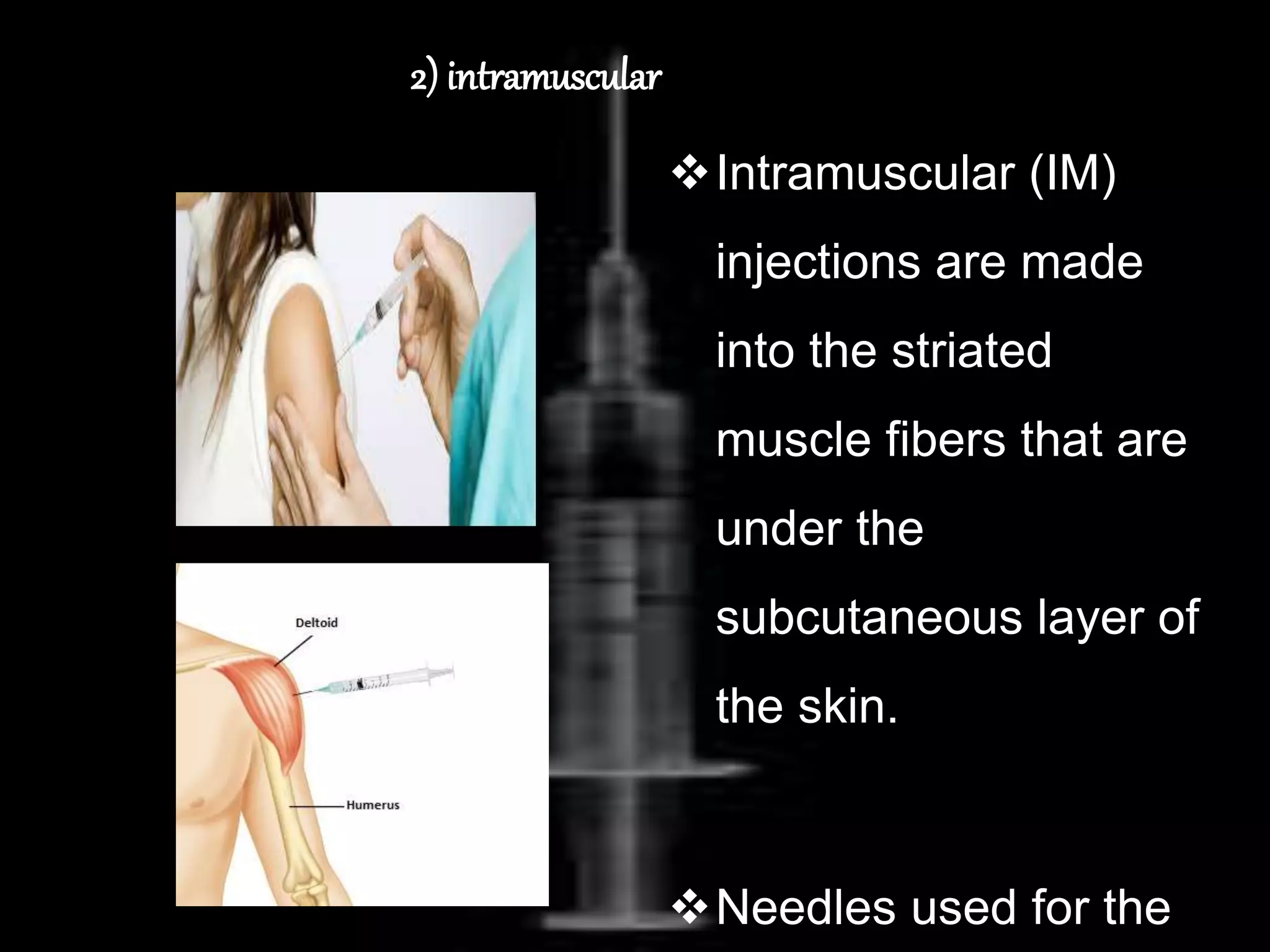
This document provides an overview of parenteral products including their definition, history, manufacturing process, quality control, packaging, types, and routes of administration. Parenterals are sterile preparations intended for injection through the skin rather than orally. Their manufacturing must ensure sterility, lack of pyrogens, and stability. Quality is tested through sterility, pyrogen, leakage, and particulate matter tests. Parenterals are packaged in containers like ampules, vials, prefilled syringes and infusion bags. They are classified as small or large volume and administered via intravenous, intramuscular or subcutaneous routes.