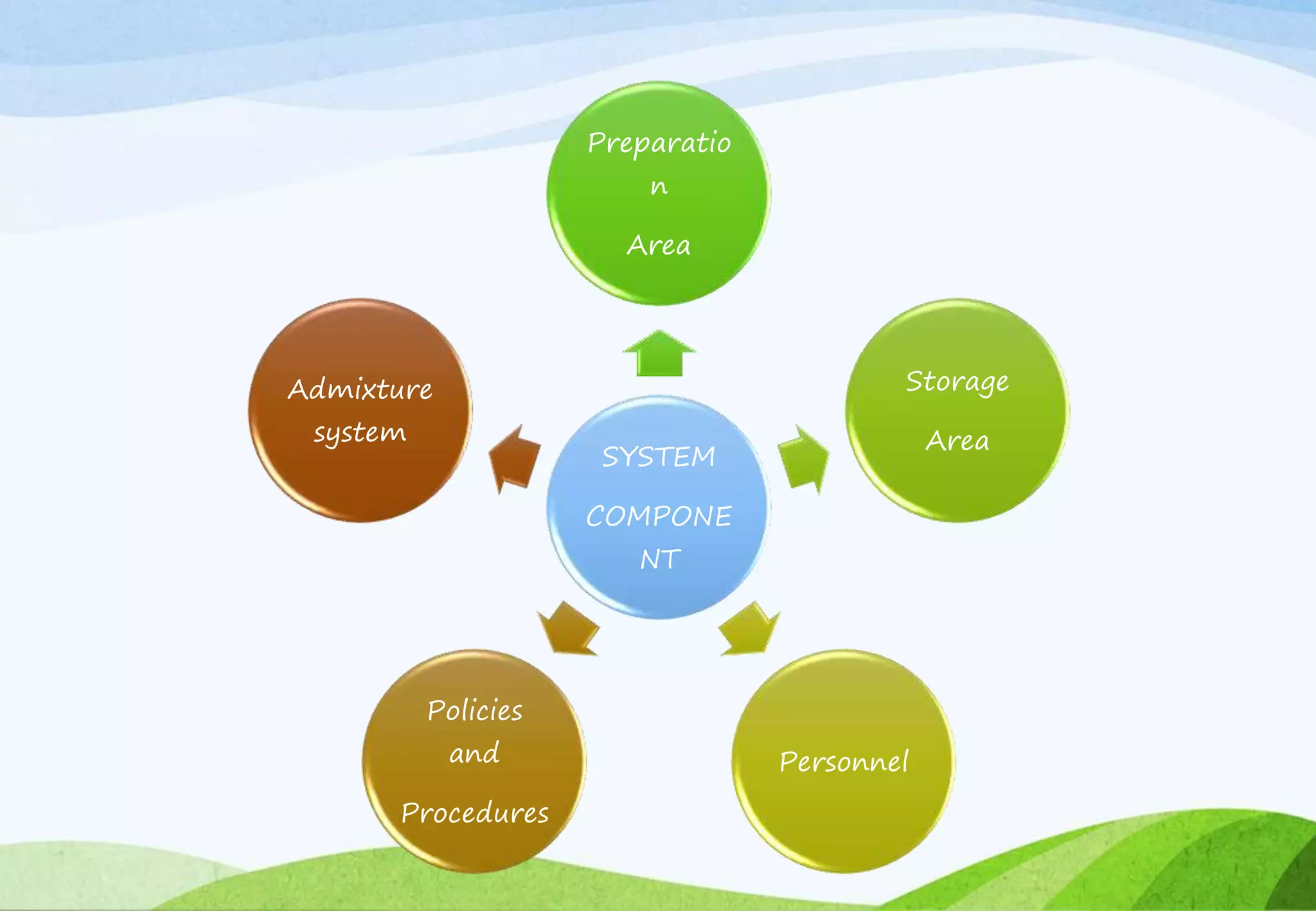
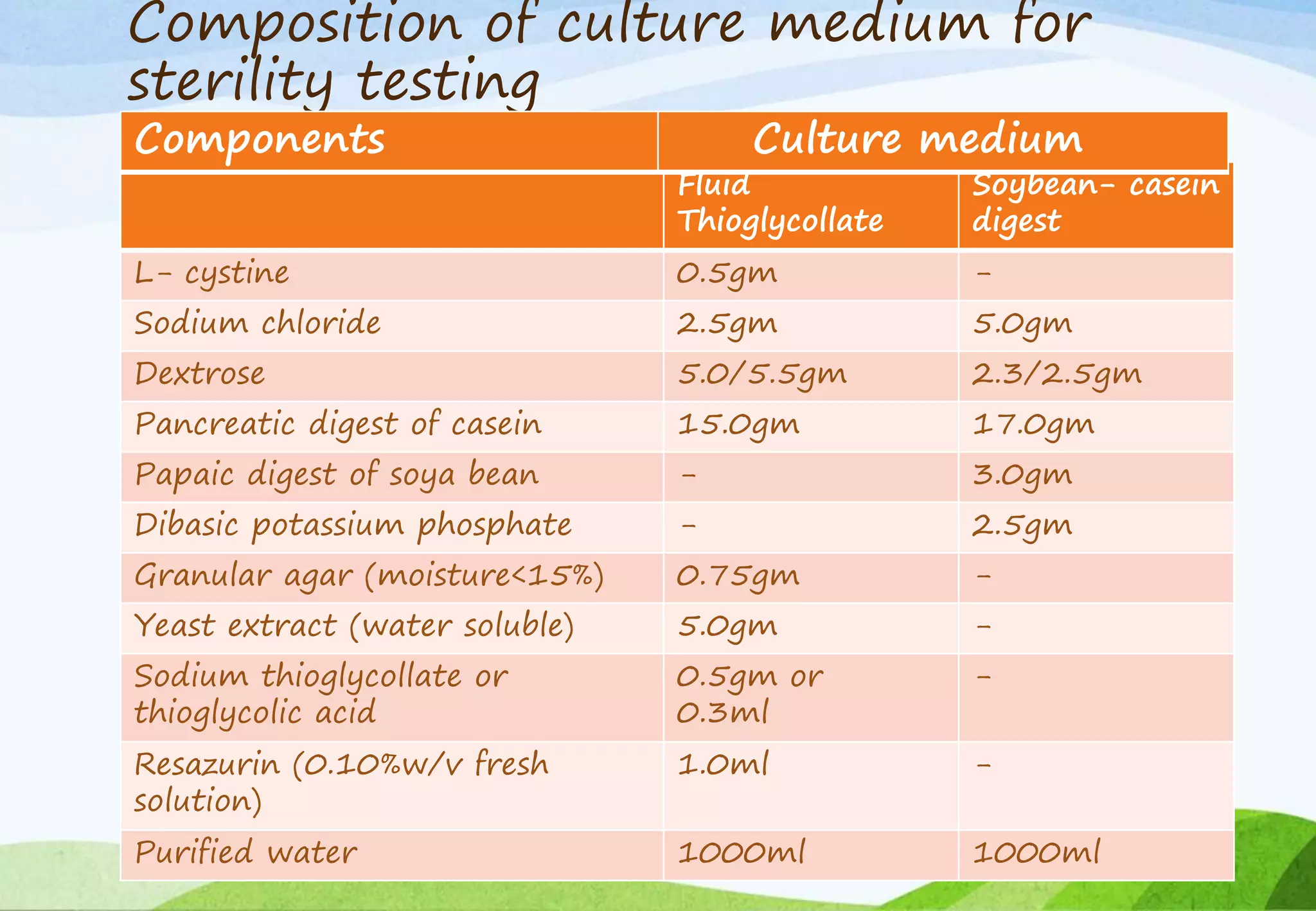
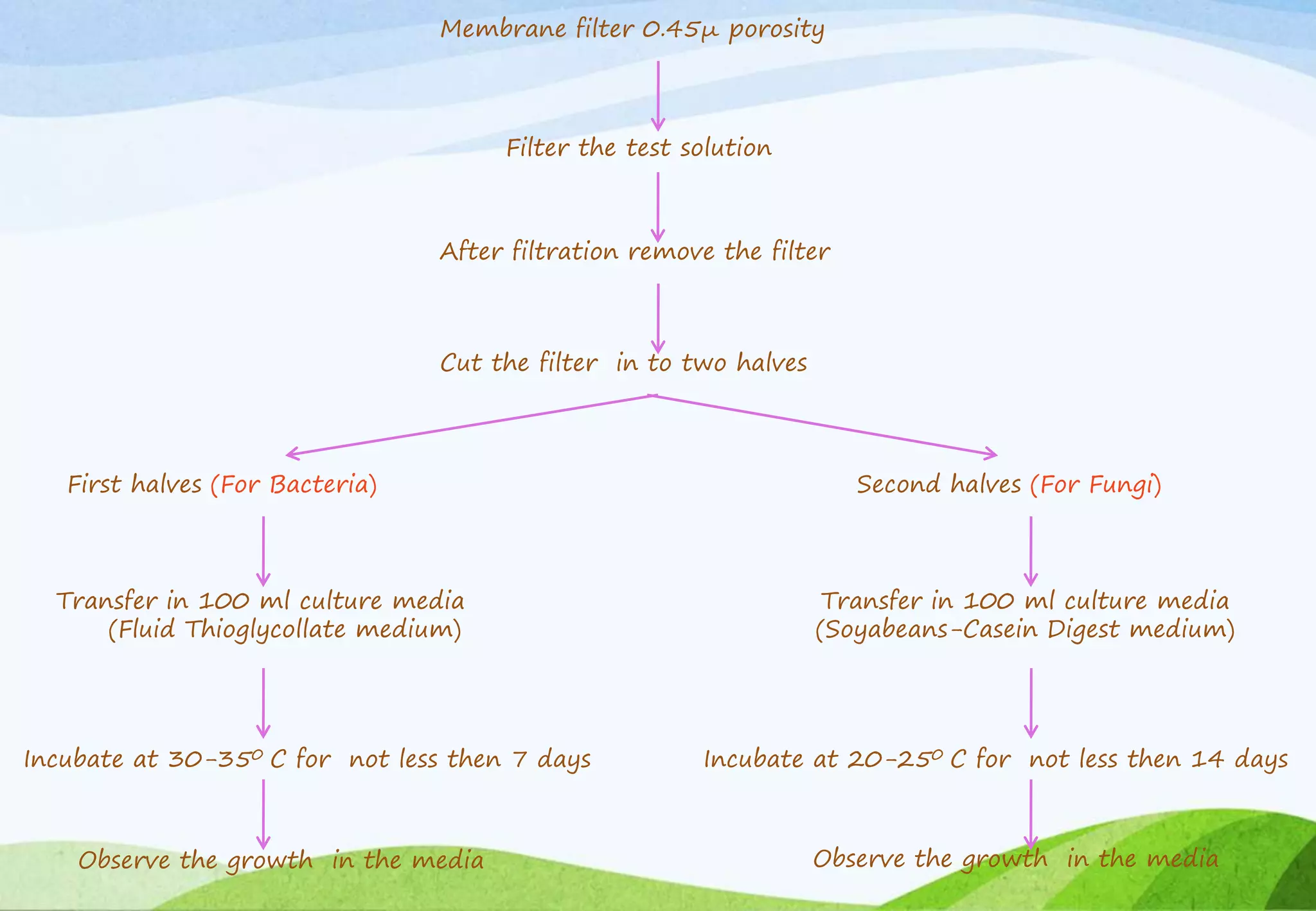
This document provides information about small volume parenterals. It begins by defining parenterals as routes of administration other than the alimentary canal. It then discusses various parenteral routes including subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous, and large volume parenteral. The document outlines the advantages and disadvantages of the parenteral route. It provides details on containers, closures, formulation, production facilities, processing, and evaluation of parenteral preparations. Evaluation includes sterility testing, clarity testing, leakage testing, pyrogen testing, and assay testing. The document emphasizes the importance of aseptic conditions for parenterals due to risk of contamination.
































![Limulus amebocyte lysate [LAL]
test
• Limulus amebocyte lysate [LAL] test another method
for the determination of pyrogenic endotoxins
• In this method the test solution is combined with a
cell lysate from the ameabocyte [blood cells] of horse
shoe crab
• Any endo toxin that might be present will be
coagulated with protien fraction of the ameabocytes
and results in the formation of a gel
• This consider to be simple,rapid and of greater
sensitivity that the rabbit test](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smallvolumeparenteral-150208123807-conversion-gate01/75/Small-volume-parenteral-36-2048.jpg)


