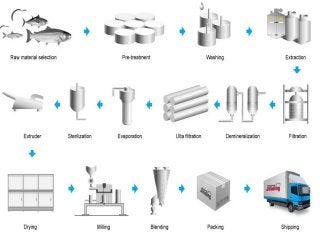
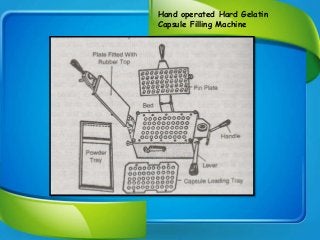
This document provides information about hard gelatin capsules, including their introduction, advantages, disadvantages, raw materials, manufacturing process, sizes, properties of filled materials, filling equipment, and evaluation standards. It discusses that hard capsules consist of two pieces (cap and body) made of gelatin, and are filled with powders. The key steps in manufacturing include dipping molds in hot gelatin solution, drying, stripping, trimming, and joining. Capsules range in size from 000 to 5 and are evaluated based on parameters like weight variation, content uniformity, and dissolution testing. Common filling equipment includes Rotosort, Rotofill, and Accogel.