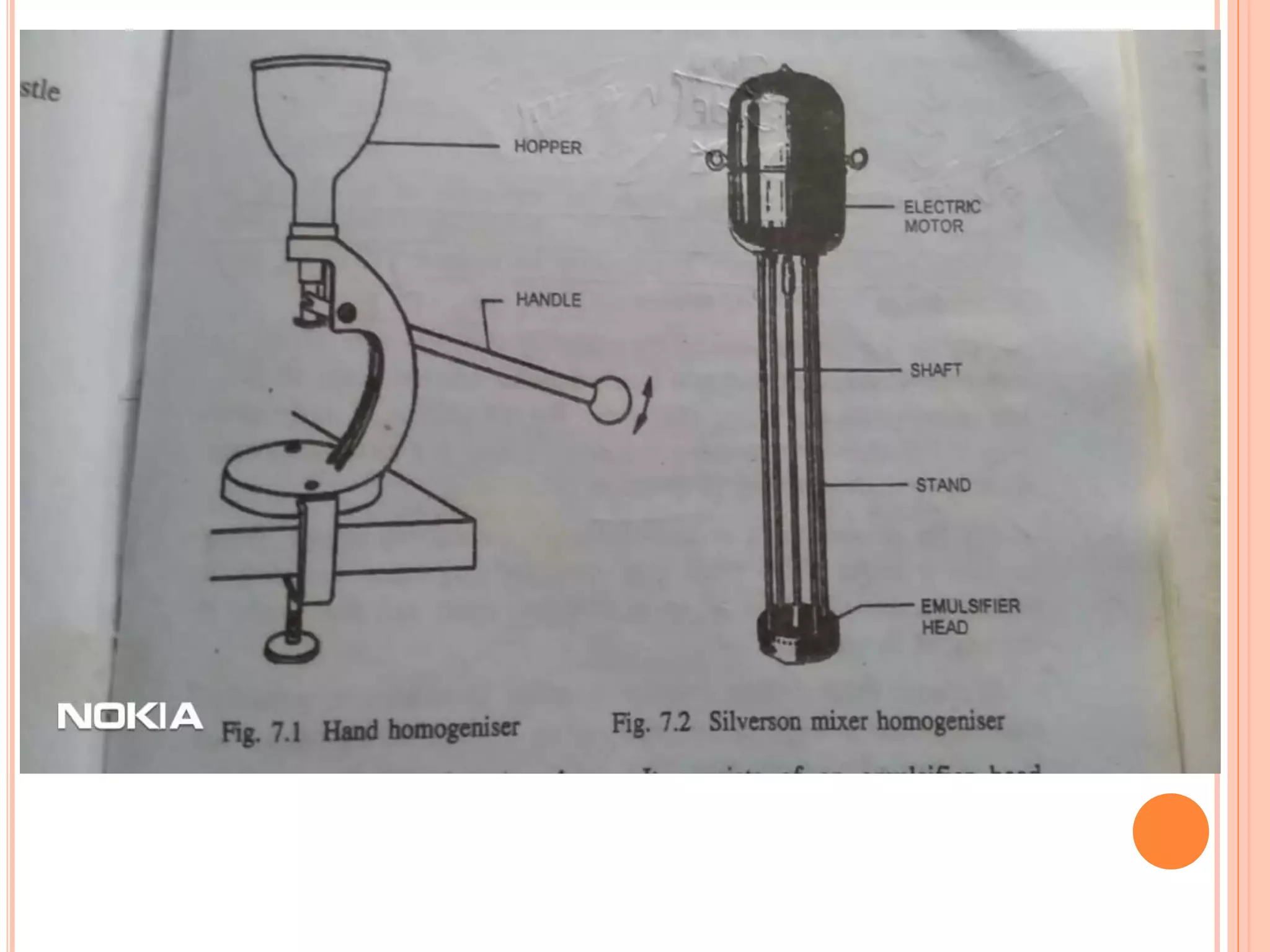
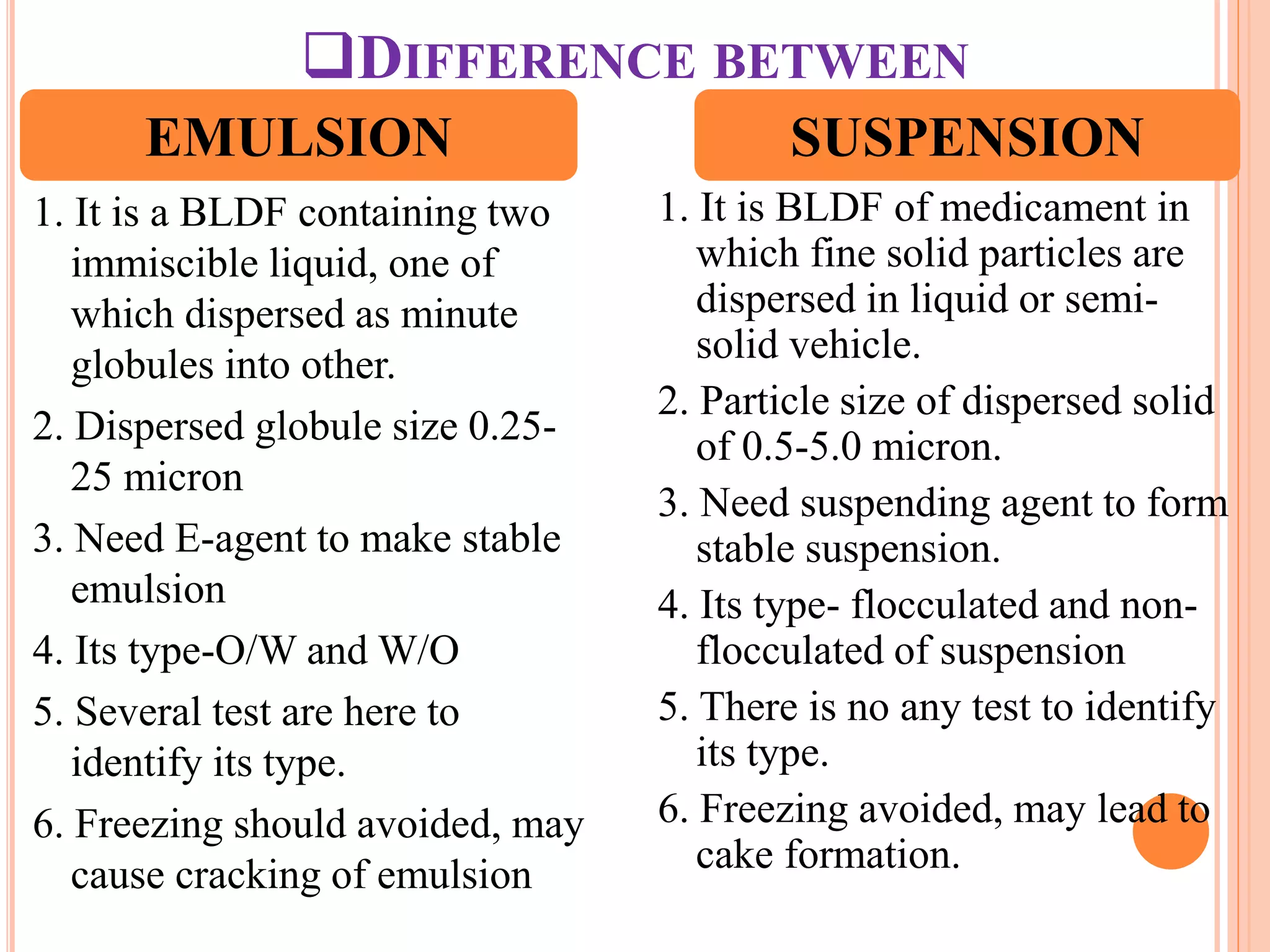
This document provides information about emulsions, including their definition, advantages, types, tests for identification, classification, formulation, preparation, stability, and differences from suspensions. Key points include:
- An emulsion is a biphasic liquid dosage form with one liquid dispersed as fine globules in another immiscible liquid, stabilized by an emulsifying agent.
- Emulsions can improve palatability, protect unstable drugs, and aid in drug absorption.
