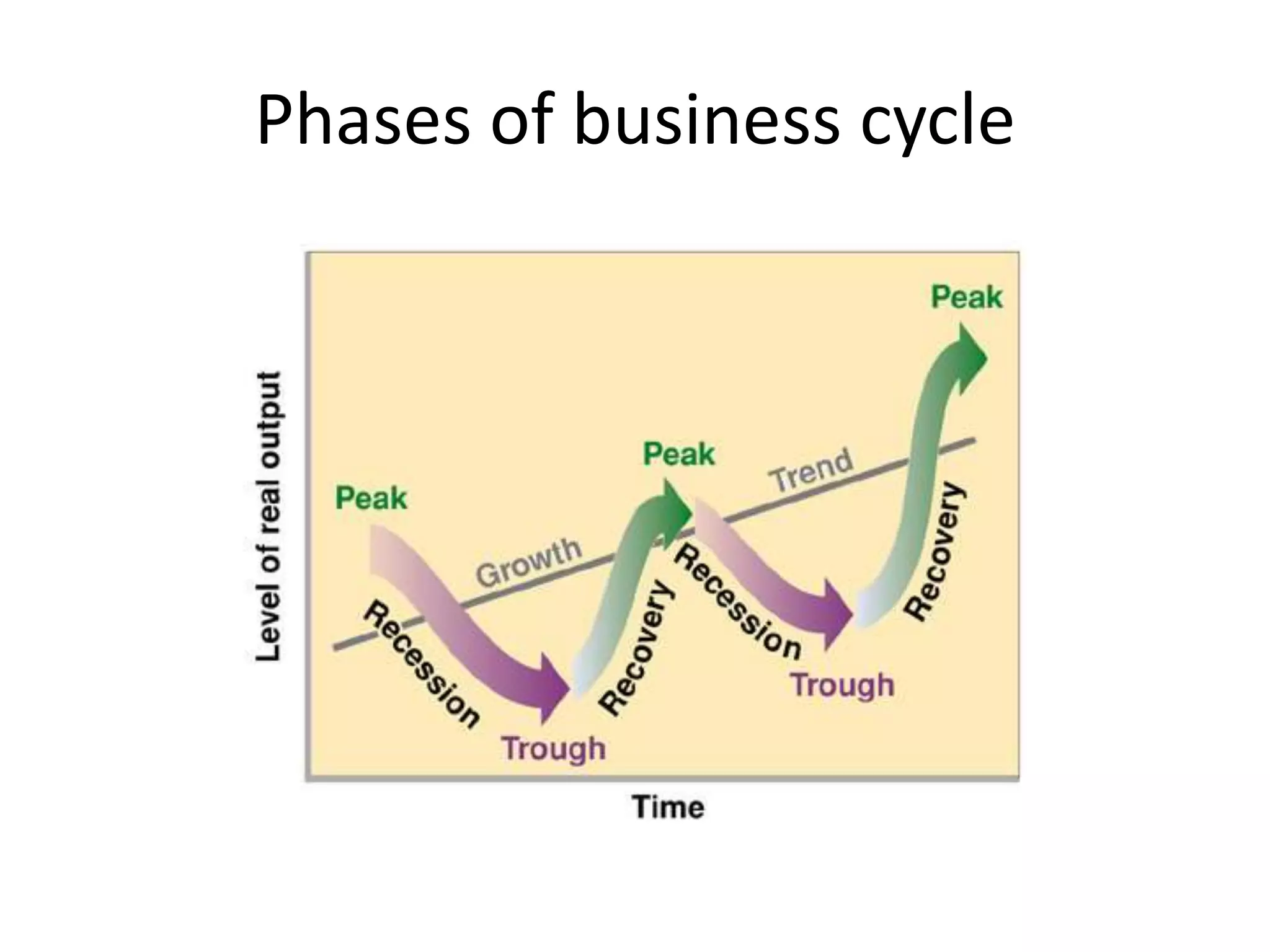
1) The business cycle refers to periodic fluctuations in economic activity between periods of expansion and contraction.
2) It involves four phases - prosperity, peak, downturn/recession, and recovery.
3) Various theories have been proposed to explain the business cycle, including the monetary, psychological, innovation, and Keynesian theories.
4) Keynes argued that decreases in aggregate demand are the primary cause of depression and unemployment. Investment can be used to increase aggregate demand and reduce downturns in the short run.