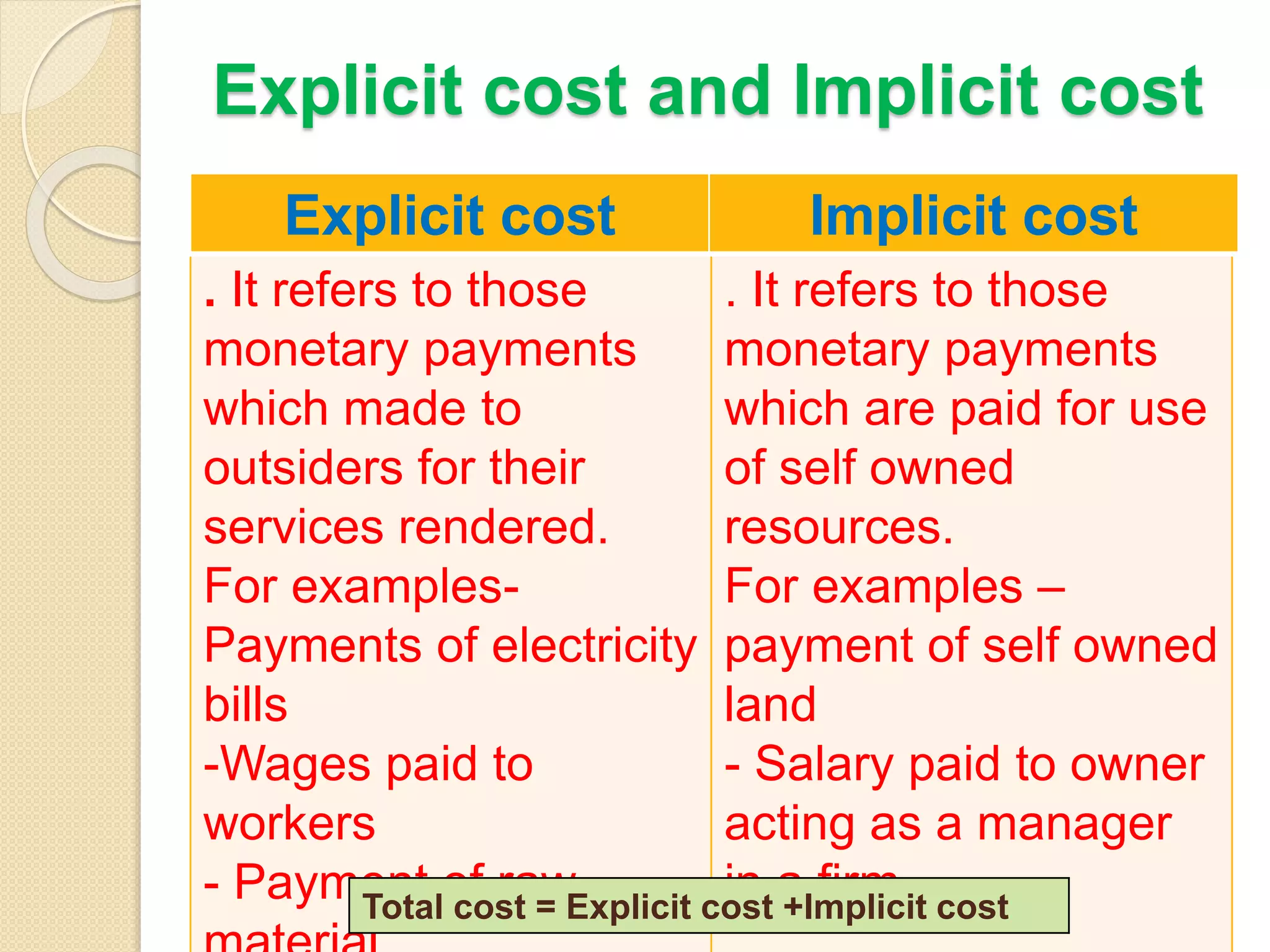
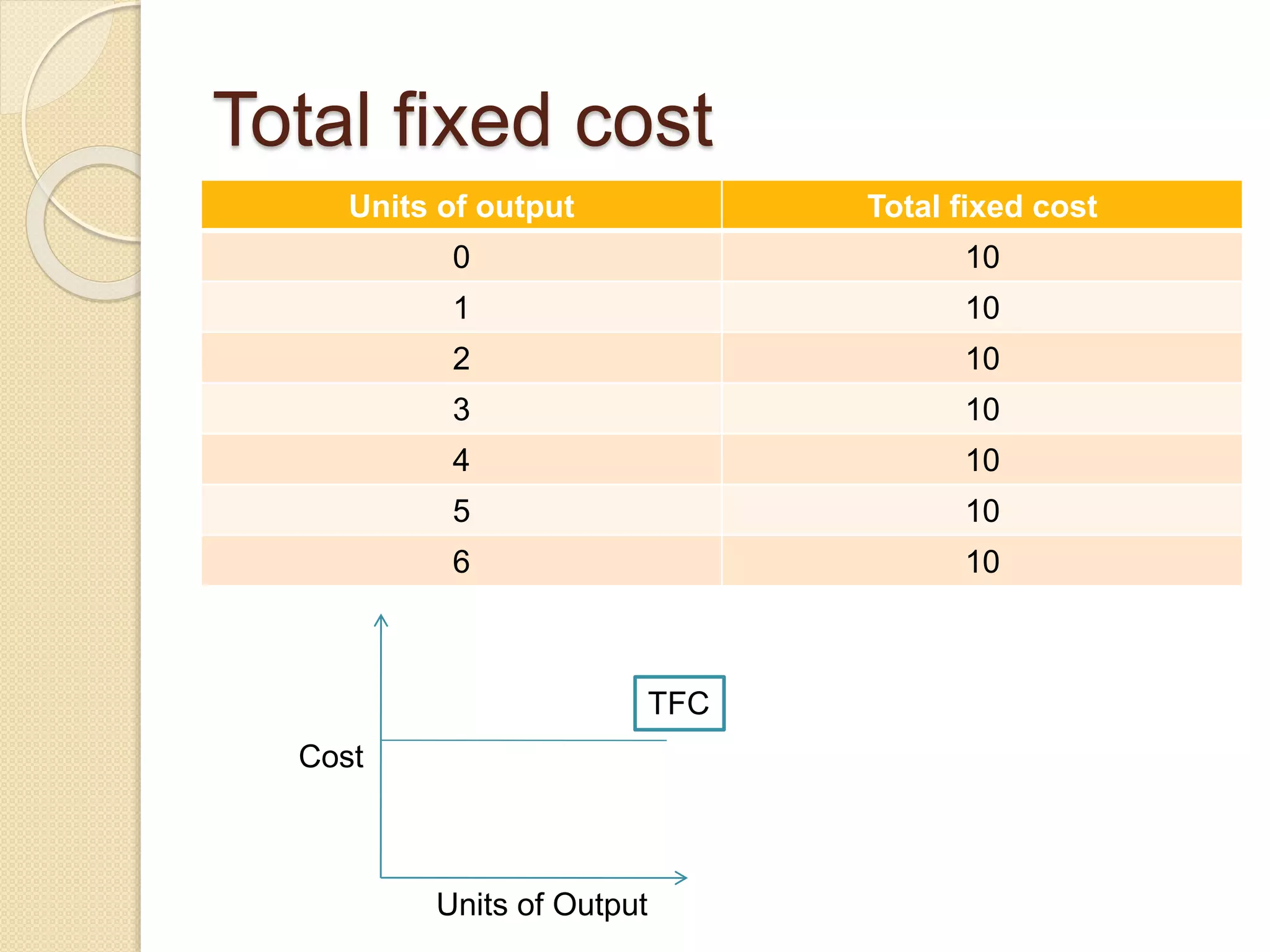
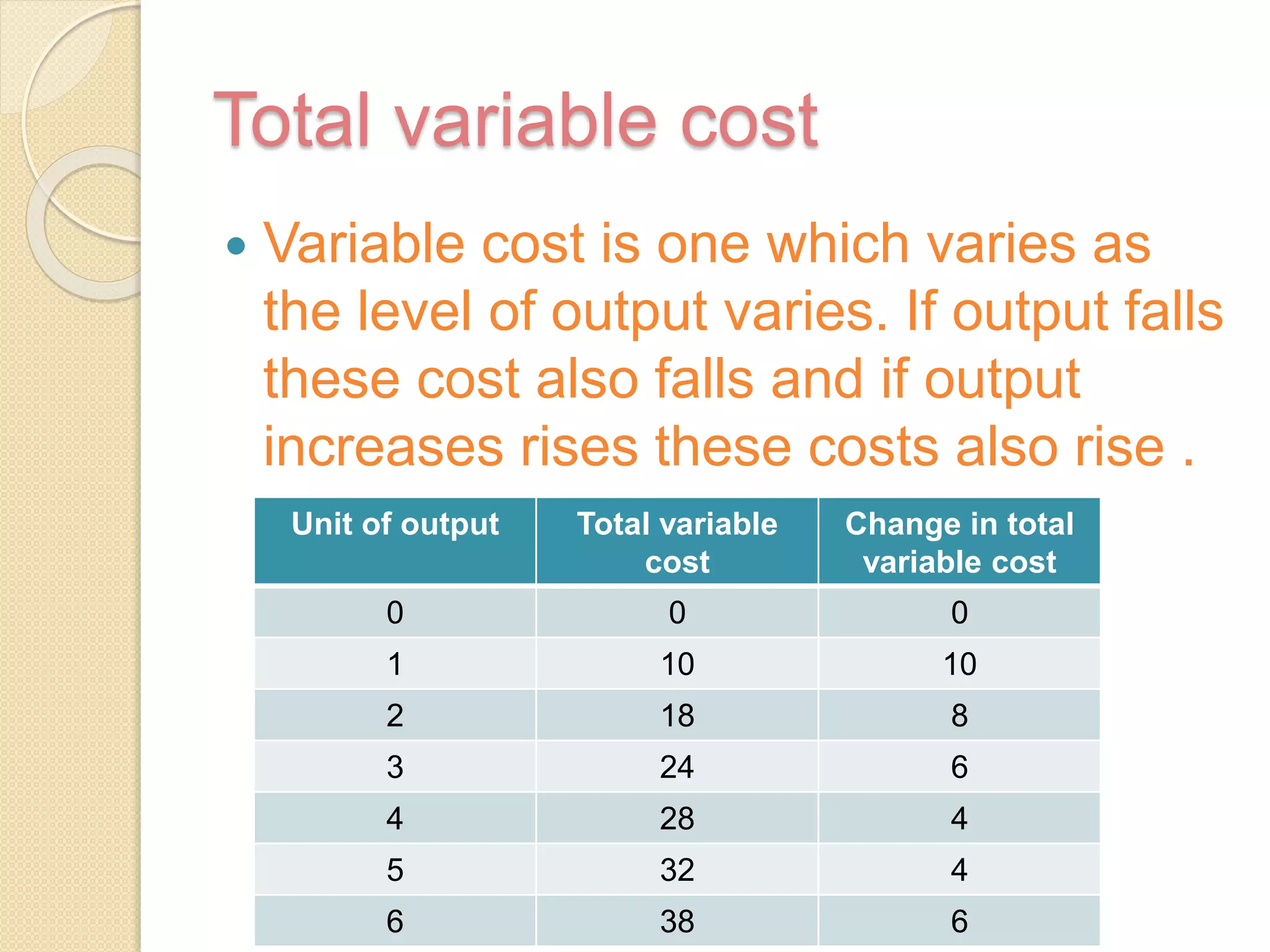
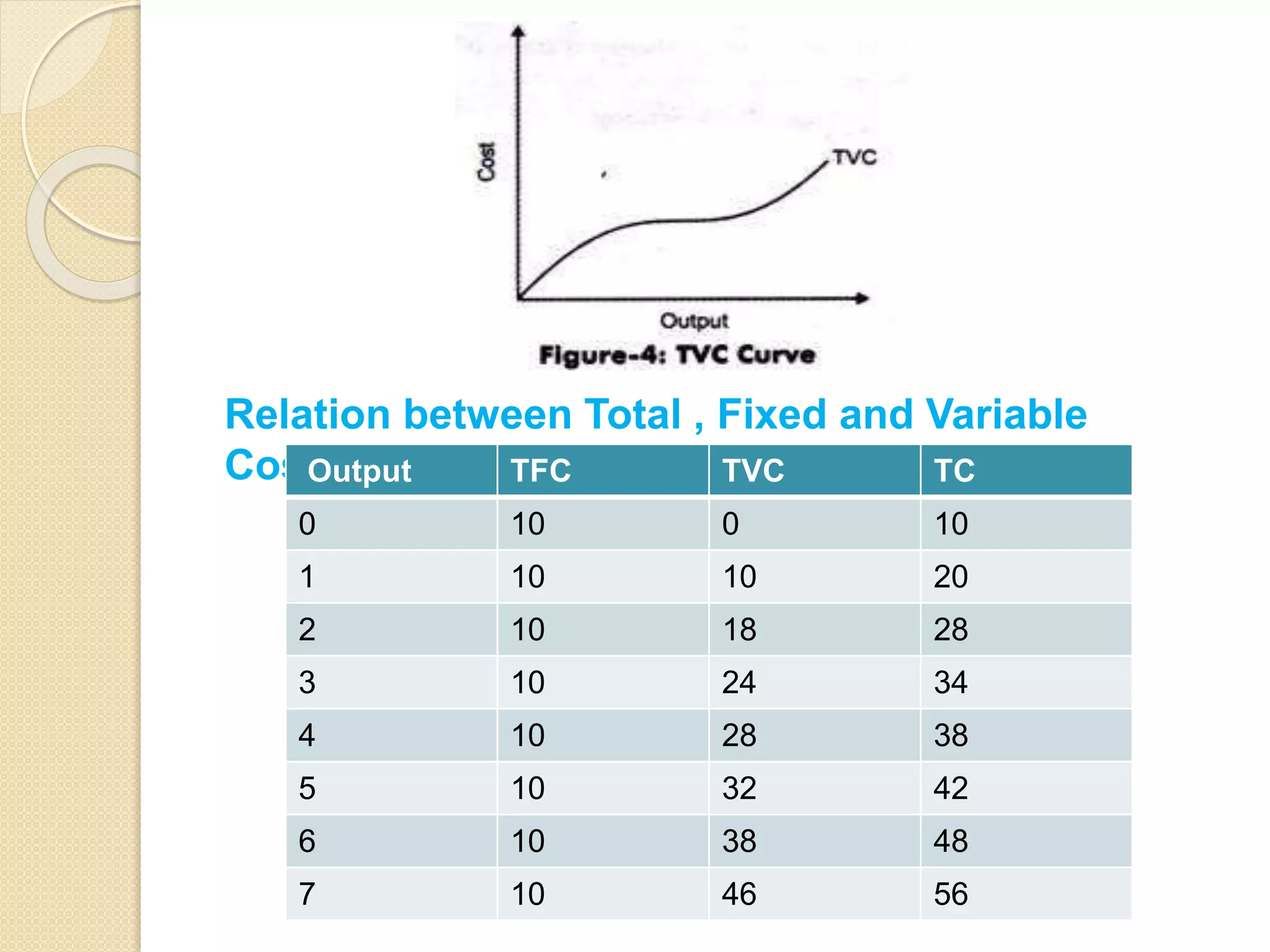
