1. The document discusses the continuity equation, which states that the flow rate of an incompressible fluid is constant at any point in a fluid system with no accumulation.
2. The formula for continuity equation is given as: ρ1A1v1 = ρ2A2v2, where ρ is density, A is cross-sectional area, and v is velocity.
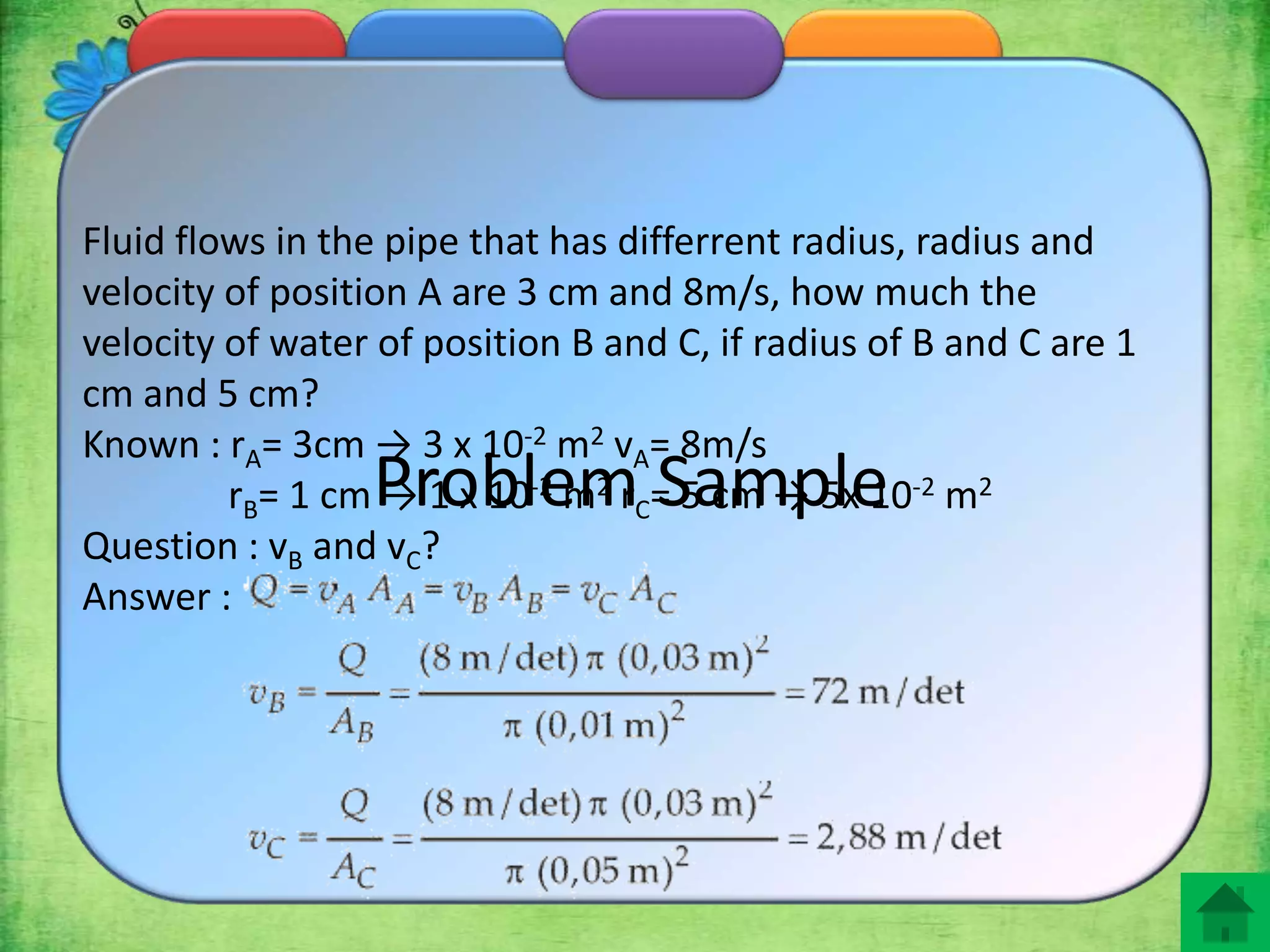
3. Examples of applications include calculating water velocity changes in pipes or rivers of varying diameters, and a sample problem is worked out calculating velocities at different pipe positions.