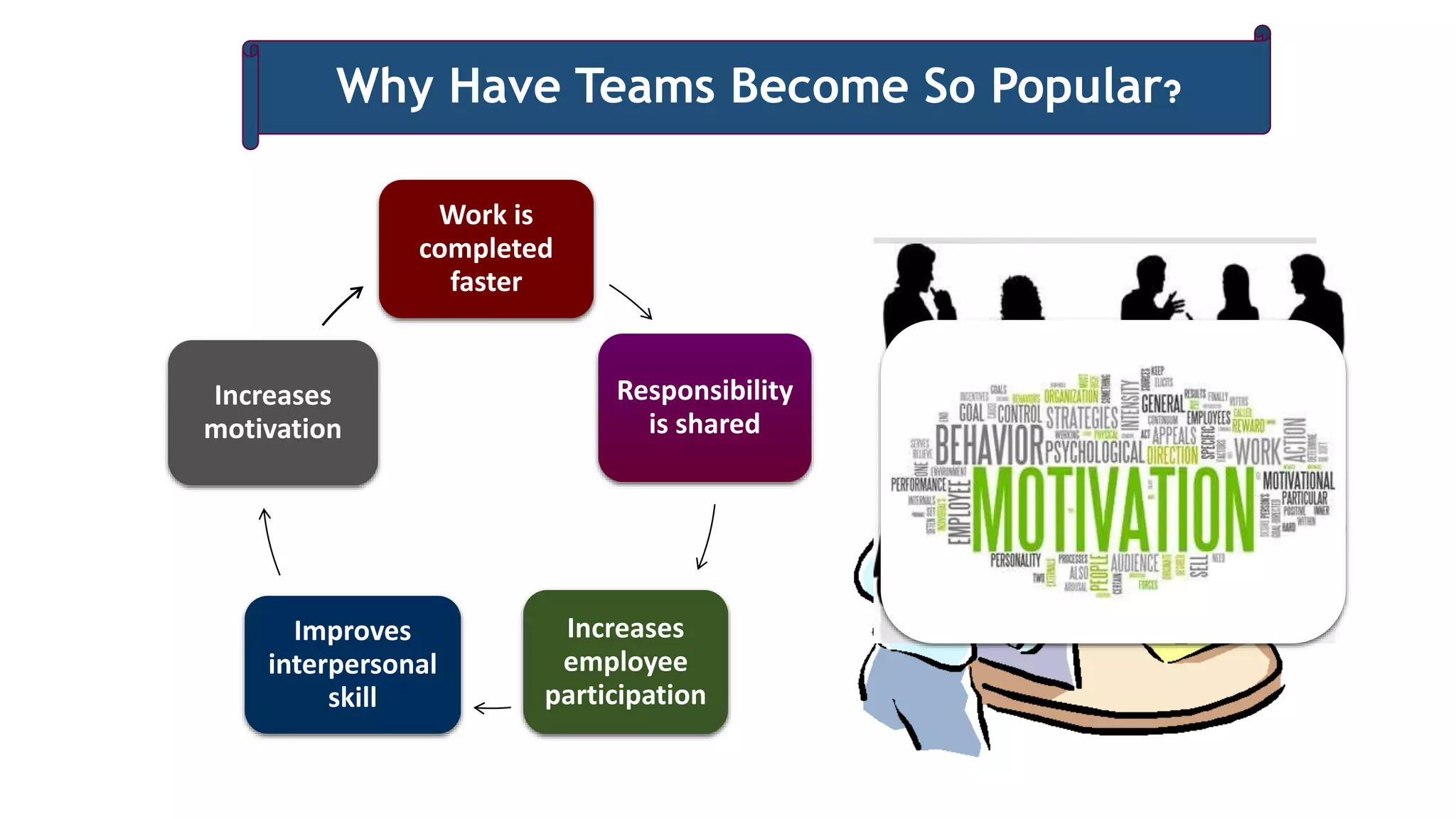
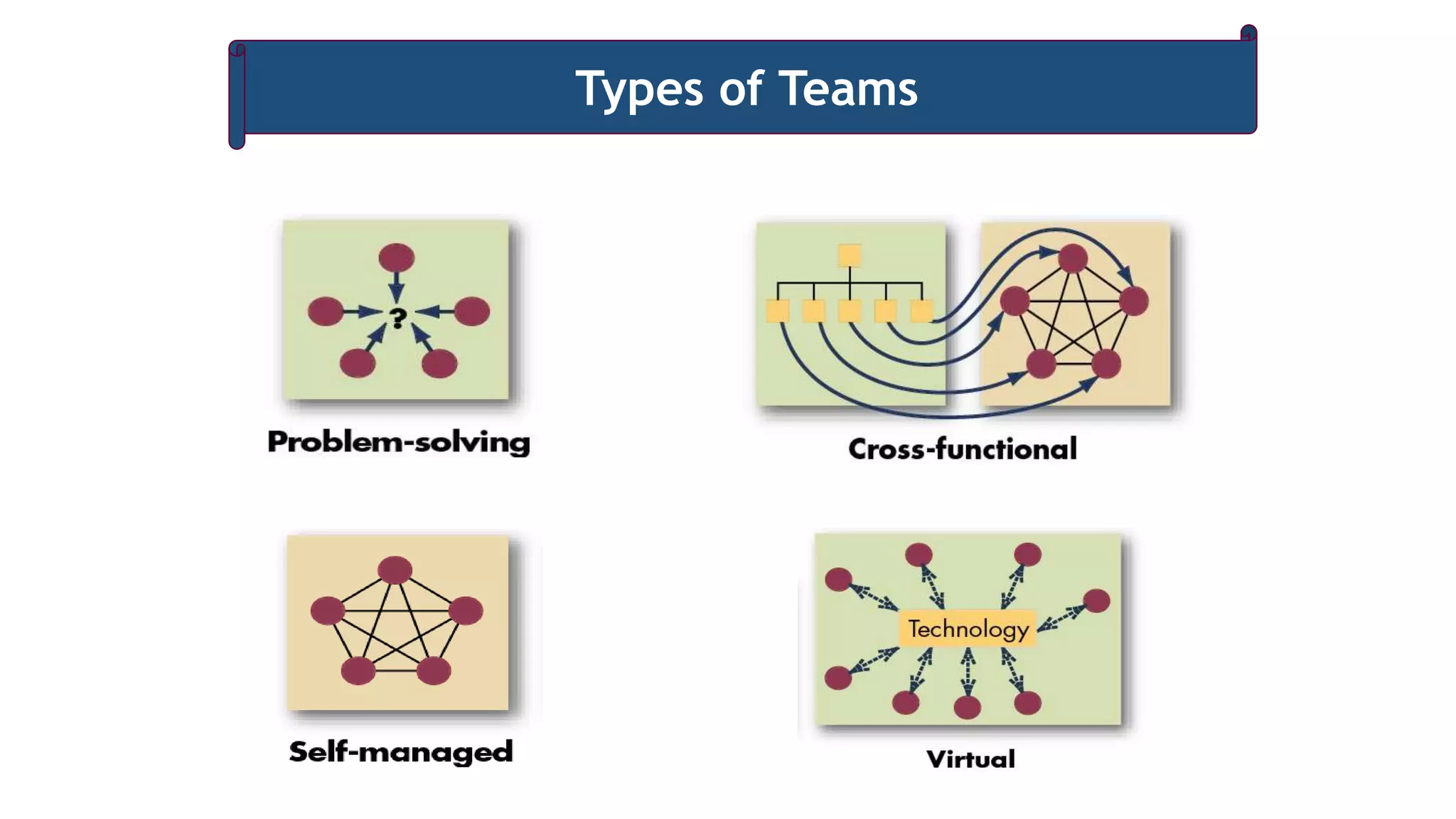
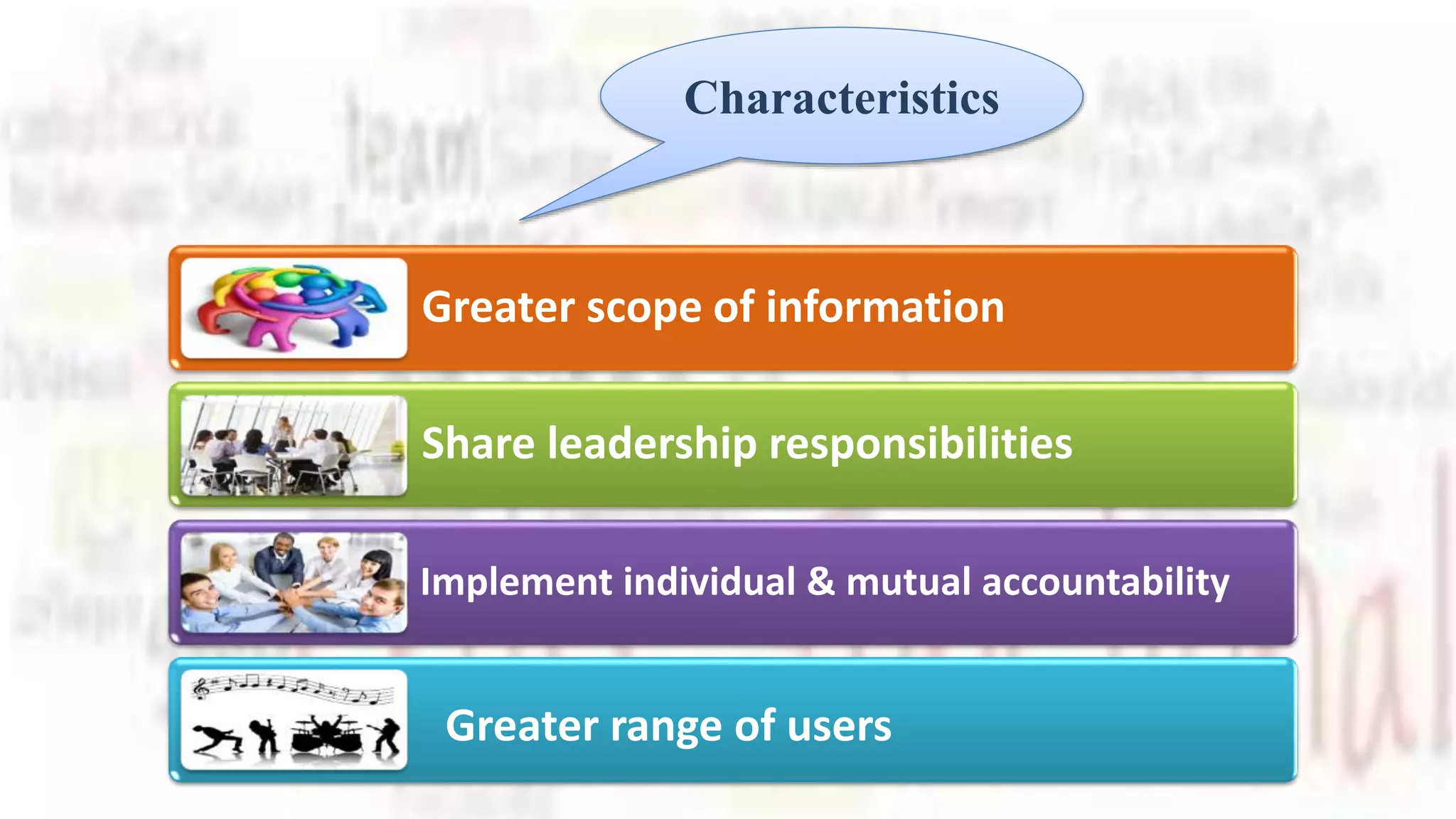
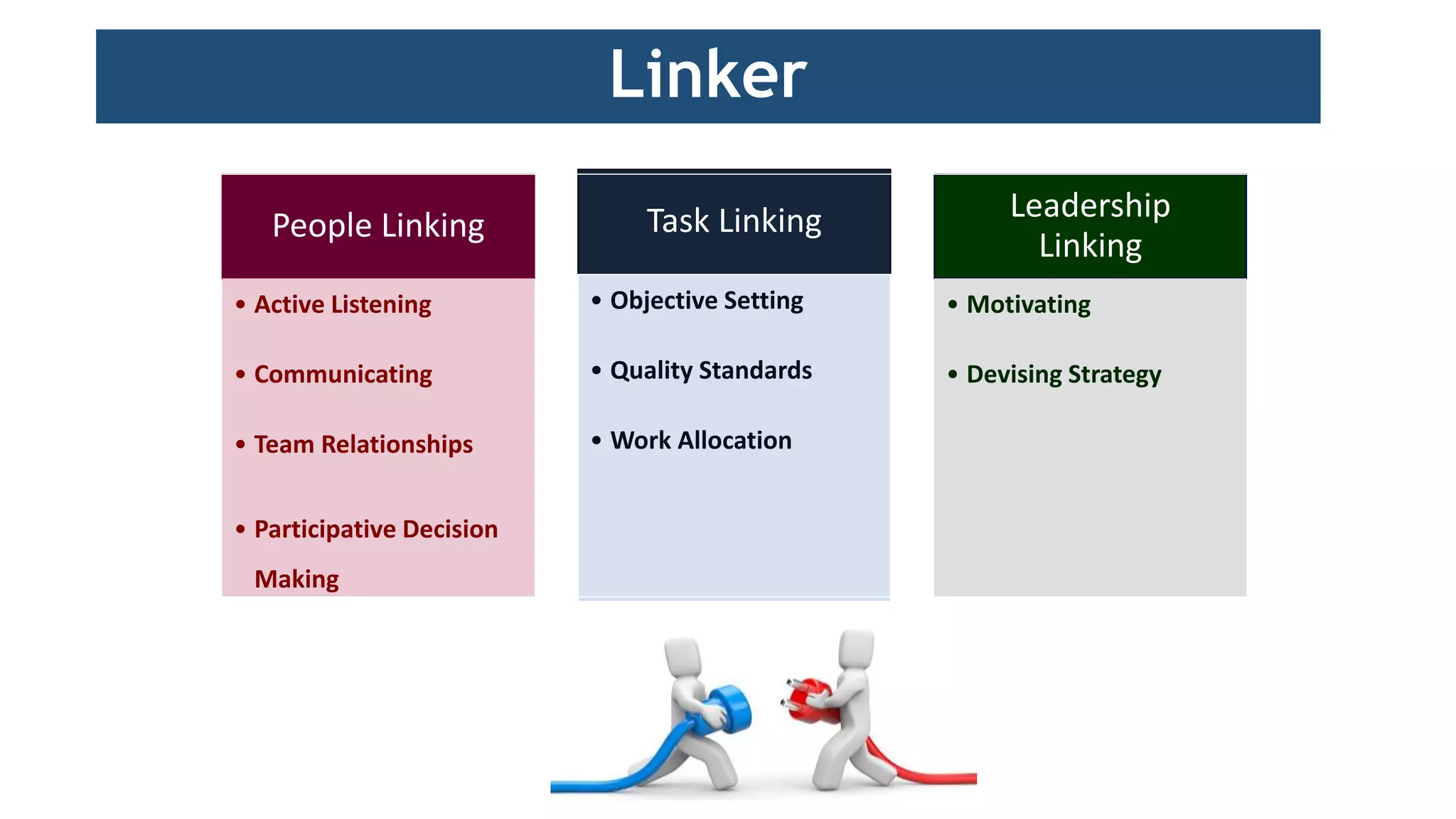
The document discusses the growing popularity of teams in organizations, contrasting different types of teams and identifying characteristics of effective teams. It emphasizes the benefits of teamwork, such as shared responsibility and increased motivation, while also outlining factors critical to creating effective teams, including team composition and process. Additionally, it addresses when to opt for individual work over teamwork, underscoring the importance of interdependence and common goals.