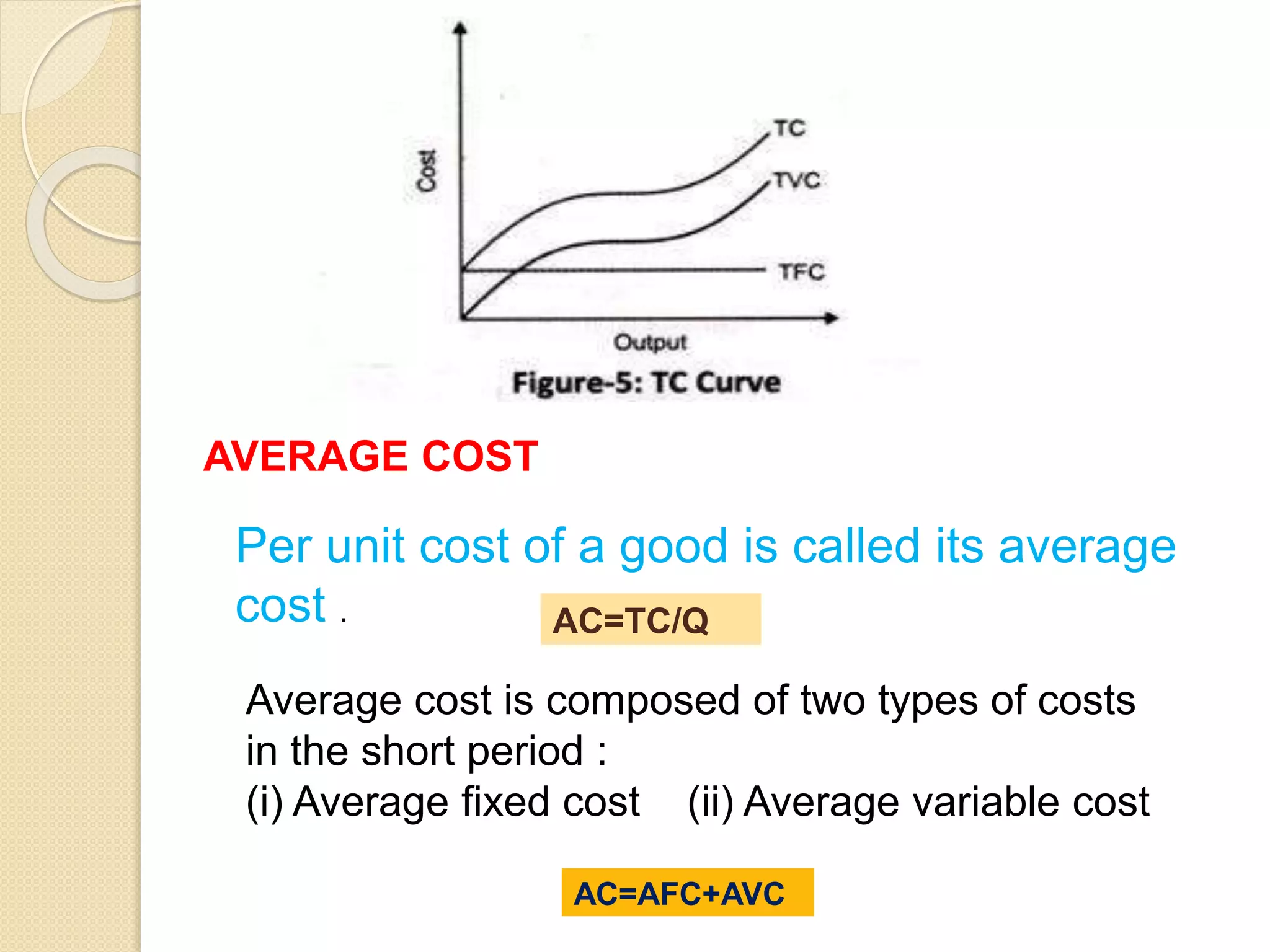
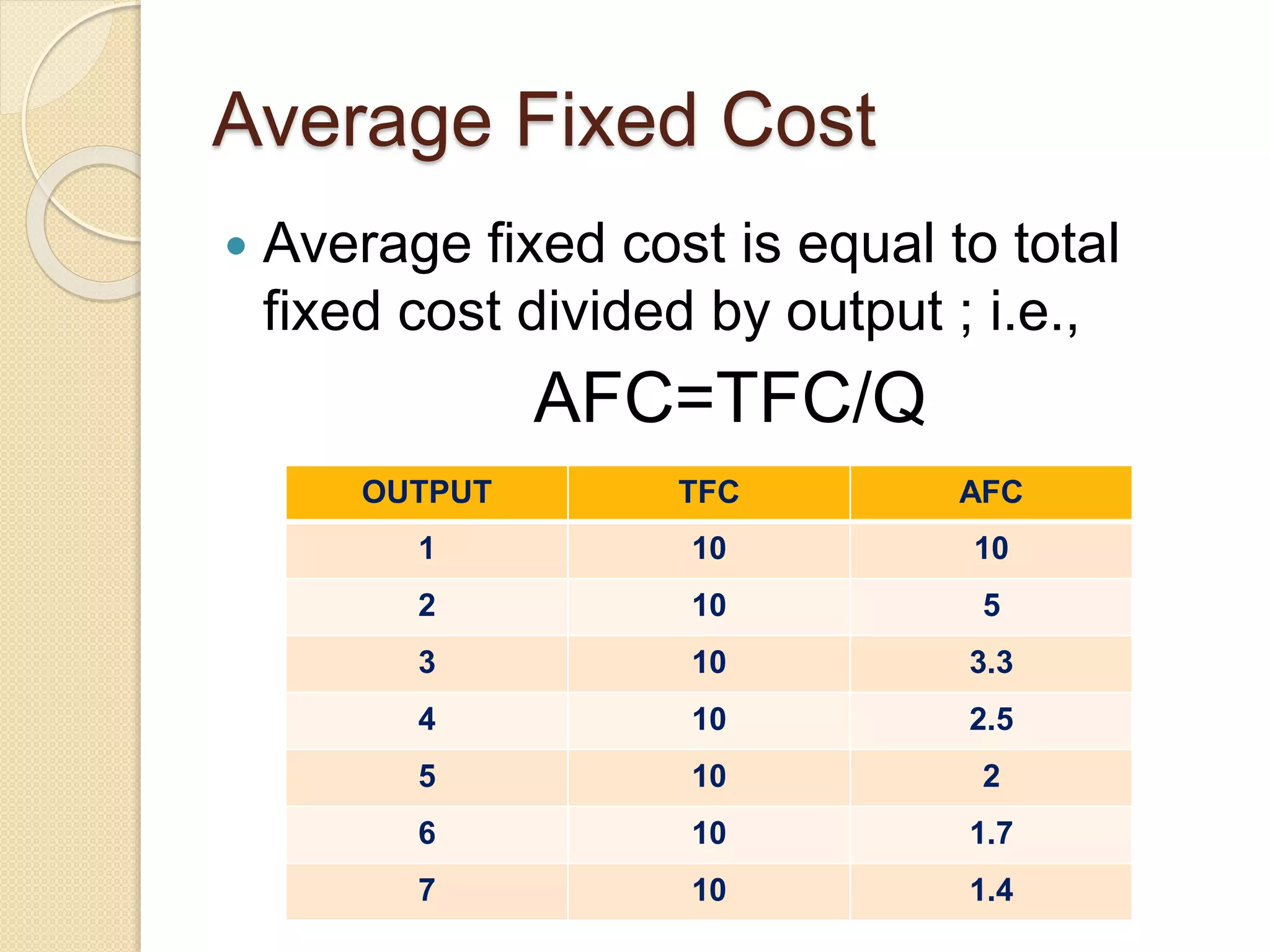
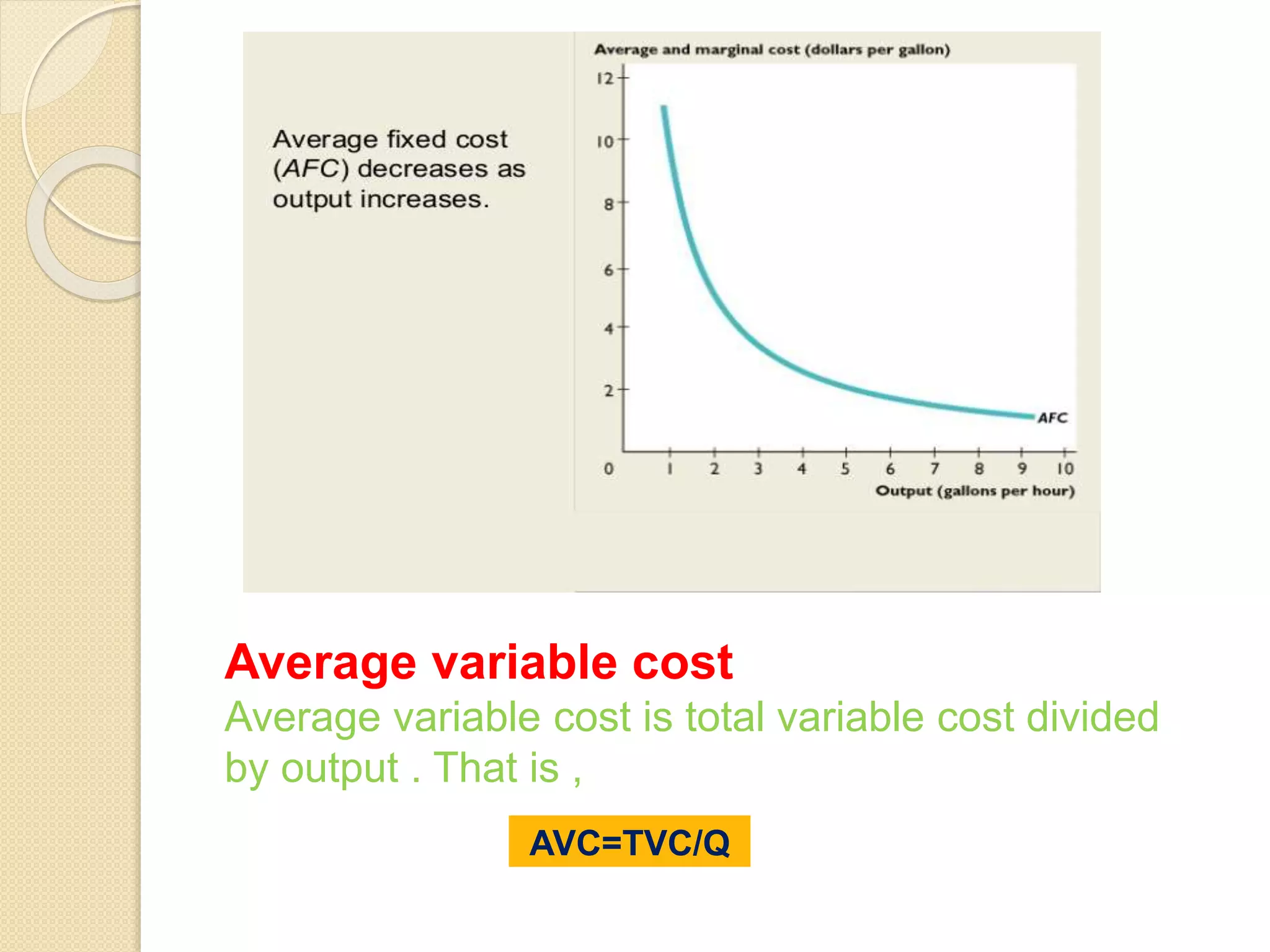
