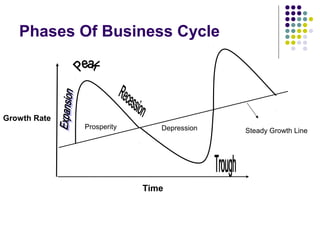
The document discusses business cycles and economic growth. It defines a business cycle as fluctuations in economic activity characterized by alternating periods of expansion and contraction. The phases of a business cycle include prosperity/peak, recession, depression/trough, and recovery. Factors that influence economic growth include human resources, natural resources, capital formation, technology development, and social/political factors. Stabilization policies aim to prevent excessive fluctuations and efficiently use resources to promote sustained growth, stability, and social equity.