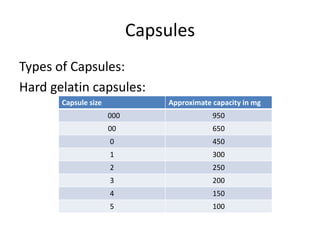
Capsules are solid dosage forms that contain a single dose of a drug enclosed in a soluble shell, typically made of gelatin. There are two main types: hard gelatin capsules and soft gelatin capsules. Capsules offer advantages like masking unpleasant tastes, ease of swallowing, and sustained release formulations. They also have some disadvantages like not being suitable for some soluble drugs. Capsules are evaluated based on weight variation, disintegration time, drug content uniformity, and dissolution testing.