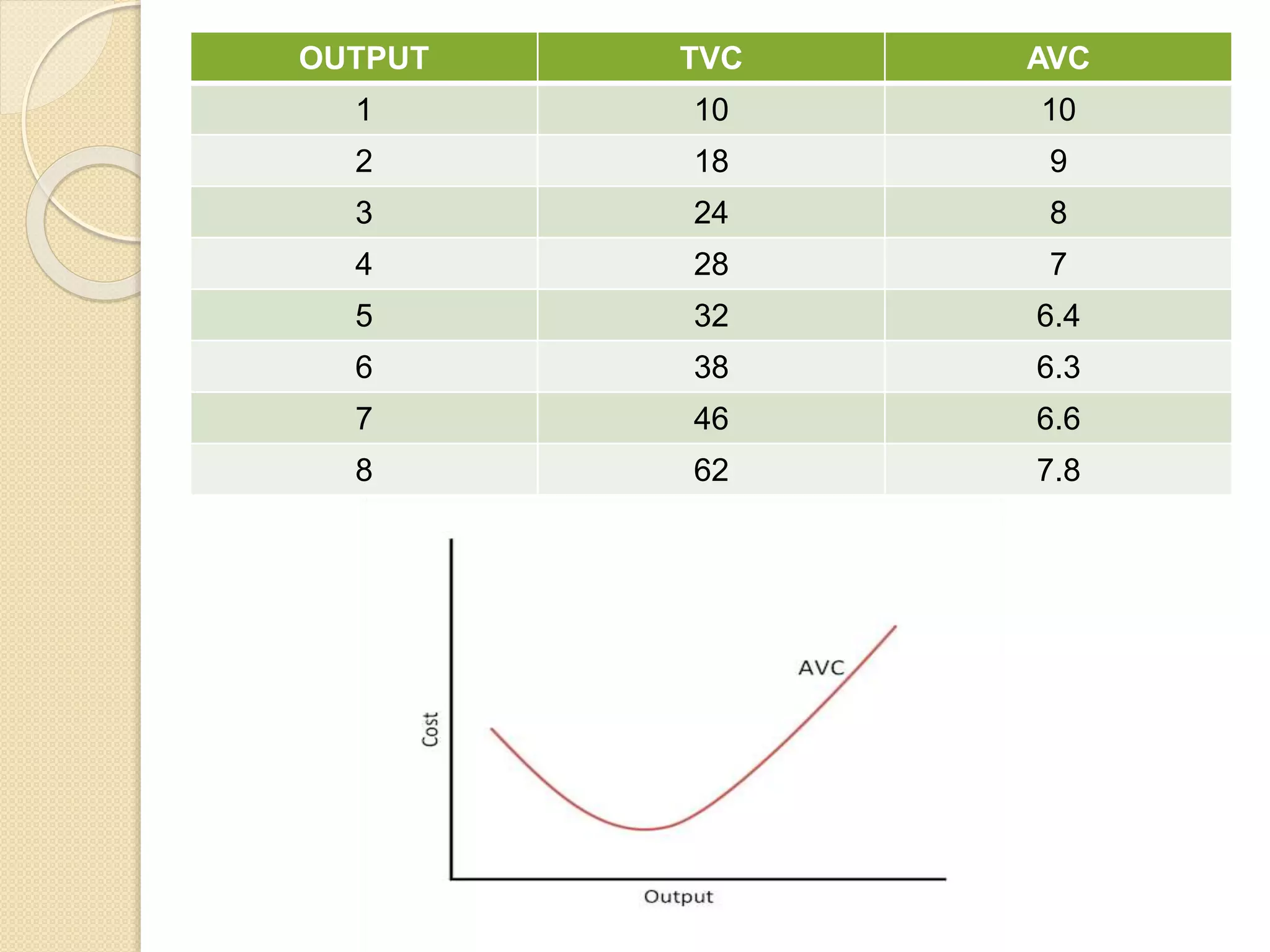
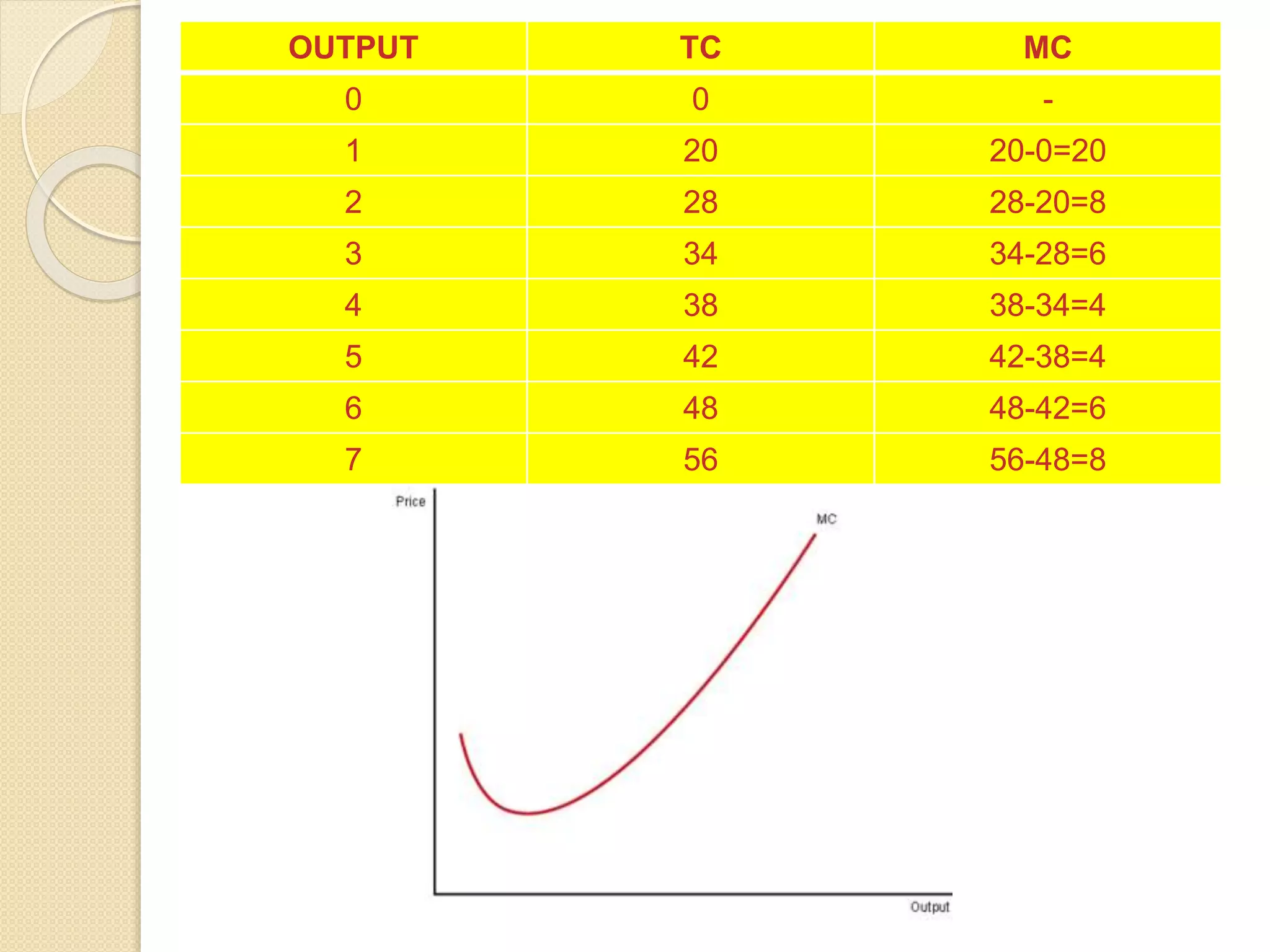
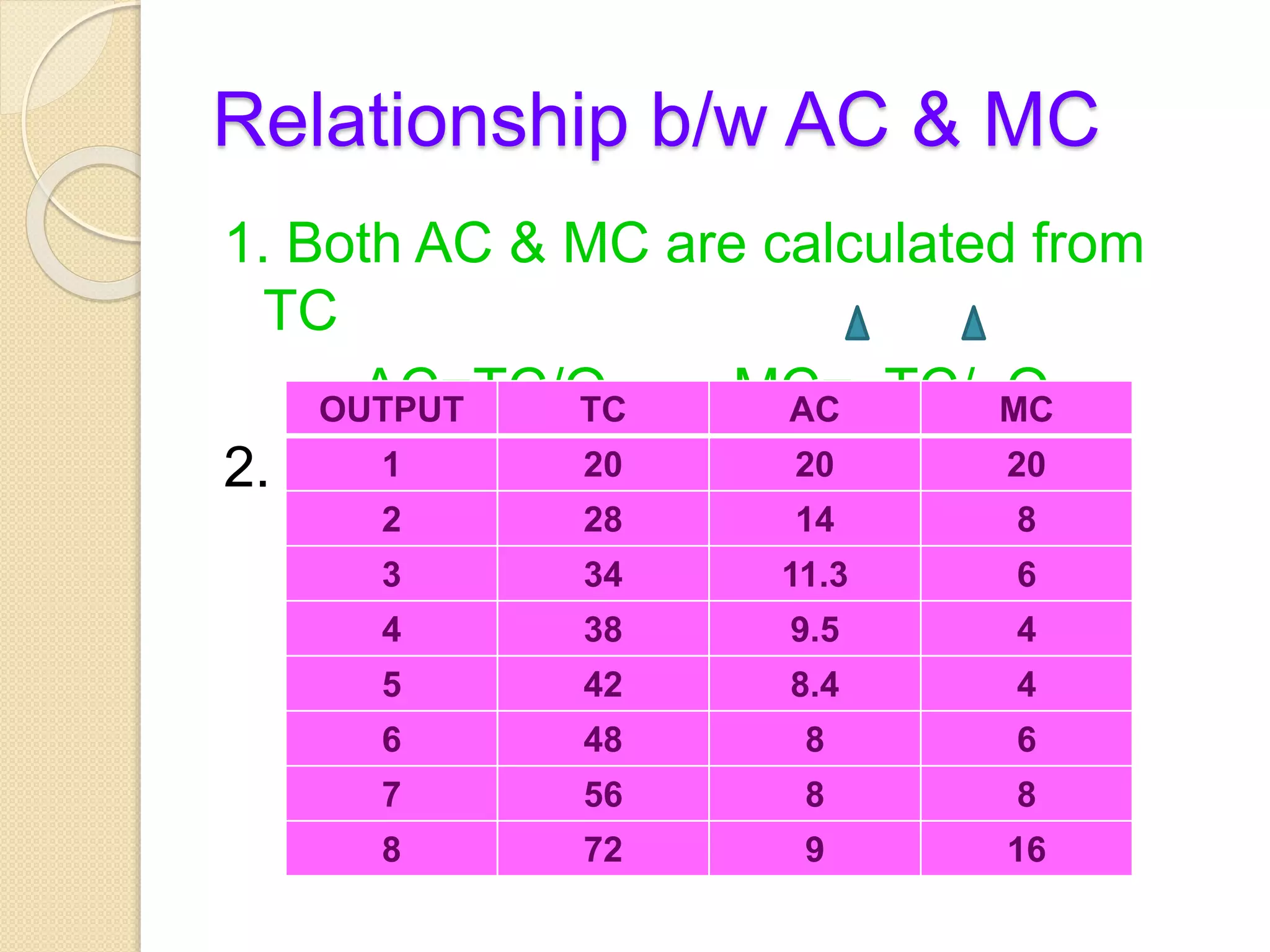
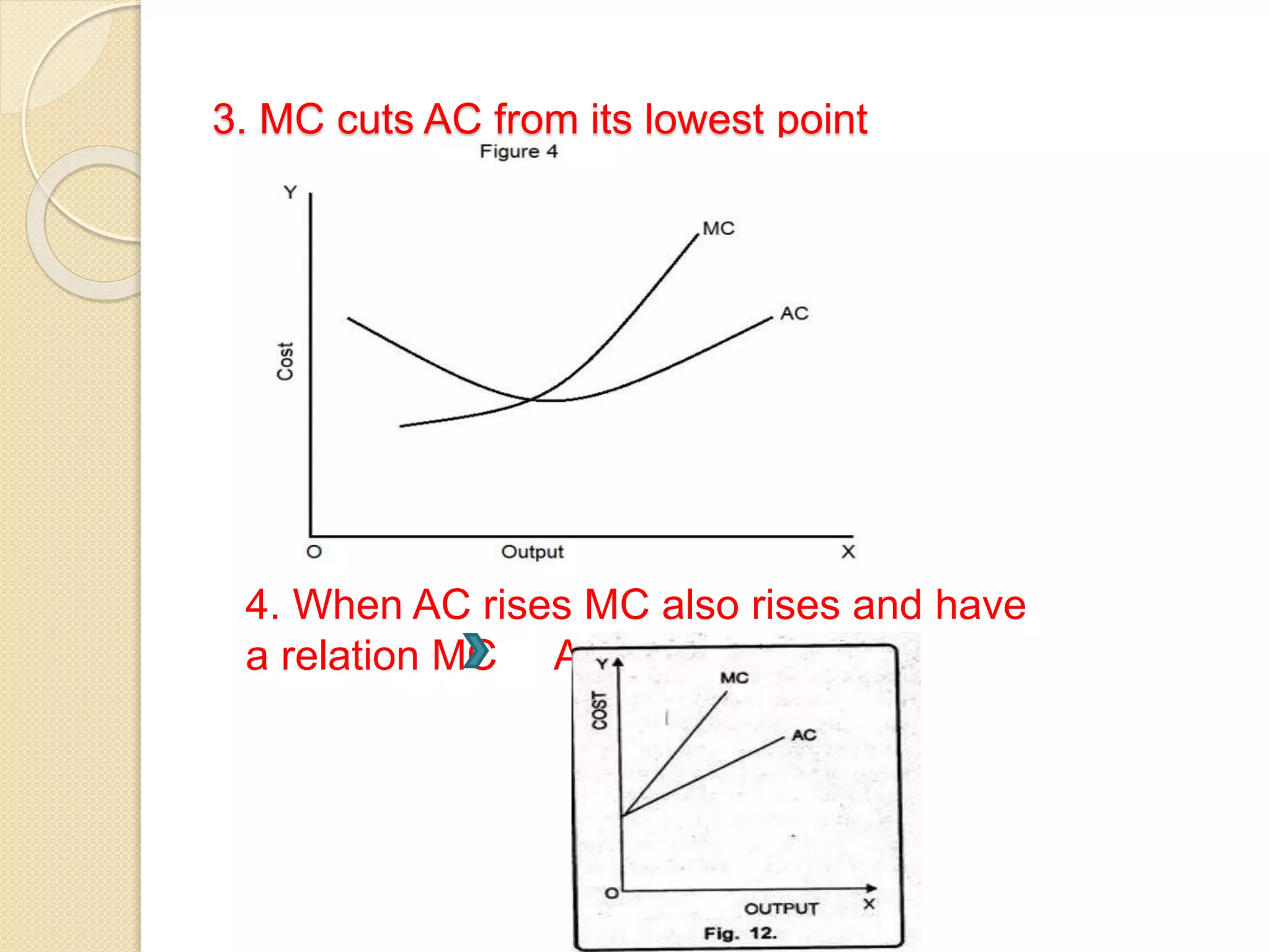
