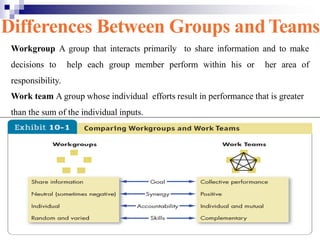
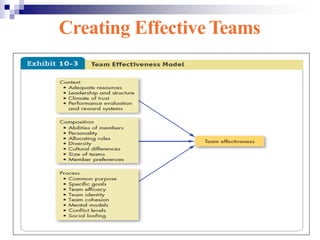
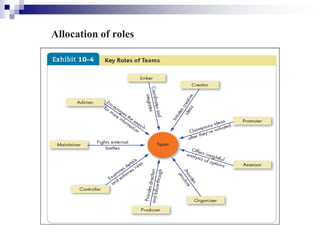
Chapter 10 of the document discusses the significance and effectiveness of work teams in organizations, highlighting their flexibility and ability to promote employee involvement. It differentiates between workgroups and work teams, outlines various types of teams, and emphasizes factors that contribute to team effectiveness such as resources, leadership, and trust. Additionally, it covers team composition, processes, and strategies for transforming individuals into team players.