The document discusses capsule dosage forms. Some key points include:
1. Capsules can be used to mask unpleasant drug tastes, smells, or appearances. They also allow powders to be dispensed uncompressed, aiding faster drug dissolution and absorption compared to tablets.
2. Capsules offer versatility in preparing varied drug doses and administration routes like oral, inhalation, and others. They can also be easier than tablets for some patients to swallow.
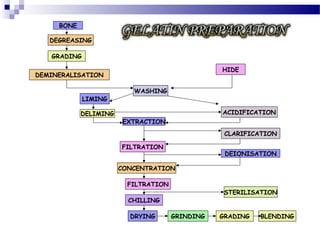
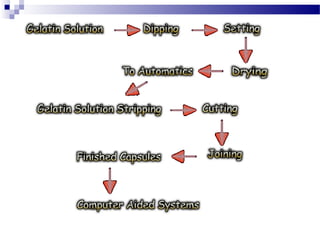
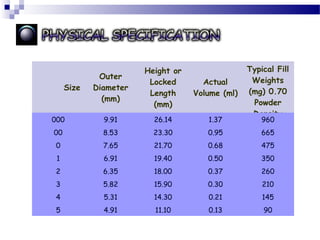
3. Capsule production involves filling empty shells with powders, granules, beads, pastes, liquids or other formulations. Both manual and automated high-output filling machines exist. Quality control ensures proper capsule appearance, weight, content uniform








![Capsule Filling, Problems in Filling & Remedies
Filling capsule with a
semisolid mass.
Forming a pipe or pouring a melt.
Pipe:
Consistency is important.
[For fluid- cornstarch or similar material for firm
cosistancy.]
Semisolid melt:
For too firm with satisfactory M.P. materials.
For enhancing the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs.
[Drug + melt of materials like PEG]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capsules-101127083830-phpapp02/85/Capsules-13-320.jpg)


![DIFFICULTIES IN CAPSULE FILLING
1. Deliquescent / Hygroscopic powders.
Remedy: Adsorbent [magnesium carbonate, heavy / light
magnesium oxide]
2. Eutectic mixture
Remedy: Use of adsorbent [magnesium carbonate, kaolin]
3. Small dose of drug
Remedy: Addition of inert powder.
4. Incompatibilities of materials
Remedy: Use of two capsules – small in large
5. Lack of adhessiveness difficult to fill by punch method
Remedy: moistened with alcohol , granules reduced to powders](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capsules-101127083830-phpapp02/85/Capsules-16-320.jpg)

![Capsule Processing
Empty Capsule
Filling [Formulation]
Finishing
# Dusting [Cloth Dusting]
# Polishing [Pan Polishing]
# Brushing
Inspection
Bottling
Labeling](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capsules-101127083830-phpapp02/85/Capsules-18-320.jpg)
![Special Techniques of Processing
Imprinting
Special purpose Capsules
[To retard solubility of gelatin to delay absorption of drug]
* Formalin treatment
* Various coatings
Separation of Incompatible materials](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capsules-101127083830-phpapp02/85/Capsules-19-320.jpg)



![In-process Quality And
Quality Control Parameters
Choice of suitable control procedure for filling operation:
[should desirable to provide 100% weight checking after filling]
Capsule Appearance
Weight veriation
Content uniformity
Solubility
Disintegration test](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capsules-101127083830-phpapp02/85/Capsules-23-320.jpg)