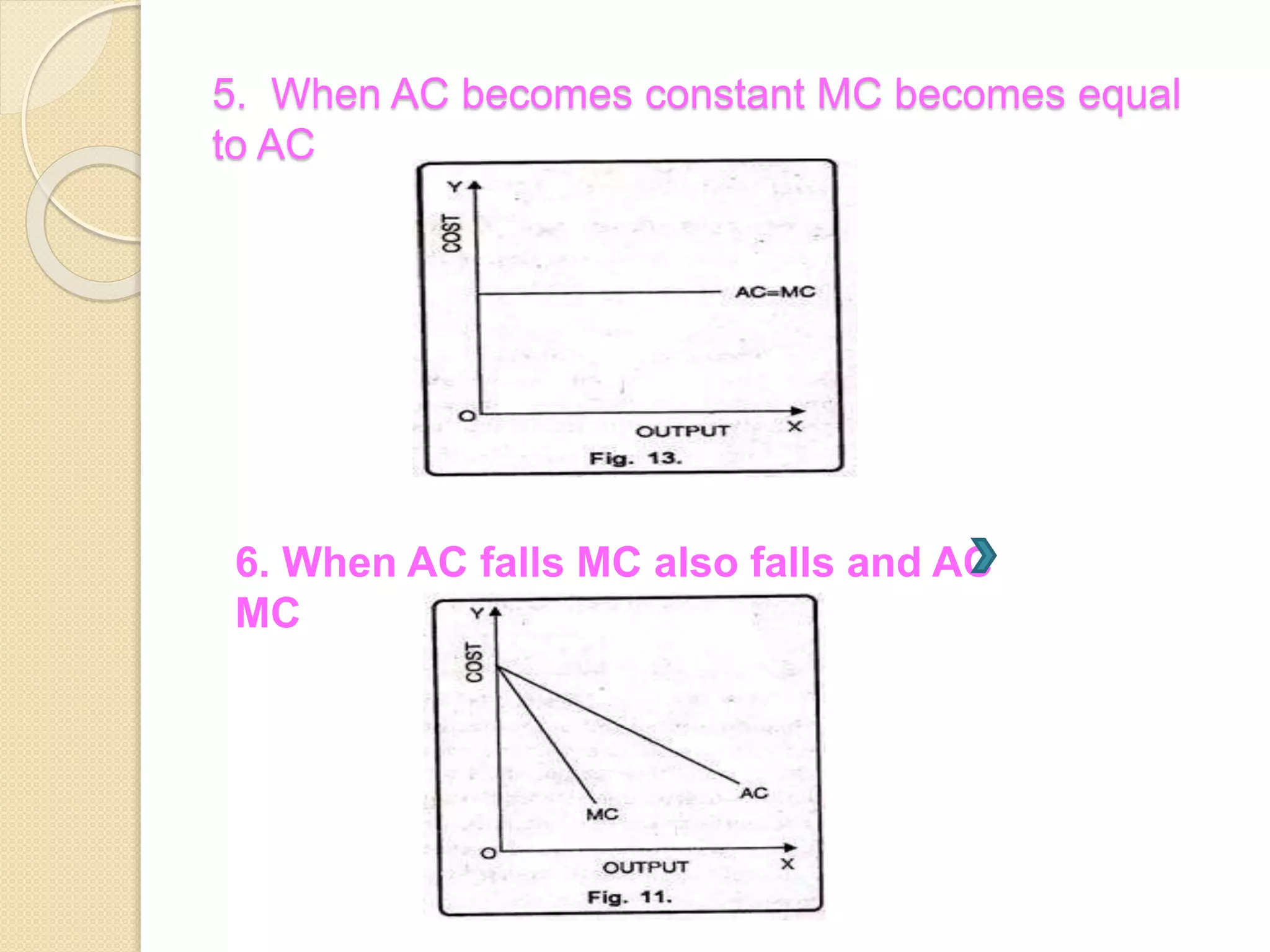
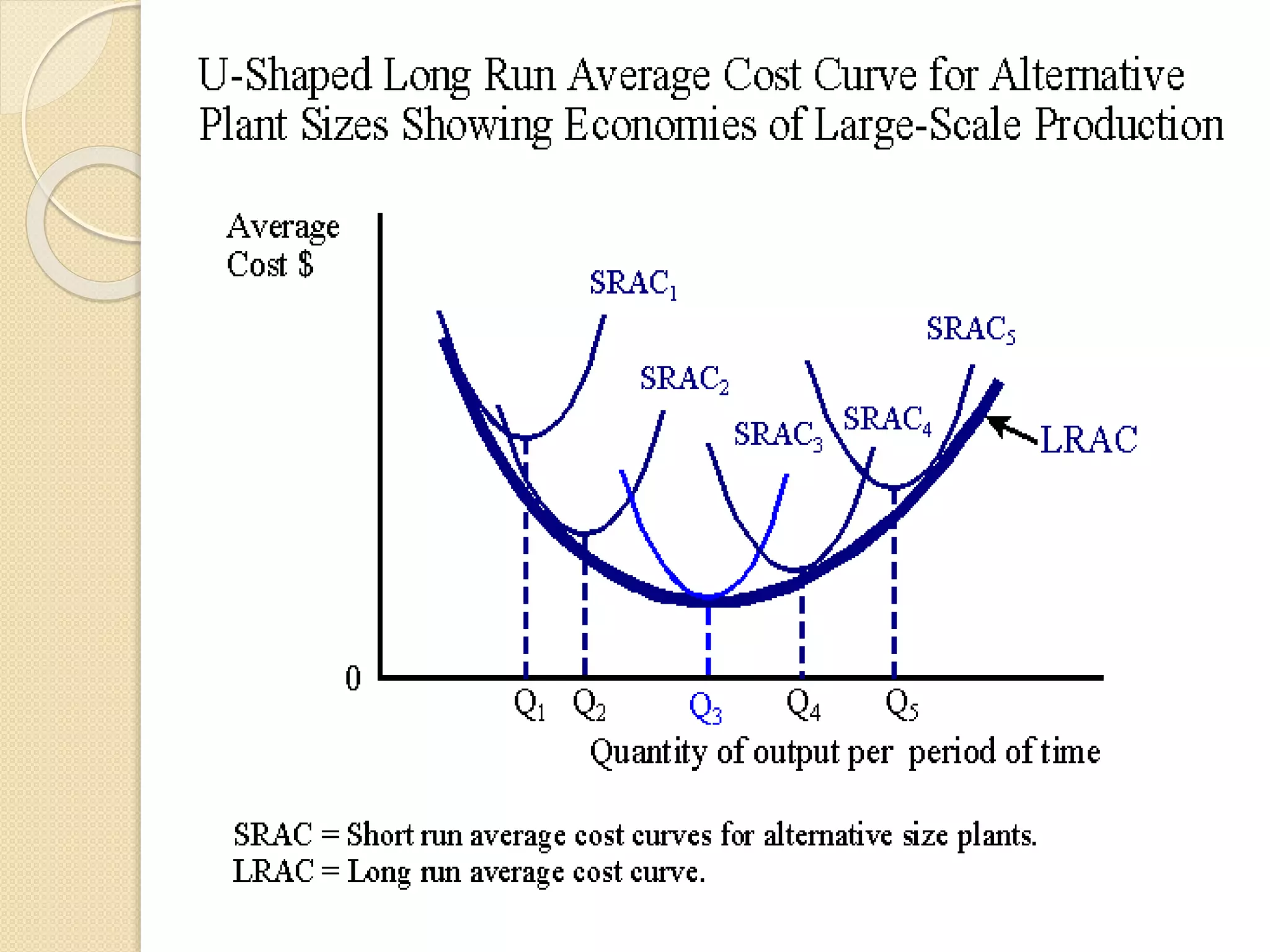
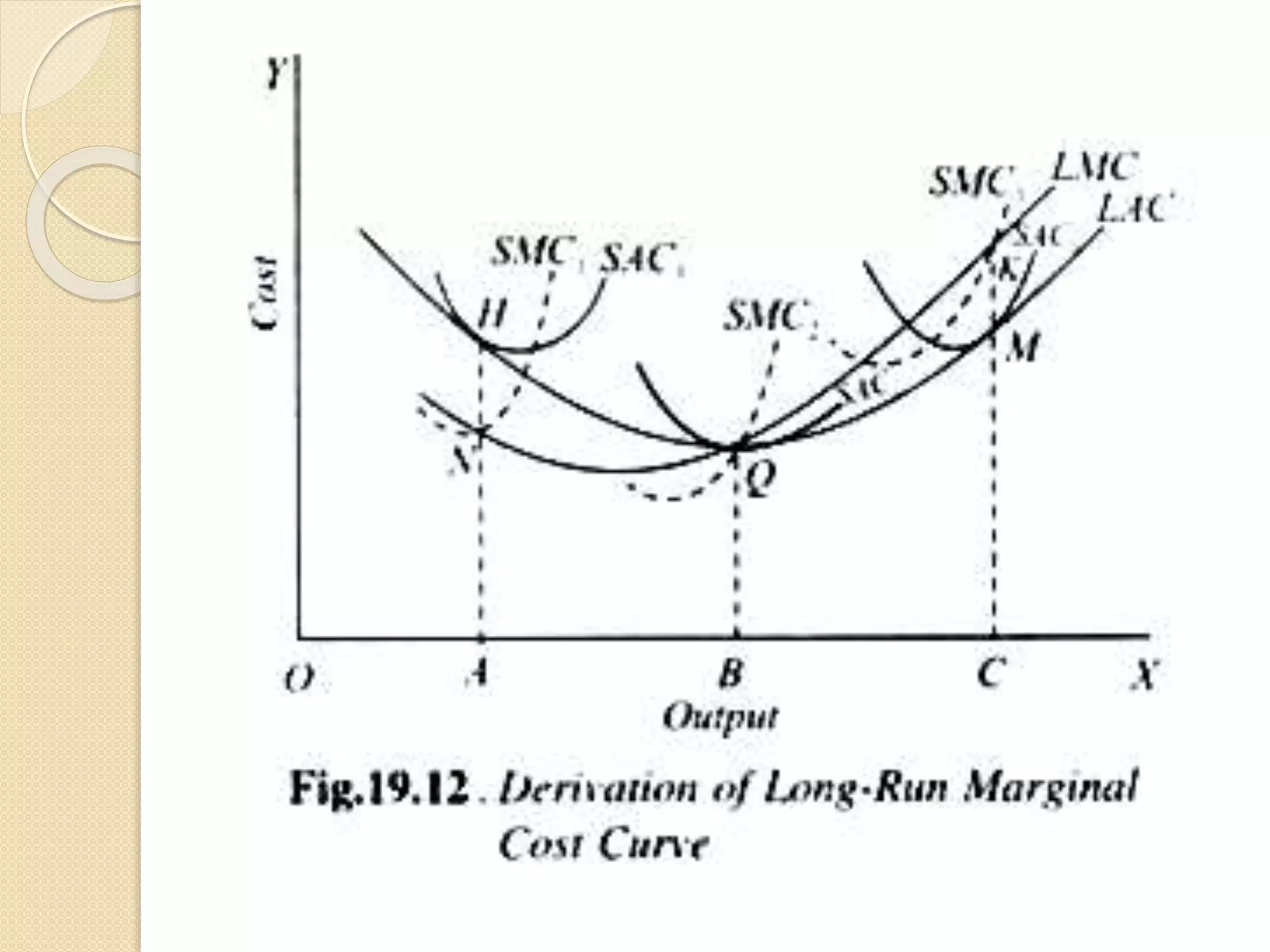
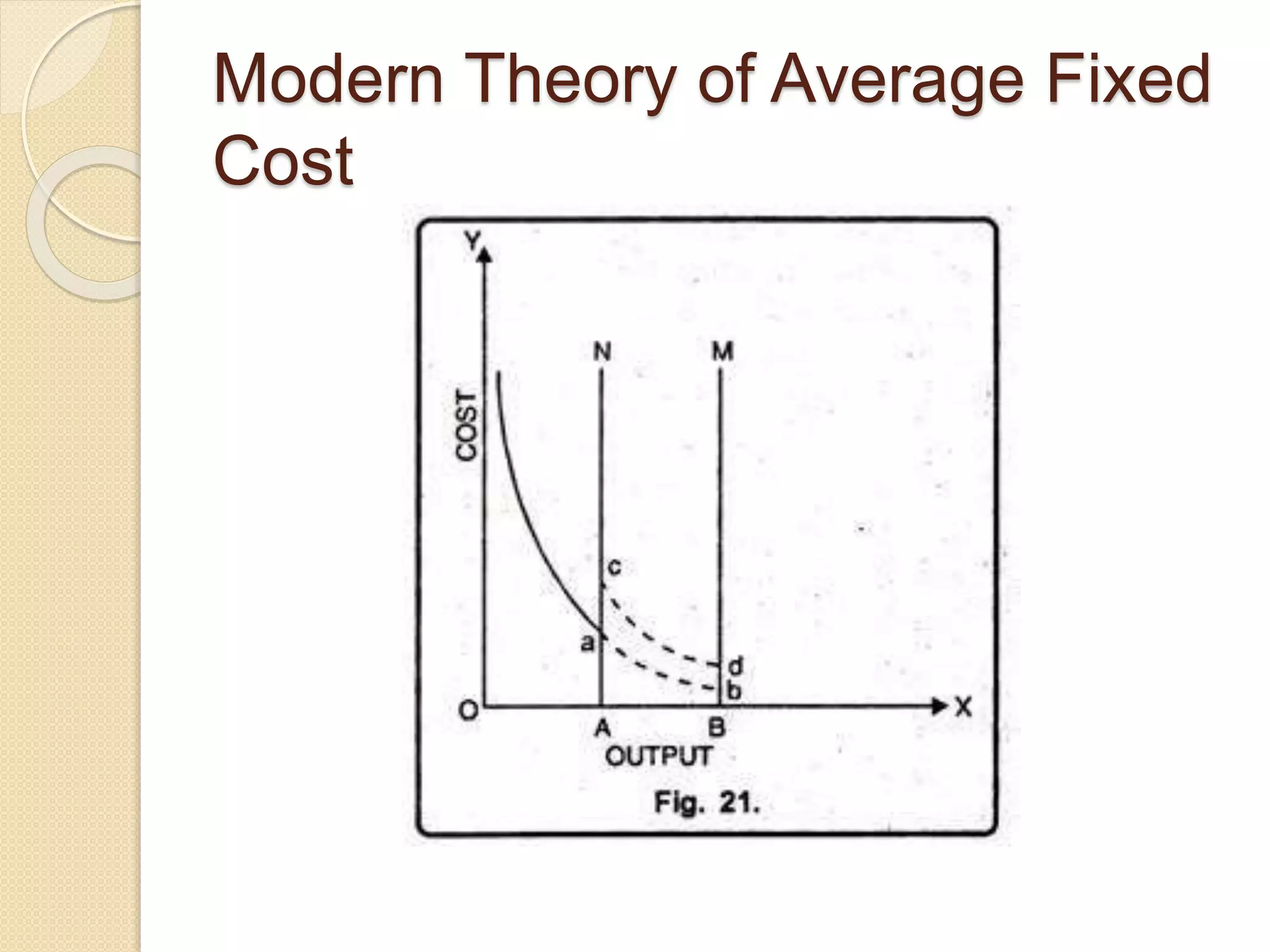
