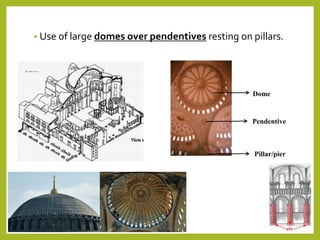
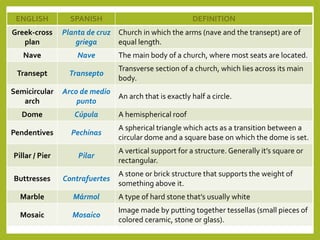
Byzantine art evolved from Roman art and was influenced by Eastern styles. Important art forms included churches decorated with mosaics and icons. Byzantine churches were characterized by Greek cross plans, semicircular arches, large domes on pendentives, and decorative mosaics. Two renowned examples were Hagia Sophia and St. Mark's Basilica. Mosaics used small colored tiles or tesserae to make images on golden backgrounds, depicting religious or imperial themes. Icons were religious paintings on wood of figures with stylized, rigid expressions on golden backgrounds.