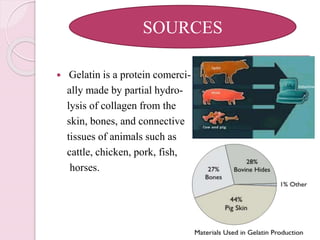
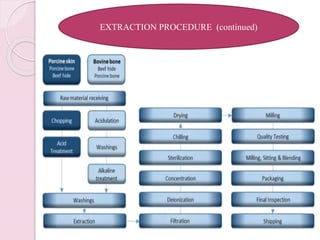
Gelatin is produced by the partial hydrolysis of collagen from animal skins, bones, and connective tissues. There are two main types: type A gelatin is derived from acid-treated precursors and type B from alkali-treated precursors. Gelatin is manufactured through a process involving acidulation, liming, washing, extraction, filtration, pH adjustment, sterilization, and drying. It is used in pharmaceutical applications such as hard and soft gelatin capsules, tablet coatings, and as a gelling or viscosity agent.