- The main types are oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions, classified based on the dispersed and continuous phases.
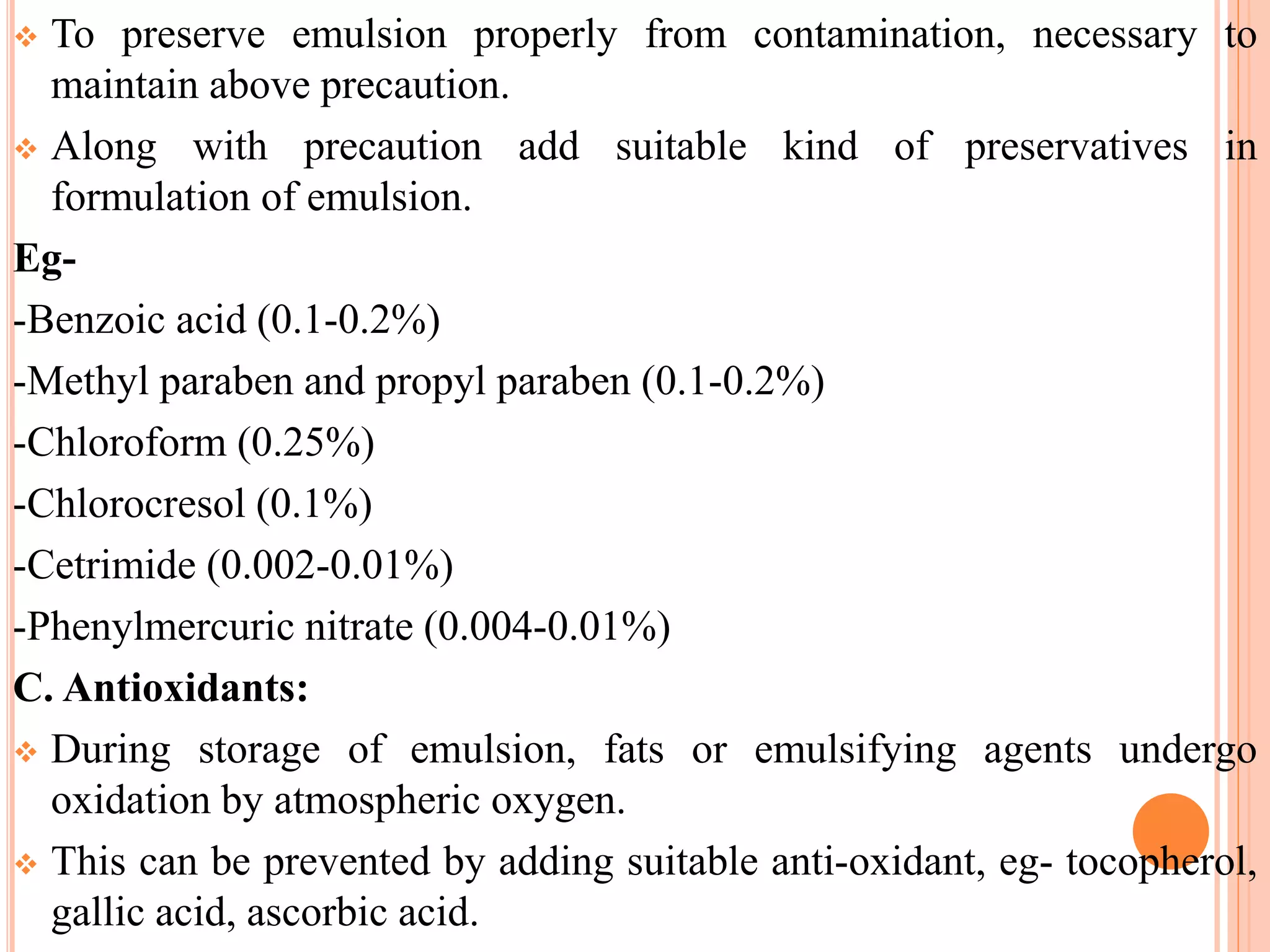
- Emulsion stability depends on factors like emulsifying agent, preservation, antioxidants, and