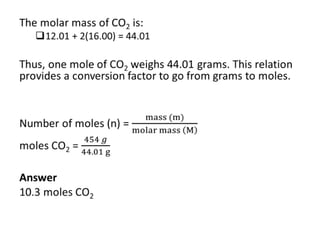
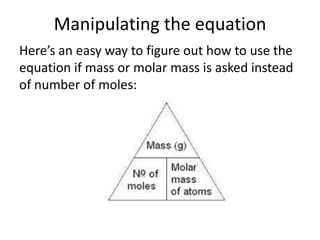
The mole is a unit used in chemistry to express amounts of substances. It represents 6.022x10^23 elementary entities, such as atoms, molecules, ions or other particles of a substance. This number is known as Avogadro's constant, after scientist Amedeo Avogadro who proposed that equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules. The mass of one mole of a substance, known as its molar mass, can be used to determine the number of moles in a given mass of that substance and vice versa through calculation.