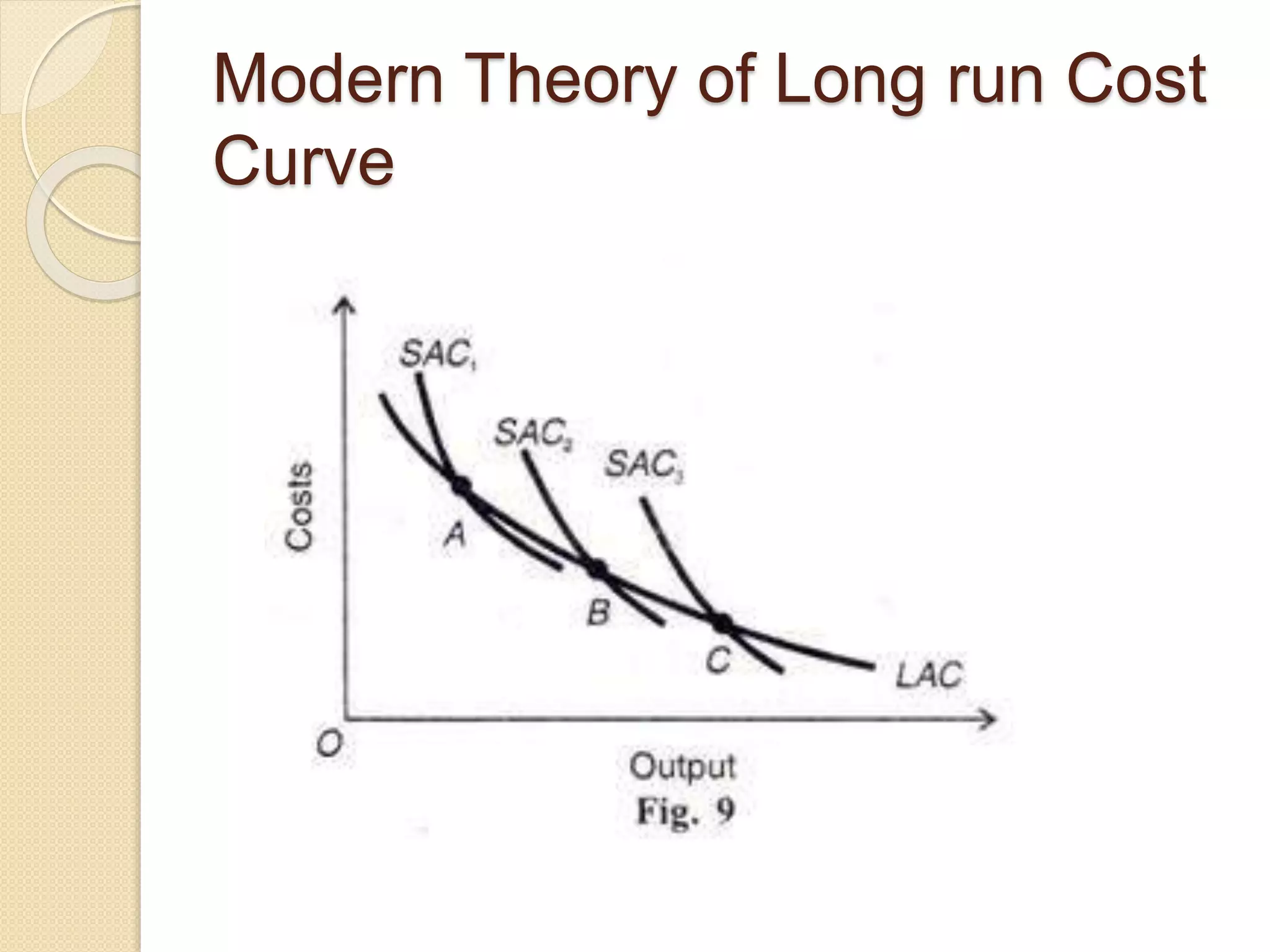
The document discusses different theories of cost, including traditional and modern theories. Under traditional theory, costs are categorized as total, average, and marginal in both the short-run and long-run. Total cost equals total fixed cost plus total variable cost. Average cost depends on average fixed and average variable cost. Marginal cost is the change in total cost from producing one additional unit. In the long-run, all costs are variable. Modern theory proposes cost curves are L-shaped rather than U-shaped as traditionally thought.