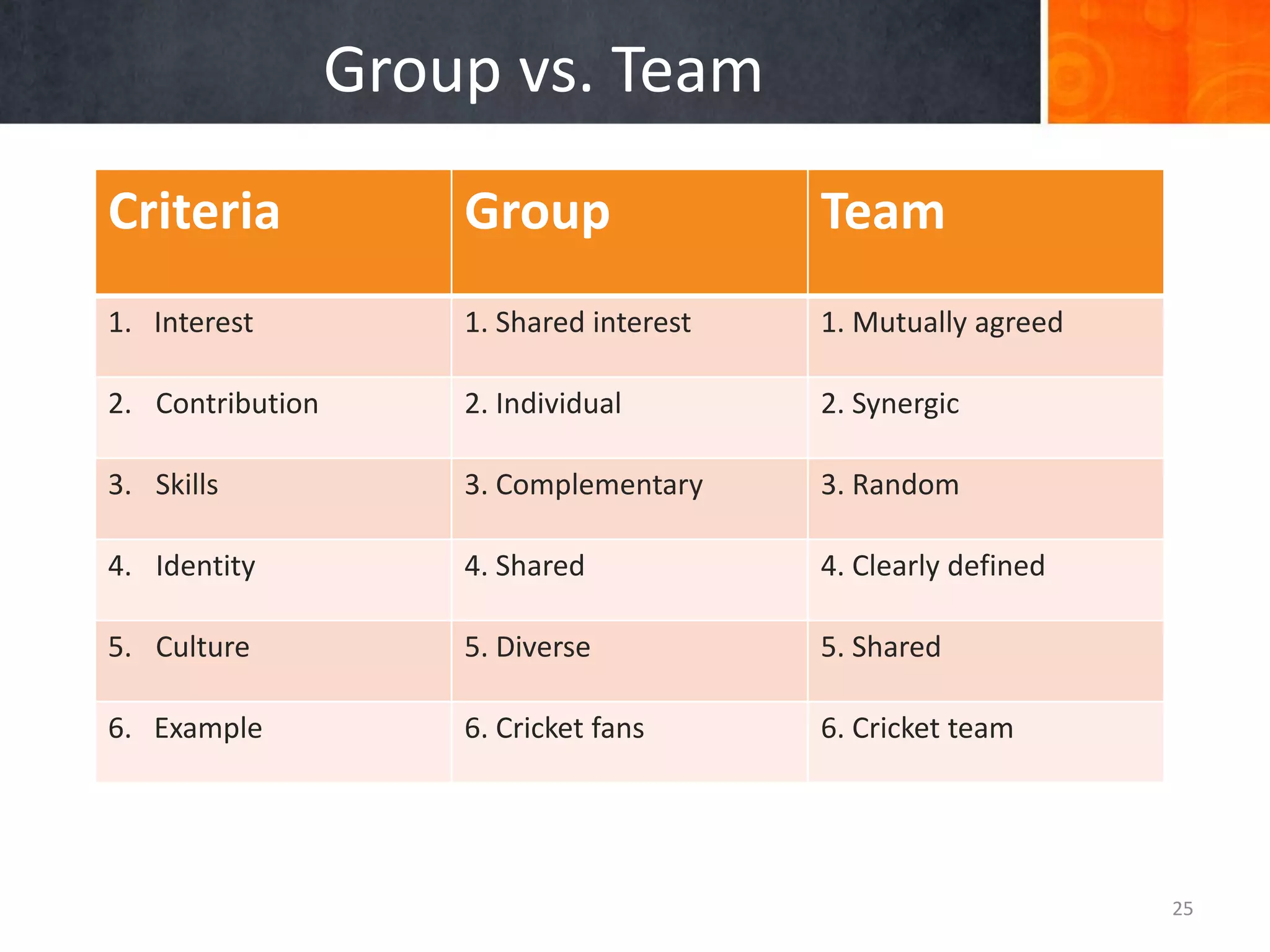
Groups are a collection of people who interact and share a common identity. They form for reasons like goal achievement and need satisfaction. Groups have characteristics like norms, roles, hierarchy, and composition. Forming teams allows pooling of talents to achieve shared objectives. The key differences between groups and teams are that teams have mutually agreed and clearly defined interests and skills while groups have diverse backgrounds and contributions. An example of a high performing team is the Indian cricket team, while departments in organizations are examples of groups.