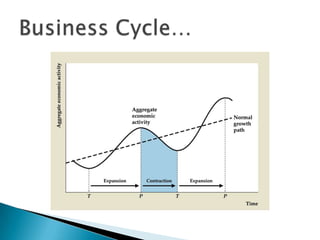
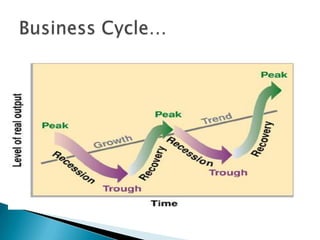
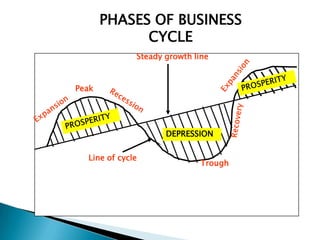
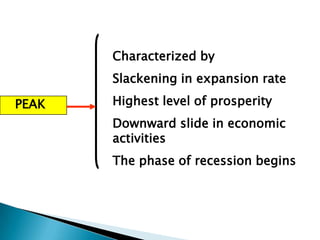
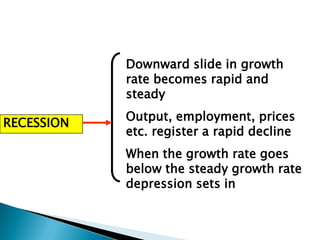
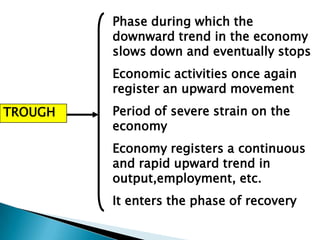
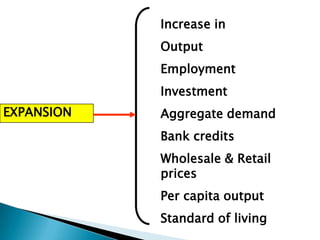
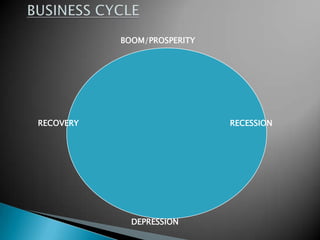
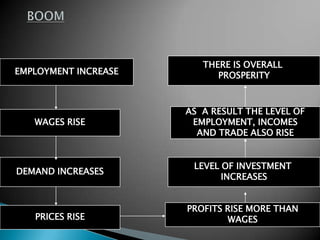
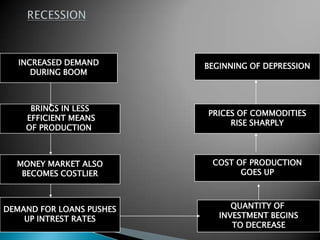
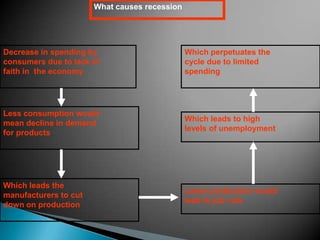
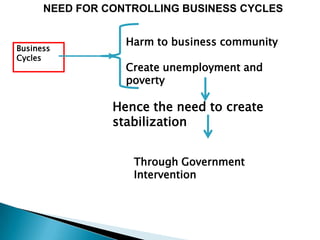
The document discusses the business cycle, which refers to periods of economic expansion and contraction over time. A business cycle consists of expansions, recessions/general contractions, and revivals. Expansions are periods of increased production, prices, and employment. Recessions involve declining output, prices, and rising unemployment. Contractions occur when the economy experiences a steep decline. Revivals mark the beginning of the next expansion phase. The phases of the business cycle - peak, recession, trough, recovery - are explained in detail. Causes of recessions and theories to explain business cycles like Keynesian and real business cycle theories are also summarized.